Debugging with GDB Manual
Page
Table of Contents
Breakpoints
Continuing and stepping Signals
Print settings Value history
Stack frames
Examining the Symbol Table
Specifying a Debugging Target
Batch Mode
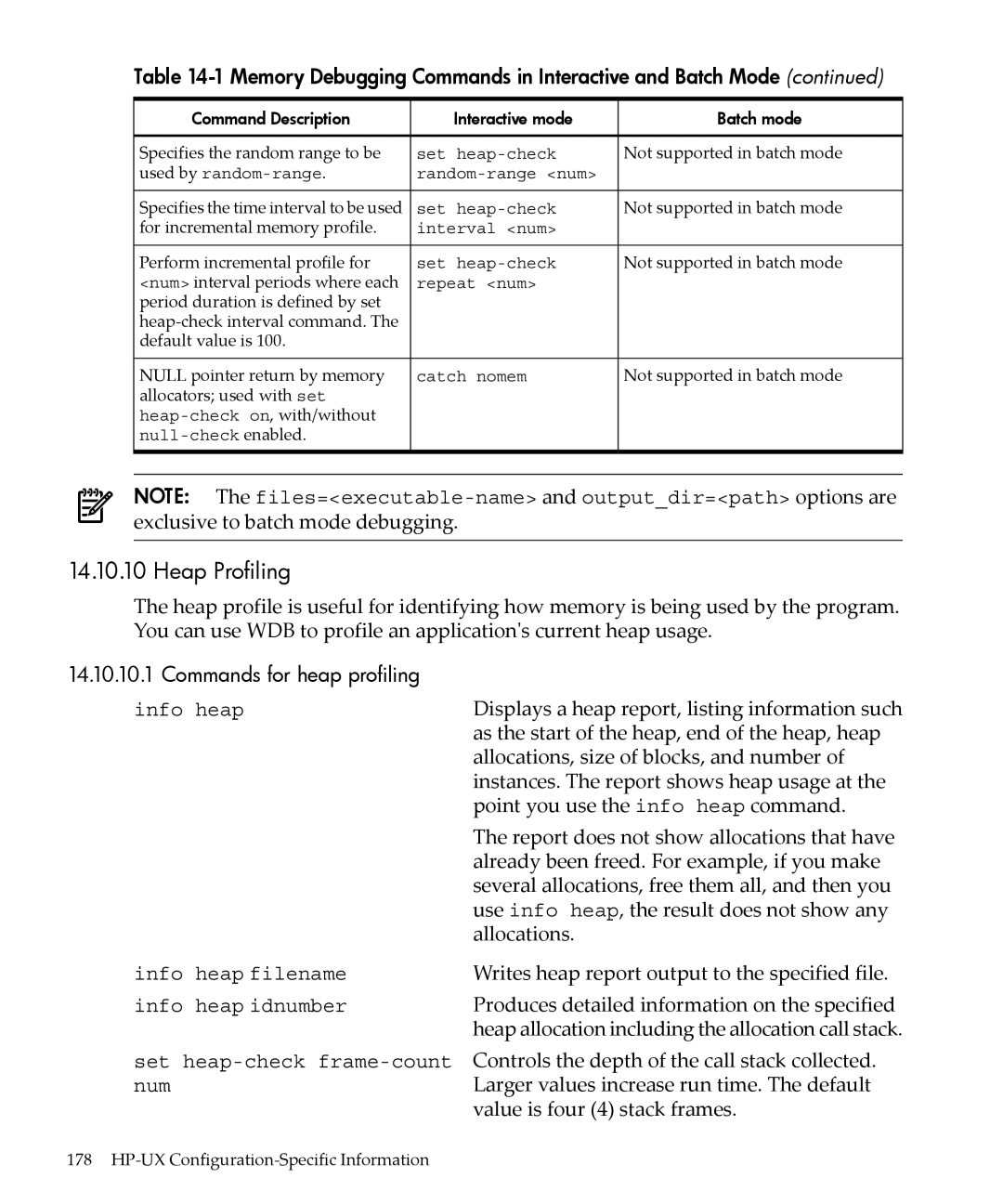
Stop when freeing unallocated or deallocated blocks
Scramble previous memory contents at malloc/free calls
Commands for heap profiling
Enhancements to the dumpcore command
Support for the info target Command
Support for the dumpcore command
Example Illustrating Execution Path Recovery
Debugging the application using GDB under Aries
Command for evaluating the address of an expression
Support for steplast command for C and C++
Detecting memory leaks using GDB under Aries
HP-UX Terminal User Interface
User-defined commands 287 18.2
Miscellaneous commands 265 16.3
Setting Command History Feature in GDB 281 17.4
Command files 289 Commands for controlled output 290
20.9 Invalidation notices 303
20.7 Errors 302 20.8
22.2 How to report bugs 361
304
List of Tables
List of Examples
Free Software
Summary of GDB
Contributors to GDB
Page
Contributors to GDB
Page
Sample GDB Session
Let us use GDB to try to see what is going on
Loading the Executable
Here we describe how to set a breakpoint
Setting Display width
Setting Breakpoints
Running the executable under GDB
Examining the Stack
Stepping into a subroutine
Printing Variable Values
Setting Variable Values During a Session
Listing Source Code
Gdb c Continuing Definebaz,defnQUOTEfooUNQUOTE Baz
Page
Getting In and Out of GDB
Invoking GDB
Choosing files
Files
Processed. See Command files
Choosing modes
Time a stack frame is displayed which includes each
GNU Emacs sets this option when it runs GDB as a
Line number in a standard, recognizable fashion each
Like two `\032 characters, followed by the file name
Emacs
Redirecting WDB input and output to a file
Quitting GDB
Interface
Shell commands
Page
Command syntax
GDB Commands
Command completion
GDB sounds bell press TAB again, to see
Getting help
Short list of named classes of commands
Help , h
Complete
Apropos reload
Results
This is intended for use by GNU Emacs
Getting help
Page
Starting your program
Running Programs Under GDB
Compiling for debugging
Arguments, so that you may use normal
Your program. SeeProgram Environment
See Arguments To Your Program
Directory
Program Environment
Arguments To Your Program
Program. See Program Input and Output
Path environment variable
For example, this command
Display the list of search paths for executables
Do not supply varname, print the names
Working directory
Program Input and Output
Debugging a Running Process
Killing the child process
Debugging programs with multiple threads
New process 35 thread
With the command argument threadno
Here are commands to get more information about threads
Thread apply command allows you to
Display a summary of all threads currently
Debugging programs with multiple processes
Set the debugger response to a program call
New process. The mode can be
Unimpeded. This is the default
Fork. The child process runs
Stopping and Continuing
Breakpoints
Setting breakpoints
See Break conditions page 59, for more
Breakpoints
Whether
Breakpoint
Catchpoint
Breakpoint is
Marked to be
When hit
Enabled
Breakpoints are
Setting catchpoints
Unloading of any dynamically loaded
Call to vfork. This is currently only
Is currently only available for HP-UX
Shared library, or the unloading
Disabling breakpoints
Deleting breakpoints
Selecting a frame page 73 . When
Break conditions
Stops your program only if the value
Breakpoint, GDB prints an error message
No symbol foo in current context
Use condition, GDB checks expression
Breakpoint command lists
Breakpoint menus
Cannot insert breakpoints
Continuing and stepping
Conditions
Function
Setting breakpoints page 52. This form of the command
Signals
Stops. See Automatic display
Info handle is an alias for info signals
Stopping and starting multi-thread programs
Stopping and Continuing
Examining the Stack
Stack frames
Stacks Without frames
Commands for Examining the Stack
Backtraces
Selecting a frame
With an argument, this command is used to select a stack
Have existed longer. n defaults to one
When used without any argument, this command does not
Information about a frame
Setting catchpoints
Page
List
Examining Source Files
Printing source lines
Show listsize
Searching source files
Specifying source directories
Show directories
Source and machine code
Contains
Select the instruction set to use when
Set disassembly-flavor
Disassemble or x/i commands
Disassembling the program via
Page
Expressions
Following forms of print command are supported
Examining Data
To See Artificial arrays page 85, for more information
Type addr
Where it is defined. See Program variables
Program variables
Normally supposed to reside at addr
You can print the contents of array with
Artificial arrays
Output formats
Print, s null-terminated string, or
Machine instruction. The default is
Examining memory
Time you use either x or print
However, the count n must come first wx4 does not work
See Output formats
Automatic display
For fmt specifying only a display format and not a size or
For fmt i or s, or including a unit-size or a number
Print settings
Symbolic form of an address
A symbol. This is the default
File name and line number of a symbol
Address
Setting number-of-elementsto zero
Default is off
Strings. When GDB starts, this limit is set to
Short strings. The default is off
Print using only seven-bit characters if this
This is the default format
Show which format GDB is using to print
Default
Show whether C++ names in assembly listings
These settings are of interest when debugging C++ programs
Default is on
Would print
Value history
Convenience variables
$exitcode
Command, in which case it is a pointer to the type of $
Format in which the data was printed
Program being debugged terminates
Or print the instruction to be executed next with
Registers
Info registers Info all-registers Info registers regname
Or add four to the stack pointer3 with3with
To get the bit pattern, try the following macro
Printing Floating Point Values
Floating point hardware
This is what the macro produces
100
List of filename extensions and languages
Using GDB with Different Languages
Switching between source languages
Cpp
Having GDB infer the source language
Setting the working language
Not skip over function prologues when stepping
Files
Type and range checking
Displaying the language
An overview of type checking
An overview of range checking
Supported languages
C++
Left shift, and right shift. Defined on integral types
Expressions is 0 for false and non-zero for true
Non-zero for true
Types and pointer types
Expressions page 83. Same precedence as , above
Class types
Double colons also represent the GDB scope operator see
C++ constants
1.3 C++ expressions
GDB expression handling can interpret most C++ expressions
Printing the variable or class returns
C++ defaults
C++ type and range checks
Breakpoint menus
GDB features for C++
GDB and C
See Breakpoint menus
Fortran types
Fortran
Fortran types supported
Greater than
Less than
Less than or equal to
Greater than or equal to
Commonblockname
Fortran special issues
Block
Examining the Symbol Table
Symbols will be read when needed
Two commands give this output
As with whatis, using ptype without an
For example, for this variable declaration
Do not replace symbol
Allow GDB to reload the symbols for
Replace symbol definitions
Once. This is the default
Tell GDB to resolve opaque types. An opaque
Setting
Is in another source file. The default is on
Class, or union―for example, struct
Altering Execution
Assignment to variables
Continuing at a different address
Stores the value 4 into that memory location
You can use the following command to return from a function
Giving your program a signal
Returning from a function
Return , return
Calling program functions
Patching programs
Is used as the return value from the function value
Patching programs
124
Commands to specify files
GDB Files
See Optional warnings and messages
Write the symbols for your program into a
Option with any of the commands that load
GDB has the entire symbol table available
Map in symbol information from this auxiliary
Section
If threshold is nonzero, symbols from all
Symbols were loaded. Both the commands list
To display or set the threshold, use the commands
New library has been loaded, until the symbol
Specifying shared library locations
Names where the desired shared libraries reside. GDB
Searching the default system directories
Megabytes
Verbose on. See Optional warnings
Errors reading symbol files
Messages
GDB circumvents the error by ignoring this
Symbol scope block as starting on the previous
Is the symbol type of the uncomprehended
Debug your program, though certain symbols
Specifying a Debugging Target
Commands for managing targets
Active targets
See Commands to specify files
Choosing target byte order
Executable
Instruct GDB to assume the target is big-endian
Instruct GDB to assume the target is little-endian
Display GDBs current idea of the target byte order
HP-UX Configuration-Specific Information
Summary of HP Enhancements to GDB
Implementation of ask mode for set follow-fork-mode
Support for setting breakpoints using shared library name
Command watchtarget
Linker Dependencies
HP-UX dependencies
Dependent Standard Library Routines for Run Time Checking
Abort Unlink Atoi
Getpid Close Srand Strchr
Supported Platforms and Modes
WDB Location
HP-UX targets
Support for Alternate root
GDB location
None
Specifying object file directories
Librtc.sl location $WDBROOT/bin Opt/langtools/ n/a
Bin $WDBROOT/bin
Fix and continue debugging
Fix and Continue compiler dependencies
Fix and Continue restrictions
Using Fix and Continue
Compile the program
Example Fix and Continue session
Run the program
Gdb edit
Gdb b main
Gdb run
Make the necessary changes. In this case, add return total
Inline Debugging in HP 9000 Systems
Inline Support
Gdb q
Inline Debugging in Integrity Systems
Breakpoint info frame disassembly
Following options available for the set inline-debugcommand
Step next list backtrace frame n info locals info args
Limitations
Debugging Inline Functions in Integrity Systems
Debugging Macros
Info frame disassembly
Viewing and Evaluating Macro Definitions
Evaluating Macros
Compiler Options to Enable Macro Debugging
Debug=none
Examples for Macro Debugging
HP-UX Configuration-Specific Information
Debugging Memory Problems
Memory debugging restrictions
When to suspect a memory leak
Memory Debugging Methodologies
Debugging Memory in Interactive Mode
Heap growth. The default value is 100. Every
Displays all current settings for memory
This command are ignored from report. If
Command discards the data existing in the file
Debugging Memory Problems
Specific pattern when it is allocated or
Debugging when the string option is set for
Have occurred and WDB reports the problem
Such as attempting to access space that is freed
Number of bytes, the debugger ignores it
Use the info command to show list of memory leaks
If the user specifies a value less than 16 for
User-specified value
Setting Configuration Options for Batch Mode
Debugging Memory in Batch Mode
Gdb info leak
Framecount=noframes or set heap-check frame-count noframes
Sets the number of frames to be printed for leak context
For 64 bit PA applications
For 32 bit IPF applications
For 64 bit IPF applications
For 64-bit IPF applications
Environment variable setting for Batch mode debugging
Ldpreload
Log file for batch mode must be
Aborts execution when heap objects
Aborts execution when out of memory
Stderr error message goes to stderr
Example for Batch Mode RTC
Complete one of the following steps
Preload the librtc library as follows
Rtcconfig file should contain entries such as the following
Run the program as follows
For 32 bit PA applications
Specifying the stack depth
Configuring memory debugging settings
Run the program Start a debugging session as follows
Specifying minimum leak size
For example, if you use
Stop when freeing unallocated or deallocated blocks
Scenarios in memory debugging
Specifying minimum block size
Syntax
Scramble previous memory contents at malloc/free calls
Interactive debugging mode set heap-check scramble on off
Detect dangling pointers and dangling blocks
Detect in-block corruption of freed blocks
Memory Debugging Commands in Interactive and Batch Mode
Off
Heap Profiling
Commands for heap profiling
Point you use the info heap command
As the start of the heap, end of the heap, heap
This example shows how to use this feature on HP-UX
Set a breakpoint
Commands to track the change in data segment value
Changes for a given run
Thread Debugging Support
Support for Enabling and Disabling Specific Threads
Backtrace Support for Thread Debugging
Advanced Thread Debugging Support
Enabling and Disabling Advanced Thread Debugging Features
Pre-requisites for Advanced Thread Debugging
Mixed-sched-policy onoff The set thread-check
Onoff command checks if an application
Unlock-not-own onoff The set thread-check unlock-not-own
Cv-multiple-mxs onoff The set thread-check cv-multiple-mxs
Command checks if any thread has terminated
This returns an Einval error to
User and prints a warning message when this
Different mutexes. The debugger transfers
Exception or a cancel without joining or
When this condition is detected. This situation
Command checks if a thread has terminated
Created with the detach attribute. When an
Condvar-id is provided, the command displays
Provided, the command displays extended
Is provided, the command displays extended
Rwlock-id is provided, the command displays
For 64-bit PA applications
Thread Debugging in Batch Mode
For 64 bit IPF applications, set
Pre-requisites for Batch mode of Thread Debugging
For 64-bit PA applications, set
And/Or
Set the environment variable Batchrtc to on as
Opt/langtools/lib/hpux64/librtc.so
Where Pid is the process id
Thread Debugging in +check Mode
Limitations in Batch mode of thread debugging
Issue
Where pid is the process identifier
Debugging MPI Programs
Support for showing unwind info
Ask mode for set follow-fork-mode
Serial mode for set follow-fork-mode
Debugger response to a program call to fork or vfork is ask
Command to Search for a Pattern in the Memory Address Space
Printing CFM and PFS registers
String value. The character pattern must be enclosed
Parameter is mandatory when end-addressis not
Specifies the length of the memory address range. This
Within double quotes. This parameter is mandatory
Example 14-1 Sample Output for the find command
Str0 Specifies the starting address
Using the /max-countparameter
Using the /size-charparameter
Specifies the pattern expr1
Debugging Core Files
Generating core files with packcore /unpackcore/getcore
Support for the info target Command
When starting from the shell prompt
Support for the dumpcore command
When starting from the HP WDB command line
Enhancements to the dumpcore command
Info rtti address
When starting from shell prompt
Support for display of run time type information
Sample Output
Info global-exec-path summary
Info exec-path summary
Exec-path updownpathindex aliased to ep
Sample Program
Example Illustrating Execution Path Recovery
Sample Debugging Session
Command to Unwind Beyond 10000 Frames
Aborting a Command Line Call
Invoking GDB Before a Program Aborts
Deferred watchpoints
Instruction Level Stepping
Enhanced support for watchpoints and breakpoints
Hardware watchpoints
Rbp
Support for procedural breakpoints
Support for template breakpoints
Rdp
Using shared library as main program
Debugging support for shared libraries
Using catch load
Setting Deferred Breakpoints in Shared Library
Privately mapping shared libraries
Selectively Mapping Shared Libraries As Private
Opt/langtools/bin/pxdb -s on executable-name
Debugging support for Decimal Floating Point data type
Setting breakpoints in shared library
Enhancement to the info shared Command
Printing Decimal Floating point data types
Handling Decimal Floating Point Data types
Following are sample commands to print NaT registers
Printing NaT Registers
Evaluating Decimal Floating Point data types
Comparison Operations
Assignment of Decimal floating point value to variable
Arithmetic Operations
Printing type of Decimal Floating Point variable
This prints the binary floating point value as oat
Additional Support for binary floating point data type
Support for Binary Floating Point constants f, l
This prints the binary floating point value as double
Language support
Java Stack Unwind Features
Enhanced Java Debugging Support
Gdb Subcommands for Java VM Debugging
Gdb help java
Info frame
Frame command of GDB has been enhanced to interpret a Java
Java and native stack frames
Stack frame
Java attach mode debugging support
Java corefile debugging support
Enhanced support for C++ templates
Syntax
Support for Complex variables in HP C
Support for fpreg data type on IPF
Support for debugging namespaces
Viewing Wide Character Strings
Command for evaluating the address of an expression
This is equivalent to executing
Support for output logging
Support for dumping array in an Ascii file
Displaying enumerators
Support for steplast command for C and C++
Support for Fortran array slices
Support for debugging typedefs
Getting information from a non-debug executable
Break Call Clear Disassem List
Debugging optimized code
Break Call Cond Jump Return Print Set var Watch Whatis
HP-UX Configuration-Specific Information
14.29.1.1 +O0 and +O1
Debugging Optimized Code at Various Optimization Levels
14.29.1.2 +O2/+O3/+O4/-ipo
Debugging with Aries
Following limitations apply when debugging optimized code
+O2 or -O
Debugging the application using GDB under Aries
Limitations of GDB Support under Aries
Detecting memory leaks using GDB under Aries
Attaching GDB to an already running emulated process
Visual Interface for WDB
Starting and stopping Visual Interface for WDB
Navigating the Visual Interface for WDB display
Visual Interface for WDB GUI display
Using the X-window graphical interface
Specifying foreground and background colors
Changing the size of the source or debugger pane
Using the TUI mode
For dterm, use the following
Saving the contents of a debugging session to a file
Using commands to browse through source files
Editing the command line and command-line history
Loading source files
Support for command line calls in a stripped executable
Support for XDB commands
GNU GDB Logging Commands
Stop in/at dbx commands
Execute the chatr -B immediate executable command
For 32-bit applications
For 64-bit applications
Command line calls to non-stripped library
Support for debugging stripped binaries
Printing of locals and globals in a stripped module
Linux support
Displaying the current block scope information
Syntax
242
Starting the TUI
Invoke the debugger using a command like the following
HP-UX Terminal User Interface
Main
Automatically running a program at startup
Screen Layouts
Source pane
Disassembly pane
Disassembly pane appears when you issue the command
Pane looks like this
Disassembly/Register pane
Source/Disassembly pane
Source/Disassembly pane appears when you issue the command
Source/Register pane appears when you issue the command
Source/Register pane
Cycling through the panes
Use the commands
Toggle split-screen mode
Changing pane focus
Fs regs Foc next
Scrolling panes
Changing the register display
Changing the pane size
Refreshing and updating the window
By-function lists of XDB commands and HP WDB equivalents
XDB to WDB Transition Guide
Invocation commands
Invocation commands
Window mode commands
Window mode commands
File viewing commands
File viewing commands
Source directory mapping commands
Data Viewing and modification commands
Data viewing and modification commands
Ll string Lm string
Stack viewing commands
Stack viewing commands
Status viewing commands
Status-viewing command
Job control commands
Job control commands
Auxiliary breakpoint commands
Overall breakpoint commands
Overall breakpoint commands
Auxillary breakpoint commands
Breakpoint creation commands
10 Breakpoint creation commands
Breakpoint status commands
11 Overall breakpoint commands
12 Global breakpoint commands
All-procedures breakpoint commands
Global breakpoint commands
Bp bpt bpx dp Dpt Dpx
Record and playback commands
Assertion control commands
Macro facility commands
13 Macro facility commands
Signal control commands
Miscellaneous commands
14 Signal control commands
16 Data format commands
Format of the print command is different in XDB and GDB
XDB data formats and HP WDB equivalents
Decimal integer
XDB location syntax and HP WDB equivalents
17 Macro facility commands
XDB special language operators and HP WDB equivalents
18 Special language operators
XDB special variables and HP WDB equivalents
19 Special variables
16.8.1 a
Alphabetical lists of XDB commands and HP WDB equivalents
XDB variable identifiers and HP WDB equivalents
20 Variable Identifiers
16.8.2 B
22 B
Through D
23 C through D
24 F through K
Through K
16.8.5 L
25 L
Through P
26 M through P
27 Q through S
Through S
16.8.8 T
28 T
Through Z
29 U through Z
Symbols
30 Symbols
Any string
Control-C # text
280
Setting Command History Feature in GDB
Setting the GDB Prompt
Setting Command Editing Options in GDB
Controlling GDB
Exits. You can access this list through history
Control the settings
To fname. This is the file where GDB reads an
Expansion or through the history command
Setting the GDB Screen Size
Supported Number Formats
Optional warnings and messages
Set confirm on
Optional messages about internal happenings
Show confirm Displays state of confirmation requests
Show debug varobj
Object debugging info
Canned Sequences of Commands
User-defined commands
User-defined command hooks
Command files
To add source directories or
Commands for controlled output
Expressions
Output formats
292
Using GDB under gnu Emacs
Update display window accordingly
Calls, like the GDB next command. Then update the display
Execute to next instruction, using the GDB nexti command
GDB up command
295
296
GDB Annotations
What is an annotation?
Server prefix
When printing a structure, GDB annotates it as follows
Values
Frames
When printing an array, GDB annotates it as follows
Frame annotation begins with
Then comes
Displays
Annotation for GDB input
Errors
Information on breakpoints
Invalidation notices
Running the program
Displaying source
Annotations We Might Want in the Future
Target-invalid
306
21.1 GDB/MI Command Syntax
GDB/MI Interface
21.1.2 GDB/MI Output syntax
Done running connected error exit
Pragmatics
Value Const tuple list String Tuple →
Simple examples of GDB/MI interaction
Here is what happens if you pass a bad command
21.2 GDB/MI compatibility with CLI
Here is an example to evaluate an expression
21.3.1 GDB/MI result records
21.4 GDB/MI command description format
21.3 GDB/MI output records
21.3.2 GDB/MI stream records
21.5 GDB/MI breakpoint table commands
-break-after Command
-break-condition command
Corresponding GDB command is condition
Corresponding GDB command is delete
-break-delete command
-break-disable command
Corresponding GDB command is disable
-break-enable command
-break-info Command
-break-insert command
Result
-break-list command
Corresponding GDB commands are watch, awatch, and rwatch
-break-watch command
Setting a watchpoint on a variable in the main function
Exec-continue running gdb
-data-disassemble command
21.6 GDB/MI Data manipulation
Disassemble from the current value of $pc to $pc +
There is no direct mapping from this command to the CLI
Disassemble 3 instructions from the start of main
-data-evaluate-expression command
Display a list of the registers that have changed
-data-list-changed-registers Command
-data-list-register-names command
On a PPC MBX board
-data-list-register-values command
Space should be quoted using the C convention
-data-read-memory command
To be read. Complex expressions containing embedded white
Word-format Word-sizenr-rowsnr-cols aschar
-display-delete command
-display-disable Command
-display-list command
-display-enable command
-display-insert Command
-environment-cd command
-environment-directory command
-environment-path command
21.7 GDB/MI program control
-environment-pwd command
Corresponding GDB command is pwd
Show the current working directory
-exec-arguments command
-exec-abort command
-exec-continue command
Corresponding GDB command is finish
-exec-finish command
-exec-interrupt command
Corresponding GDB command is interrupt
Corresponding GDB command is next
-exec-nextcommand Synopsis
-exec-next-instruction command
Corresponding GDB command is nexti
Corresponding GDB command is return
-exec-return command
-exec-runcommand Synopsis
Corresponding GDB command is run
-exec-show-arguments command
Example -exec-stepCommand Synopsis
Corresponding GDB command is stepi
-exec-step-instruction command
-exec-until command
Regular stepping
Corresponding GDB command is until
-file-exec-and-symbols command
-file-exec-file command
Corresponding GDB command is file
-file-list-exec-source-files command
-file-list-exec-sections command
-file-list-shared-libraries command
-file-symbol-file command
Miscellaneous GDB commands in GDB/MI
-file-list-symbol-files command
-gdb-exitcommand Synopsis
-gdb-showcommand Synopsis
-gdb-setcommand Synopsis
-gdb-version command
-stack-info-frame command
21.9 GDB/MI Stack Manipulation Commands
-stack-info-depth command
-stack-list-arguments command Synopsis
For a stack with frame levels 0 through
-stack-list-frames command
Show frames between lowframe and highframe
Corresponding GDB commands are backtrace and where
Full stack backtrace
Show a single frame
-stack-select-frame command
-stack-list-locals command
Info locals in GDB, gdbgetlocals in gdbtk
-symbol-info-file command
21.10 GDB/MI Symbol query commands
-symbol-info-address command
-symbol-info-function command
-symbol-list-functions command
-symbol-info-line command
-symbol-info-symbol command
-symbol-list-types command
-symbol-locate command
-symbol-list-variables command
-symbol-type command
-target-compare-sections command
21.11 GDB/MI Target Manipulation Commands
-target-attach command
-target-detach command
Name of the section
-target-download command
Corresponding GDB command is load
At the end, a summary is printed
-target-exec-status command
-target-list-current-targets command
-target-list-available-targets command
-target-list-parameters command
-thread-info command
21.12 GDB/MI thread commands
-target-select command
-thread-list-all-threads command
-thread-list-ids command
-thread-select command
Tracepoint commands are not yet implemented
21.13 GDB/MI tracepoint commands
21.14 GDB/MI variable objects
GDB/MI Operations
-var-create command
Description and use of operations on variable objects
-var-show-format command
-var-delete command
-var-set-format command
-var-info-num-children command
-var-info-expression command
-var-list-children command
-var-info-type command
-var-show-attributes command
-var-assign command
-var-update command
360
Reporting Bugs in GDB
How to report bugs
Have you found a bug?
Reporting Bugs in GDB
How to report bugs
364
Installing GDB
Gdb-gdb-199991101/mmalloc
Compiling GDB in another directory
Package
Specifying names for hosts and targets
To use the source in the directory dirname. configure
Configure options
Separate directories. configure writes configuration
Srcdir= dirname
Target=target
All available targets