Hp 17bII+ Financial Calculator
Edition June January
Printing History
Welcome to the hp17bII+
Welcome to the hp 17bII+
Contents
Using Parentheses in Calculations
Error Messages
Power Function Exponentiation
Saving and Reusing Numbers
Time Value of Money
Interest Rate Conversions
Cash Flow Calculations
Depreciation
Bonds
10 121 Running Total and Statistics
11 141 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
12 153 The Equation Solver
14 190 Additional Examples
More About Calculations
Assistance, Batteries, Memory, and Service
RPN The Stack
Menu Maps RPN Summary
RPN Selected Examples Error Messages Index
List of Examples
List of Examples
General Business Calculations
Currency Exchange Calculations
Interest Rate Conversions
How to Use the Equation Solver
Time, Alarms, and Date Arithmetic
Bonds and Notes
Running Total and Statistical Calculations
Important Information
Important Information
Adjusting the Display Contrast
Power On and Off Continuous Memory
Getting Started
Getting Started
What You See in the Display
Setting the Language
Keys for language Key Description
18 1 Getting Started
Backspacing and Clearing
Shift Key @
Keys for Clearing
Keys Display Description
20 1 Getting Started
Keys DisplayDescription
Doing Arithmetic
Using the Menu Keys
Keying in Negative Numbers
22 1 Getting Started
Menu Labels Menu Keys
Main Menu
24 1 Getting Started
Main Menu Menu Label Operations Done Covered This Category
Choosing Menus and Reading Menu Maps
Using the MU%C menu
26 1 Getting Started
Displaying the MU%C menu
Calculations Using Menus
Exiting Menus e
Clearing Values in Menus
28 1 Getting Started
= Cost
Solving Your Own Equations Solve
30 1 Getting Started
Typing Words and Characters the ALPHAbetic Menu
Keys
Editing ALPHAbetic Text
Characters
Alphabetic Editing Operation Label or Key to Press
Calculating the Answer Calc
Keyboard
32 1 Getting Started
KeysDisplayDescription
Decimal Places
Controlling the Display Format
Internal Precision
Temporarily SHOWing ALL
Exchanging Periods and Commas in Numbers
Rounding a Number
Modes
Error Messages
36 1 Getting Started
Double Space. Press
Number of bytes Percentage of total Memory still free
Calculator Memory @M
Calculator Line
Arithmetic
VDoing Calculations
38 2 Arithmetic
VUsing Parentheses in Calculations
Keys Display
Arithmetic
VThe Percent Key
Mathematical Functions
40 2 Arithmetic
VThe Power Function Exponentiation
Shifted Math Functions
Key
Math Menu Labels
Math Menu
42 2 Arithmetic
Description
History Stack of Numbers
Saving and Reusing Numbers
VReusing the Last Result @L
VKeys Display
44 2 Arithmetic
VKeys Display Description
Storing and Recalling Numbers
Keys New Register Contents
Doing Arithmetic Inside Registers and Variables
Arithmetic in Registers
Scientific Notation
48 2 Arithmetic
Range of Numbers
Business Percentages BUS Menus Description
Percentage Calculations Business
Examples Using the BUS Menus
Using the BUS Menus
Percent Change %CHG
50 3 Percentage Calculations in Business
Percent of Total %TOTL
Markup as a Percent of Cost MU%C
Markup as a Percent of Price MU%P
52 3 Percentage Calculations in Business
Sharing Variables Between Menus
Currency Exchange Calculations
Currx Menu
54 4 Currency Exchange Calculation
Currx Menu
Selecting a Set of Currencies
Currency Exchange Calculation
Menu Key
Currencies
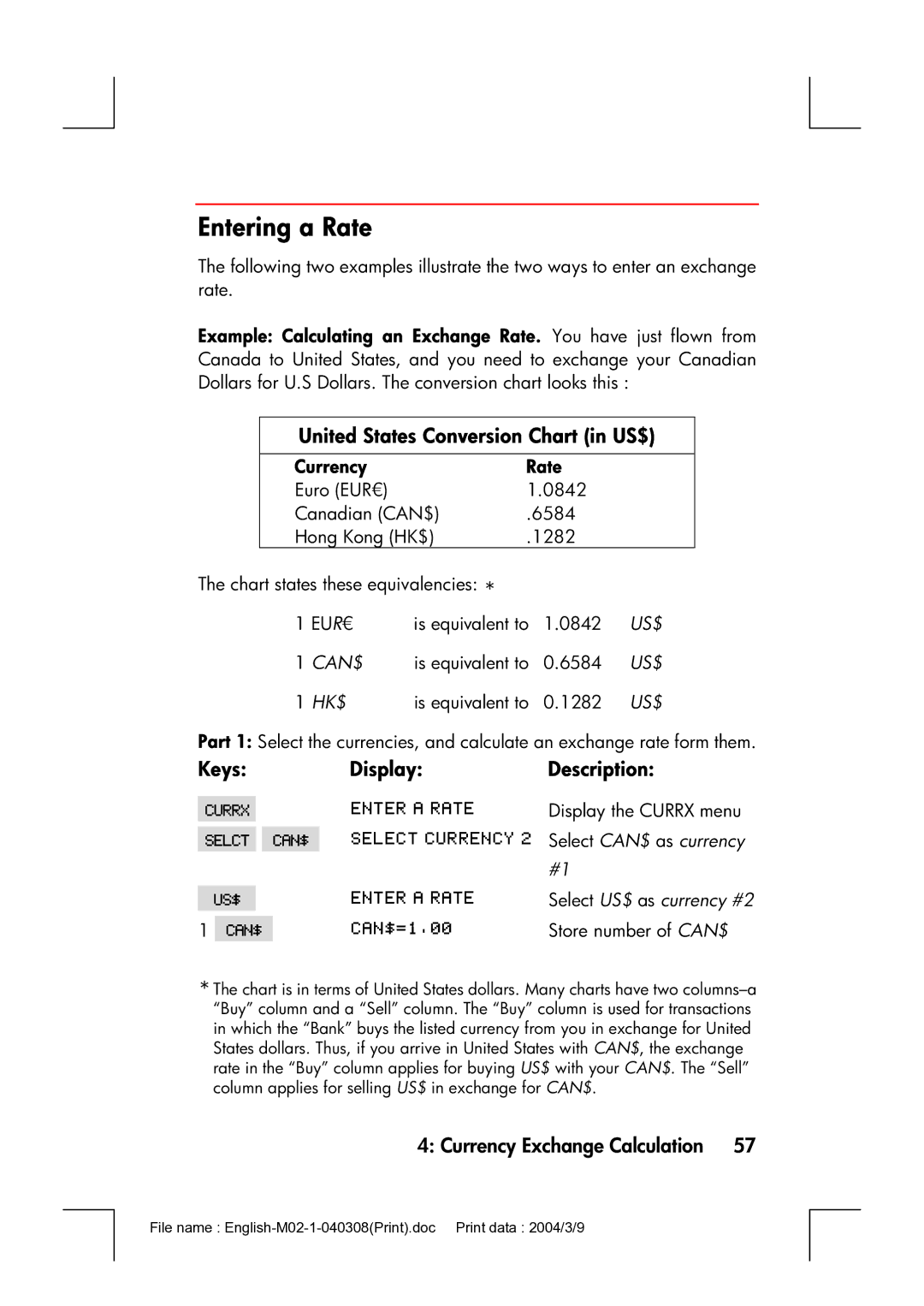
Entering a Rate
United States Conversion Chart in US$
Currency Rate
Select CAN$ as currency
Select HK$ as currency
58 4 Currency Exchange Calculation
Converting Between Two Currencies
Storing and Recalling Sets of Currencies
Example Converting between Hong Kong and U.S Dollars
60 4 Currency Exchange Calculation
Clearing the Currency Variables
Time Value of Money
TVM Menu
Time Value of Money
Second Level of TVM
First Level of TVM
First Level
TVM Menu Labels
Second Level
Shortcut for N Multiplies the number in the display by
64 5 Time Value of Money
Cash Flow Diagrams and Signs of Numbers
FV is
66 5 Time Value of Money
Using the TVM Menu
Loan Calculations
Figures and stores number
68 5 Time Value of Money
@c
Figures and stores
70 5 Time Value of Money
000
Savings Calculations
72 5 Time Value of Money
Figures and stores number
74 5 Time Value of Money
Leasing Calculations
76 5 Time Value of Money
Amortization Amrt
Amrt Menu Labels
Displaying an Amortization Schedule
Label
78 5 Time Value of Money
Time Value of Money
Next successive set of payments authorized
80 5 Time Value of Money
First year
82 5 Time Value of Money
Printing an Amortization Table Table
Calculates and prints
84 6 Interest Rate Conversions
Interest Rate Conversions
Icnv Menu
Converting Interest Rates
Interest Rate Conversions
86 6 Interest Rate Conversions
Compounding Periods Different from Payment Periods
88 6 Interest Rate Conversions
90 6 Interest Rate Conversions
Cash Flow Calculations
Cflo menu
Cash Flow Calculations
92 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Cflo Menu Labels
Cash Flows Ungrouped
94 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Creating a Cash-Flow List
For grouped cash flows The display now shows
Entering Cash Flows
96 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Prompting for #TIMES #T?. When the calculator displays
Display Description
Viewing and Correcting the List
Naming and Renaming a Cash-Flow List
Copying a Number from a List to the Calculator Line
98 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Deleting Cash Flows from List. Pressing
Clearing a Cash-Flow List and Its Name
Starting or GETting Another List
Viewing the Name of the Current List. Press , then e
100 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Cash-Flow Calculations IRR, NPV, NUS, NFV
Calc Menu for Cflo Lists Menu Label
102 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Calculates NPV
104 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Group Number Amount
Prompts for next cash
106 7 Cash Flow Calculations
Doing Other Calculations with Cflo Data
Bonds
Bond Menu
108 8 Bonds
Bond Menu Labels
Menu Description Label
Bonds
Doing Bond Calculations
110 8 Bonds
To calculate the price or yield of a bond
Since there is no call on
112 8 Bonds
MM.DDYYYY format
Depreciation
Deprc Menu
114 9 Depreciation
Depreciation
Deprc Menu Labels
DB, SOYD, and SL Methods
Doing Depreciation Calculations
116 9 Depreciation
To calculate the depreciation for an asset
Basis Salv 4,000
Acrs Method
Year Percentage Deductible Keys Display Description
118 9 Depreciation
Partial-Year Depreciation
120 9 Depreciation
Calendar Year Depreciation Value
Running Total and Statistics
Running Total and Statistics
SUM Menu
SUM Menu Labels
122 10 Running Total and Statistics
Entering Numbers and Viewing the Total
Creating a SUM List
124 10 Running Total and Statistics
Date
Amount Date
Transaction
126 10 Running Total and Statistics
Naming and Renaming a SUM List
Doing Statistical Calculations Calc
Clearing a SUM List and Its Name
Calculations with One Variable
Calc Menu for SUM Lists Menu Key
128 10 Running Total and Statistics
Expense
Month Phone
130 10 Running Total and Statistics
Calculations with Two Variables Frcst
Calc Total Mean Medn Stdev Range More MIN MAX Sort Frcst
132 10 Running Total and Statistics
Frcst Menu Labels
Logarithmic Curve Fit
Curve Fitting and Forecasting
To do curve fitting and forecasting
134 10 Running Total and Statistics
Number of Minutes Dollar Sales
Radio
Advertising Values
Minutes
136 10 Running Total and Statistics
Minutes
138 10 Running Total and Statistics
Weighted Mean and Grouped Standard Deviation
Rent
Summation Statistics
140 10 Running Total and Statistics
Doing Other Calculations with SUM Data
Time, Appointments, Date Arithmetic
Viewing the Time and Date
Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
Time Menu
Time Menu Labels
142 11 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
SET Menu Labels
Setting the Time and Date SET
Menu Label Description
Or DD.MMYYYY
Adjusting the Clock Setting Adjst
Changing the Time and Date Formats SET
144 11 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
Viewing or Setting an Appointment APT1-APT10
Menu Labels for Setting Appointments Description
Appointments Appt
146 11 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
To set an appointment or view its current setting
Acknowledging an Appointment
Clearing Appointments
Unacknowledged Appointments
148 11 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
To acknowledge a past-due appointment
Date Arithmetic Calc
Calculating the Number of Days between Dates
Determining the Day of the Week for Any Date
Calc Menu Labels for Date Arithmetic
150 11 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
Calculating Past or Future Dates
DATE2
152 11 Time, Appointments, and Date Arithmetic
Equation Solver
Solver Example Sales Forecasts
Equation Solver
Next =OLD
154 12 The Equation Solver
Menu Label
Solve Menu
156 12 The Equation Solver
Keys
Entering Equations
Solve Menu Labels
To make an entry into the Solver list
Calculating Using Solver Menus Calc
To do a calculation using a Solver menu
158 12 The Equation Solver
Rmenu label
Eqty
160 12 The Equation Solver
Naming an Equation
Editing an Equation Edit
Shared Variables
Finding an Equation in the Solver List
Clearing Variables
162 12 The Equation Solver
Deleting a variable is quite different from clearing it
Deleting Variables and Equations
Deleting One Equation or Its Variables Delet
Writing Equations
Deleting All Equations or All Variables in the Solver @c
164 12 The Equation Solver
100
⋅ C
⋅ E
What Can Appear in an Equation
166 12 The Equation Solver
+ 5 ⋅ E
Using the Alpha Menu
Using a Typing Aid
Solver Functions
168 12 The Equation Solver
DDAYSd1d2cal
Solver Functions for Equations Description
HH.MMSS format
170 12 The Equation Solver
IFcond expr 1 expr
Svariable name
SIZECCFLO-listname
Cfr c 1 c 2 s expr
SIZESSUM-listname
#TCFLO-listnameflow#
172 12 The Equation Solver
Days
Conditional Expressions with if
OperatorKeys
≥ = ≤ = ≠ 174 12 The Equation Solver
Examples of Conditional Equations
Rating
VALUE=FIRST+1 ⎟ FIRST. If FIRST=0, then VALUE=FIRST
Percent Salary Increase
176 12 The Equation Solver
Summation Function ∑
Accessing Cflo and SUM Lists from the Solver
178 12 The Equation Solver
Creating Menus for Multiple Equations S Function
How the Solver Works
180 12 The Equation Solver
Halting and Restarting the Iterative Search
Entering Guesses
182 12 The Equation Solver
184 13 Printing
Printing
Double-Space Printing
Printer’s Power Source
Printing the DisplayP
Printing
Printing Variables, Lists, and Appointments List
Printing Other Information @p
Printer Menu Labels
186 13 Printing
Printing Descriptive Messages MSG
Trace Printing Trace
188 13 Printing
Keys Print-out
How to Interrupt the Printer
Loans
Additional Examples
Simple Annual Interest
190 14 Additional Examples
Additional Examples
Yield of a Discounted or Premium Mortgage
Figures and stores total
192 14 Additional Examples
See appendix F for RPN keystrokes for the next two examples
Annual Percentage Rate for a Loan with Fees
194 14 Additional Examples
11.5
Loan with an Odd Partial First Period
@c e
Solver Equation for Odd-Period Calculations
196 14 Additional Examples
Canadian Mortgages
Solver Equation for Canadian Mortgages
198 14 Additional Examples
Solver Equation for Advance Payments
Advance Payments Leasing
Savings
Value of a Fund with Regular Withdrawals
200 14 Additional Examples
Displays periodic
202 14 Additional Examples
Deposits Needed for a Child’s College Account
Additional Examples
204 14 Additional Examples
Flow of Withdrawals
For FLOW1
206 14 Additional Examples
Value of a Tax-Free Account
35
208 14 Additional Examples
Value of a Taxable Retirement Account
Modified Internal Rate of Return
Group No. of Months Cash Flow, $ Flow no
210 14 Additional Examples
V8 /12
180000
FLOW0
200000 I
V13 /12
212 14 Additional Examples
Solver Equation for Insurance Price
Price of an Insurance Policy
214 14 Additional Examples
Bonds
216 14 Additional Examples
Discounted Notes
Moving Average
Statistics
Solver Equation for Moving Averages
218 14 Additional Examples
Chi-Squared χ2 Statistics
Use
If necessary
If the expected values vary
220 14 Additional Examples
Number
Keystroke Display Description
Assistance, Batteries, Memory, and Service
Assistance, Batteries Memory, and Service
Answers to Common Questions
Obtaining Help in Operating the Calculator
Assistance, Batteries, Memory, and Service
Power and Batteries
Low-Power Indications
Do not use rechargeable batteries
Installing Batteries
Assistance, Batteries, Memory, and Service
Managing Calculator Memory
Reset hole
Resetting the Calculator
Erasing Continuous Memory
For English language
For the other languages
Clock Accuracy
Determining If the Calculator Requires Service
Environmental Limits
„ If the calculator won’t turn on
Assistance, Batteries, Memory, and Service
Confirming Calculator Operation Self-Test
Warranty
Assistance, Batteries, Memory, and Service
Europe Country Telephone numbers
Service
Asia Pacific Country Telephone numbers
America Country Telephone numbers
HP Invent
Regulatory information
Canada
Japan
IRR% Calculations
More About Calculations
Possible Outcomes of Calculating IRR%
More About Calculations
Storing a Guess for IRR%
Halting and Restarting the IRR% Calculation
Solver Calculations
Direct Solutions
O F I T = P R I C E - C O S T
S T = P R I C E - P R O F I T
= a R E a ⎟ W
E a = L x W
Iterative Solutions
More About Calculations
More About Calculations
More About Calculations
Actuarial Functions
Equations Used by Built-in Menus
Percentage Calculations in Business BUS
Time Value of Money TVM
Amortization
Cash-Flow Calculations
Interest Rate Conversions
NOM % P
NPV = CF0 + ∑CFj x Uspv i% nj x Sppv i% Nj
NUS = Uspv i% N Total = ∑nj ⋅ CFj
Bond Calculations
DB = Basis ⋅ Fact % /100
Depreciation Calculations
Sum and Statistics
Forecasting
Model Transformation
SXY = Σ X
Equations Used in Chapter
− M
SX 2 ⋅ SY
Odd-Period Calculations
Advance Payments
Modified Internal Rate of Return
Menu Maps
Menu Maps
Figure C-2. Currx Menu
Figure C-3. FIN Menu
Figure C-3 . FIN Menu
Figure C-4. SUM Menu
Figure C-5. Time Menu
Figure C-6. Solve Menu
About RPN
RPN Summary
About RPN on the hp 17bII+
RPN Summary
To select RPN mode Press @
Setting RPN Mode
Function Definition Key to Use Name
Where the RPN Functions Are
~ same as
Same as
Doing Calculations in RPN
Arithmetic Topics Affected by RPN Mode
Simple Arithmetic
↓. Except in Cflo and SUM lists, Efunction and the key also
To Calculate Press Display
27 %
RPN Mode ALG Mode
Calculations with STO and RCL
Chain Calculations-No Parentheses
Display
To Calculate Press
RPN The Stack
What the Stack Is
RPN The Stack
Exchanging the X- and Y-Registers in the Stack
Reviewing the Stack Roll Down
Arithmetic-How the Stack Does It
Lost
How Enter Works
Clearing Numbers
Reusing Numbers
Last X Register
Retrieving Numbers from Last
Chain Calculations
Exercises
Solution 23 @w13 E9 *-7@t+
RPN Selected Examples
RPN Selected Examples
KeysDisplay
Calculates annual interest
#TIMES1 for FLOW1
For E, press =, not
I11 I
Annual payment deposit
Error Messages
Error Messages
Error Messages
Error Messages
Error Messages
Index
Special Characters
Index
147
169
166
156
,
174-76
31-32
145
149
144
116
162-64
229
181-83
Examples
133
138-39
168-71
72-73
,
213-15
239
, 132 , 109 , 49, 53 , 52, 128 , 128 , 128 , 128
242-46
143-44
Memory. See also Continuous Memory
92-94
, 101 , 101 , 101 , 157 , 56 , 56 , 56 , 42
175
164-67
, 56 , 42 , 18 @p, 186 P
PMT. See also Payments in TVM, 63 rounded amortization
Repeating appointments past-due, 148 setting
Using
128
146-47
176
243-46
171
178
148
133-34
This regulation applies only to The Netherlands