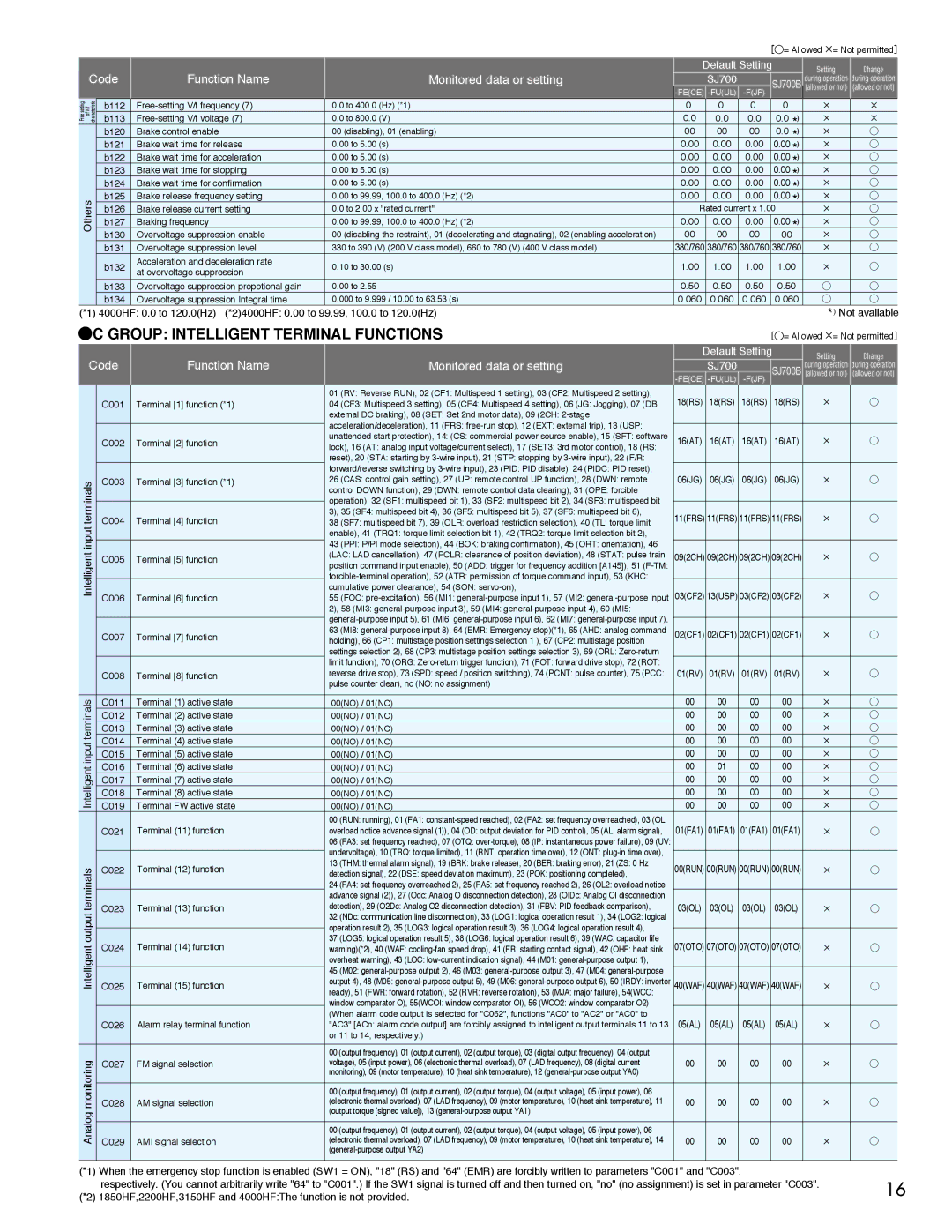
Monitored data or setting | Default Setting | Setting | Change |
| SJ700 | | | during operation | during operation |
| | SJ700B (allowed or not) | (allowed or not) |
| -FE(CE) -FU(UL) | -F(JP) |
01 (RV: Reverse RUN), 02 (CF1: Multispeed 1 setting), 03 (CF2: Multispeed 2 setting), | 18(RS) | 18(RS) | 18(RS) | 18(RS) | × | ○ |
04 (CF3: Multispeed 3 setting), 05 (CF4: Multispeed 4 setting), 06 (JG: Jogging), 07 (DB: |
external DC braking), 08 (SET: Set 2nd motor data), 09 (2CH: 2-stage | | | | | | |
acceleration/deceleration), 11 (FRS: free-run stop), 12 (EXT: external trip), 13 (USP: | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
unattended start protection), 14: (CS: commercial power source enable), 15 (SFT: software | 16(AT) | 16(AT) | 16(AT) | 16(AT) | × | ○ |
lock), 16 (AT: analog input voltage/current select), 17 (SET3: 3rd motor control), 18 (RS: | | | | | | |
reset), 20 (STA: starting by 3-wire input), 21 (STP: stopping by 3-wire input), 22 (F/R: | | | | | | |
forward/reverse switching by 3-wire input), 23 (PID: PID disable), 24 (PIDC: PID reset), | 06(JG) | 06(JG) | 06(JG) | 06(JG) | × | ○ |
26 (CAS: control gain setting), 27 (UP: remote control UP function), 28 (DWN: remote |
control DOWN function), 29 (DWN: remote control data clearing), 31 (OPE: forcible | | | | | | |
operation), 32 (SF1: multispeed bit 1), 33 (SF2: multispeed bit 2), 34 (SF3: multispeed bit | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
3), 35 (SF4: multispeed bit 4), 36 (SF5: multispeed bit 5), 37 (SF6: multispeed bit 6), | 11(FRS) | 11(FRS) | 11(FRS) | 11(FRS) | × | ○ |
38 (SF7: multispeed bit 7), 39 (OLR: overload restriction selection), 40 (TL: torque limit |
enable), 41 (TRQ1: torque limit selection bit 1), 42 (TRQ2: torque limit selection bit 2), | | | | | | |
43 (PPI: P/PI mode selection), 44 (BOK: braking confirmation), 45 (ORT: orientation), 46 | | | | | | |
(LAC: LAD cancellation), 47 (PCLR: clearance of position deviation), 48 (STAT: pulse train | 09(2CH) | 09(2CH) | 09(2CH) | 09(2CH) | × | ○ |
position command input enable), 50 (ADD: trigger for frequency addition [A145]), 51 (F-TM: | | | | | | |
forcible-terminal operation), 52 (ATR: permission of torque command input), 53 (KHC: | | | | | | |
cumulative power clearance), 54 (SON: servo-on), | 03(CF2) | 13(USP) | 03(CF2) | 03(CF2) | × | ○ |
55 (FOC: pre-excitation), 56 (MI1: general-purpose input 1), 57 (MI2: general-purpose input |
2), 58 (MI3: general-purpose input 3), 59 (MI4: general-purpose input 4), 60 (MI5: | | | | | | |
general-purpose input 5), 61 (MI6: general-purpose input 6), 62 (MI7: general-purpose input 7), | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
63 (MI8: general-purpose input 8), 64 (EMR: Emergency stop)(*1), 65 (AHD: analog command | 02(CF1) | 02(CF1) | 02(CF1) | 02(CF1) | × | ○ |
holding), 66 (CP1: multistage position settings selection 1 ), 67 (CP2: multistage position | | | | | | |
settings selection 2), 68 (CP3: multistage position settings selection 3), 69 (ORL: Zero-return | | | | | | |
limit function), 70 (ORG: Zero-return trigger function), 71 (FOT: forward drive stop), 72 (ROT: | 01(RV) | 01(RV) | 01(RV) | 01(RV) | × | ○ |
reverse drive stop), 73 (SPD: speed / position switching), 74 (PCNT: pulse counter), 75 (PCC: |
pulse counter clear), no (NO: no assignment) | | | | | | |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 01 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00(NO) / 01(NC) | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
00 (RUN: running), 01 (FA1: constant-speed reached), 02 (FA2: set frequency overreached), 03 (OL: | 01(FA1) | 01(FA1) | 01(FA1) | 01(FA1) | × | ○ |
overload notice advance signal (1)), 04 (OD: output deviation for PID control), 05 (AL: alarm signal), |
06 (FA3: set frequency reached), 07 (OTQ: over-torque), 08 (IP: instantaneous power failure), 09 (UV: | | | | | | |
undervoltage), 10 (TRQ: torque limited), 11 (RNT: operation time over), 12 (ONT: plug-in time over), | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
13 (THM: thermal alarm signal), 19 (BRK: brake release), 20 (BER: braking error), 21 (ZS: 0 Hz | 00(RUN) | 00(RUN) | 00(RUN) | 00(RUN) | × | ○ |
detection signal), 22 (DSE: speed deviation maximum), 23 (POK: positioning completed), |
24 (FA4: set frequency overreached 2), 25 (FA5: set frequency reached 2), 26 (OL2: overload notice | | | | | | |
advance signal (2)), 27 (Odc: Analog O disconnection detection), 28 (OIDc: Analog OI disconnection | 03(OL) | 03(OL) | 03(OL) | 03(OL) | | |
detection), 29 (O2Dc: Analog O2 disconnection detection), 31 (FBV: PID feedback comparison), | × | ○ |
32 (NDc: communication line disconnection), 33 (LOG1: logical operation result 1), 34 (LOG2: logical | | | | | | |
operation result 2), 35 (LOG3: logical operation result 3), 36 (LOG4: logical operation result 4), | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
37 (LOG5: logical operation result 5), 38 (LOG6: logical operation result 6), 39 (WAC: capacitor life | 07(OTO) | 07(OTO) | 07(OTO) | 07(OTO) | × | ○ |
warning)(*2), 40 (WAF: cooling-fan speed drop), 41 (FR: starting contact signal), 42 (OHF: heat sink |
overheat warning), 43 (LOC: low-current indication signal), 44 (M01: general-purpose output 1), | | | | | | |
45 (M02: general-purpose output 2), 46 (M03: general-purpose output 3), 47 (M04: general-purpose | | | | | | |
output 4), 48 (M05: general-purpose output 5), 49 (M06: general-purpose output 6), 50 (IRDY: inverter | 40(WAF) | 40(WAF) | 40(WAF) | 40(WAF) | × | ○ |
ready), 51 (FWR: forward rotation), 52 (RVR: reverse rotation), 53 (MJA: major failure), 54(WCO: | | | | | | |
window comparator O), 55(WCOI: window comparator OI), 56 (WCO2: window comparator O2) | | | | | | |
(When alarm code output is selected for "C062", functions "AC0" to "AC2" or "AC0" to | 05(AL) | 05(AL) | 05(AL) | 05(AL) | × | ○ |
"AC3" [ACn: alarm code output] are forcibly assigned to intelligent output terminals 11 to 13 |
or 11 to 14, respectively.) | | | | | | |
00 (output frequency), 01 (output current), 02 (output torque), 03 (digital output frequency), 04 (output | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
voltage), 05 (input power), 06 (electronic thermal overload), 07 (LAD frequency), 08 (digital current |
monitoring), 09 (motor temperature), 10 (heat sink temperature), 12 (general-purpose output YA0) | | | | | | |
00 (output frequency), 01 (output current), 02 (output torque), 04 (output voltage), 05 (input power), 06 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
(electronic thermal overload), 07 (LAD frequency), 09 (motor temperature), 10 (heat sink temperature), 11 |
(output torque [signed value]), 13 (general-purpose output YA1) | | | | | | |
00 (output frequency), 01 (output current), 02 (output torque), 04 (output voltage), 05 (input power), 06 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | × | ○ |
(electronic thermal overload), 07 (LAD frequency), 09 (motor temperature), 10 (heat sink temperature), 14 |
(general-purpose output YA2) | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |