Hardware and Bios Technical Reference Manual
Hewlett-Packard Company
Ordering the Phoenix Bios Manual
Preface
Conventions
Bibliography
Contents
Overview
Bios version GX.07.xx
System Board Ns D3657-63001 and D3661-63001
Cache Memory Main Memory
Summary of the HP/Phoenix Bios
Video Controllers
Index
HP Vectra 500 Series
Introduction
Introduction
System Overview
D4051-63001 Models
D4051-63001- Desktop Models
D4051-63001 Minitower Models
D3657-63001 Models
D3657-63001 Desktop Models
D3657-63001 Minitower Models
System Features
D3661-63001 Model
D3661-63001 Minitower Model
Shading Description
HP Service Part Number
Component Desktop Minitower
Principal Features
Physical and Environmental Specifications
Computer Characteristic Type Description
These Operating temperature +5C to +40C +40F to +104F
Kcal per hour 360 BTU per hour
Keyboard Flat
Inches by 7 inches by 1.3 inches
Power Consumption
+ 5
+ 12
+ 5 5A maximum per slot + 12 1A maximum per slot
Rear Panel Connectors
Display Connector
Parallel Device Connector
CD-ROM Drive Specifications
HP Vectra 500 Series
System Board SiS Chipset Part Number D4051-63001
Overview
Overview
Configuration
Supported Processor P54CS Level-2 L2 256 KB cache sockets
System Board Architecture
System Board Architecture
Bios
System Board Physical Layout
SiS Chipset
SiS Chipset
Pentium Processor
Level-2 Cache Host Bridge & Memory Controller SiS
Control Main Memory Video
SiS
Host/PCI Bridge SiS 5511 Chip
EDO Dram
Feature Summary
Data Path SiS 5512 Chip
PCI/ISA Bridge SiS 5513 Chip
Timer/Counter
ISA Bus Controller
DMA Controller
Interrupt Controller
System Board Switches and Jumpers D4051-63001
SW1 Switch
Switch Default
SW2 Switch
Jumper J7 Settings
CPU Bus Frequency Jumper
Processor Speeds
Space-Bar Power-On Feature Jumper
Power-on Spacebar enabled Spacebar disabled
Cache Jumper
Synchronous Asynchronous
Processor Socket D4051-63001
Memory Sockets D4051-63001
Backplane D4051-63001
Desktop Backplane
Minitower Backplane
ISA PCI
Devices on the Processor Local Bus D4051-63001
Main Memory UMA
Cache Memory D4051-63001
Memory Total 12 MB
Level-1 Cache Memory
Level-2 Cache Memory
Pentium Processor D4051-63001
Superscalar Architecture
Floating Point Unit
Dynamic Branch Prediction
Instruction and Data Cache
Advanced Power Management
Data Integrity
Devices on the PCI Bus
Graphics/Integrated Video D4051-63001
Video Controller
Devices on the PCI Bus
Desktop Configuration Connections to Data Cables
Integrated Drive Electronics IDE Controller
Desktop Minitower
Configuration Connections to Data Cables
Transfer Rates Versus Modes of Operation
Mode
Disk Capacity Versus Modes of Addressing
Cylinders Heads per
Bytes per
Devices on the ISA Bus
Super I/O Chip NS 87308 or NS
Functions
Function Features
Serial/Parallel Ports
Floppy Drive Controller
Keyboard and Mouse Controller
Bios version GX.07.xx
HP Setup Program
Bios version GX.07.xx
Flash ROM
System Board Ns D3657-63001 and D3661-63001
Desktop Models
Minitower Models
Configuration Summary
D3661-63001 Models
Pentium Processor 256 KB Level-Two Cache Local Bus
PCI Bus
IDE Controller Channel Video
IDE Controller Channel
System Board Physical Layout
Principal Components and Features
Principal Components and Features
PCI Chipset
Host Bus
SB82437FX-66 Feature Summary
PCI, Cache and Memory Controller SB82437FX-66
Data Path Unit SB82438FX
Memory address map
Pentium reads and writes
Optional buffering of PCI memory writes
SB82438FX and SB82371FB Feature Summary
PCI/ISA Bridge and IDE Controller SB82371FB
System Board Configuration Switches
Processor Socket
VRM Socket
Main Memory Sockets
Advanced Power Management APM
HP Vectra 500 Series Desktop Backplane
HP Vectra 500 Series Minitower Backplane
Devices on the Processor Local Bus
Pentium Processor
Devices on the Processor Local Bus
Floating Point Unit FPU
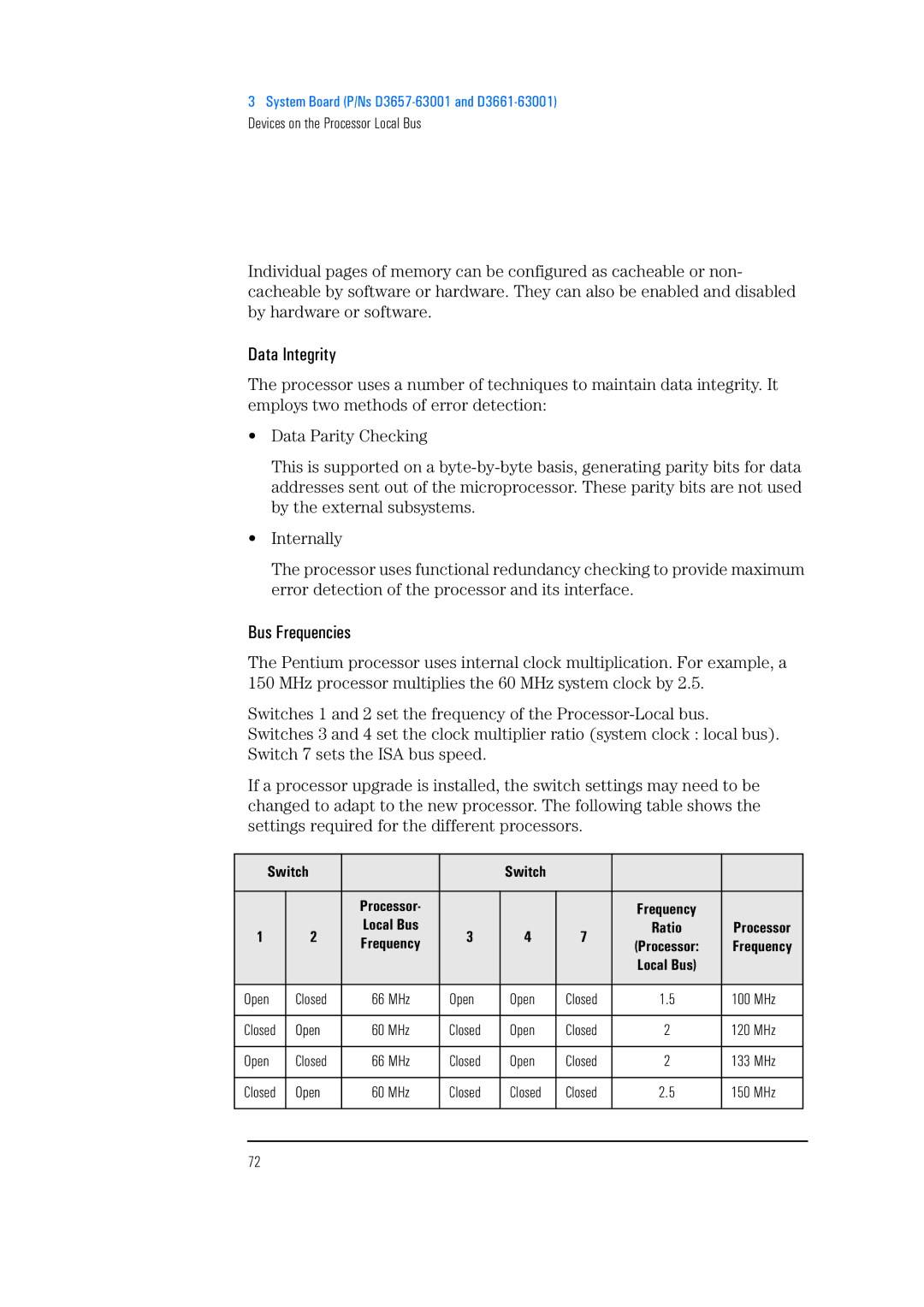
Switch
Bus Frequencies
Cache Memory
166 MHz
180 MHz
Closed 200 MHz
Main Memory
Video Controller
Video Resolutions Supported
S3 Trio 64PnP Video Controller
Video Dram
Other PCI Accessory Devices
Super I/O Chip SMC FDC37C932
Serial/Parallel Communications Ports
Floppy Drive Controller FDC
Real-Time Clock RTC
Serial Eeprom
Other ISA Accessory Devices
System ROM
Summary of the HP/Phoenix Bios
HP/Phoenix Bios Description
Updating the System ROM
Error Diagnostics and Suggested Corrective Actions
HP/Phoenix Bios Description
Little Ben
HP/Phoenix Bios Bios version GX.07.xx
Setup Program Bios version GX.07.xx
Main Menu Bios version GX.07.xx
HP/Phoenix Bios Bios version GX.07.xx
Configuration Menu Bios version GX.07.xx
Configuration T e g r a t e d I / O P o r t s
Enables or disables
Parallel port 378h IRQ7 On board parallel port
Security Menu Bios version GX.07.xx
Power Menu Bios version GX.07.xx
Summary Configuration Screen Bios version GX.07.xx
PCI Slot Not Installed ISA PnP
System RAM 15 MB
Bank a MB EDO
Bank B 8MB EDO
Addresses Used by the System Bios version GX.07.xx
System Memory Map Bios version GX.07.xx
Bios I/O Port Map Bios version GX.07.xx
Address Ports Function Bits
System Board Components Bios version GX.07.xx
DMA Channel Controllers Bios version GX.07.xx
Used for PCI configuration1
0378-037F Parallel port 03B0-03BB
Interrupt Controllers
First DMA controller used for 8-bit transfers
Second DMA controller used for 16-bit transfers
IRQ Interrupt Vector Interrupt Request Description
PCI Interrupt Request Lines Bios version GX.07.xx
Power-On Self-Test Bios version GX.07.xx
Test Description System Bios Tests
Abort
To abort
Process to abort
Display, but the boot process continues
Using
Failure causes an error code to display
Internal Cache
Error Messages Bios version GX.07.xx
Message Corrective Action and/or Explanation
Beep Codes Bios version GX.07.xx
Numeric Beep Pattern Code Description
HP/Phoenix Bios Bios version GJ.07.xx
Setup Program Bios version GJ.07.xx
Main Menu Bios version GJ.07.xx
HP/Phoenix Bios Bios version GJ.07.xx
Preferences Menu Bios version GJ.07.xx
Configuration Menu Bios version GJ.07.xx
Security Menu Bios version GJ.07.xx
Power Menu Bios version GJ.07.xx
102
Summary Configuration Screen Bios version GJ.07.xx
Copyright 1995 Hewlett-Packard
Addresses Used by the System Bios version GJ.07.xx
System Memory Map Bios version GJ.07.xx
MB plus- Extended Memory
104
Bios I/O Port Map Bios version GJ.07.xx
0378-037F Parallel Port 03B0-03DF
105
DMA Channel Controllers Bios version GJ.07.xx
Used for PCI Configuration1 0496-0497 HP Reserved 0678-067A
0778-077A
106
107
PCI Interrupt Request Lines
Free, if not used used for serial port2
Free, if not used used for parallel port3
108
Power-On Self-Test Bios version GJ.07.xx
Shadow Ram Bios version GJ.07.xx
109
Error code to display and the boot process to abort
Post Test
Video Tests
Initialize the Video
System Board Tests
Code to display 111
Causes an error code to display
Processor. Test failure causes an error code to display
Ports. Test failure causes an error code to display
Test failure causes an error code to display
Error Messages Bios version GJ.07.xx
Device 0079 on system board
113
Beep Codes Bios version GJ.07.xx
Message
114
Video Controllers
115
SiS 6205 Video Controller
SiS 6205 Video Controller Summary
SiS 6205 Video Controller
116
Upgradeable to
Upgrading Video Memory UMA
Using the HP Dynamic Video Feature
Typical Windows 95 Video Resolutions SiS 6205 Chip
Resolution Number of colors
Memory
Vesa Feature Connector SiS 6205 Chip
119
Upgradeable
Integrated Ultra VGA Video Controller
S3 Trio 64 Video Controller Summary
S3 Trio 64 Video Memory
S3 Trio 64 Video Modes
121
Extended Video Modes with 1 MB Dram S3 Trio
122
Mode No
123
124
Typical Windows 95 Video Resolutions S3 Trio
640 x 256, 64K 60, 72 800 x 56, 60, 72 1024 x I43 1 60, 70
Vesa Connector
126
Matrox MGA Millennium Video Controller Card
Matrox MGA Millennium Video Controller Card
127
MGA Connectors
MGA Video Memory
128
Available MGA Video Resolutions
Resolution
Refresh Rate Hz
640 x 256, 64K, 16M 120 800 x 1024 x 1280 x 1600 x 1200
256 64 K 16.7 M
Number 256 64 K 16.7 M
MGA Video Bios
Further Information About MGA
131
DB15 Connector Pinout
DB15 Connector Pinout
132
Aztech AT3300 Audio Fax/Data Modem
134
Communications Options
135
Tone or pulse dialing
136
European Firmware and Telephone Line Configuration
Configuring the firmware code
Using the Aztech AT3300 Localisation Utility
Aztech AT3300 Localisation Utility
138
Select the Country
139
Using the HyperTerminal Application
140
Comments Modem
142
Index
143
144
S3 Trio
145
UMA
146