HPjmeter 4.2 Users Guide
Document Notice
Table of Contents
Monitoring Applications
Analyzing Garbage Collection Data
116
Unfinalized Objects
Live Objects Bytes
187
192
197
199
About This Document
Intended Audience
Typographic Conventions
Additional HPjmeter Documents Related Information
Publishing History
HP Encourages Your Comments
Features
Introducing HPjmeter
JVM Agent
Concepts
Node Agent
Completing Installation of HPjmeter
Platform Support and System Requirements
Agent Requirements
Console Requirements
Completing the installation
File Locations
Attaching to the JVM Agent of a Running Application
Preparing to run Java
Example Usage
On Java
Showing Version Information
JVM Agent Options
Selecting Other JVM Agent Options
Include=filter1filter2..., exclude=filter1filter2
To specify a file name
Noalloc
JVM Options Usage Examples
Security Awareness
Working with Firewalls
Configuring User Access
Using HPjmeter to Monitor Applications
Getting Started
To connect to a node agent via a SecureShell SSH tunnel
Using HPjmeter to Monitor Applications
Set Session Preferences
When the Optional Port Box Is Not Used
Getting Started
Changing Session Preferences During a Session
Using HPjmeter to Analyze Profiling Data
View Monitoring Metrics During Your Open Session
Configure your application
Using HPjmeter to Analyze Garbage Collection Data
Monitoring Demonstration Instructions
Memory Leak Applications
Thread Deadlock Sample
See also Heap Usage Notification
Thread Deadlock Example Display
Monitoring Applications
Setting Data Collection Preferences
Controlling Data Collection and Display
Managing Node Agents
Managing Node Agents On HP-UX
Running Node Agent as a Daemon
Verifying HP-UX Daemon is Running
Node Agent Access Restrictions
Saving Monitoring Metrics Information
Running Multiple Node Agents
Stopping Node Agents
Diagnosing Errors When Monitoring Running Applications
Naming Monitoring Data Files
Saving Data from the Console
Identifying Unexpected CPU Usage by Method
Viewing the Application Load
Checking for Application Paging Problems
Checking for Long Garbage Collection Pauses
Identifying Excessive Calls to System.gc
Reviewing the Percentage of Time Spent in Garbage Collection
Monitoring Applications
Confirming Java Memory Leaks
Checking for Proper Heap Sizing
Determining the Severity of a Memory Leak
Identifying Excessive Object Allocation
Identifying the Site of Excessive Object Allocation
Identifying Abnormal Thread Termination
Identifying Multiple Short-lived Threads
Identifying Deadlocked Threads
Identifying Excessive Lock Contention
Identifying Excessive Thread Creation
Identifying Excessive Method Compilation
Example Metric Method Compilation Count
Using the JMX Viewer
Identifying Too Many Classes Loaded
Understanding the JMX Summary View
JMX Summary Tab
Appearance of the Summary JMX Viewer When First Opened
JMX Memory Tab
JMX Viewer with Summary Memory Tab Selected
JMX Threads Tab
JMX Viewer with Summary Threads Tab Open
JMX Runtime Tab
Changing Mbean Values and Monitoring the Result
JMX Notifications Tab
Using the Functions in the JMX Server View
MBean Filter
MBean Attribute Tab
MBean Operations Tab
10 MBean Operations Tab Open for Display
MBean Notifications Tab
MBean Information Tab
12 MBean Information Tab Open for Display
Profiling Applications
Profiling Overview
Tracing
Tuning Performance
Sampling
Preparing a Benchmark
Collecting Profile Data
Profiling with -Xeprof
If timeon=sig... has not been specified, the default is
Profiling with Zero Preparation
Profiling with -agentlibhprof
Following options are useful
Supported -agentlibhprofoptions
Naming Profile Data Files
Generate more complete call graphs
Inclusive Method CPU Times
Profiling with -Xeprof Profiling with -agentlibhprof
Approaches to Analyzing Performance Data
Considerations in Interpreting the Data
Looking at the Data from the Bottom Up
Looking at the Data from the Top Down
Locating Summary Information for Saved Data Sets
Inclusive Versus Exclusive Time
Time Units
CPU Versus Clock Time
Adjusting Scope
Estimate menus
Comparing Profiling Data Files
Scaling Comparison Data
Reading Profiling Histograms
Key to Thread States Reported by
Interpreting the Histogram Presentation
Using Call Graph Trees
Interpreting Call Graph Data
Example of Node Color Display
Using Sub-Trees
Options for Manipulating the Call Tree Display
Tree Pruning
Auto-Expanding the Call Tree
Using Heuristics to Locate Possible Hot Spots
Searching the Trees
Using Heuristics to Locate Possible Hot Spots
Obtaining Garbage Collection Data
Analyzing Garbage Collection Data
Data Collection with -Xverbosegc
Java ... -Xverbosegchelp
13, Old generation, in bytes. These spaces are reported
Collecting GC Data with Zero Preparation
Collecting Glance Data for Viewing in HPjmeter
Data Collection with -Xloggc
Related Topics
Using -XX+PrintGCDetails and -XX+PrintHeapAtGC Together
Naming GC Data Files
Comparing Garbage Collection Data Files
Basic Garbage Collection Concepts
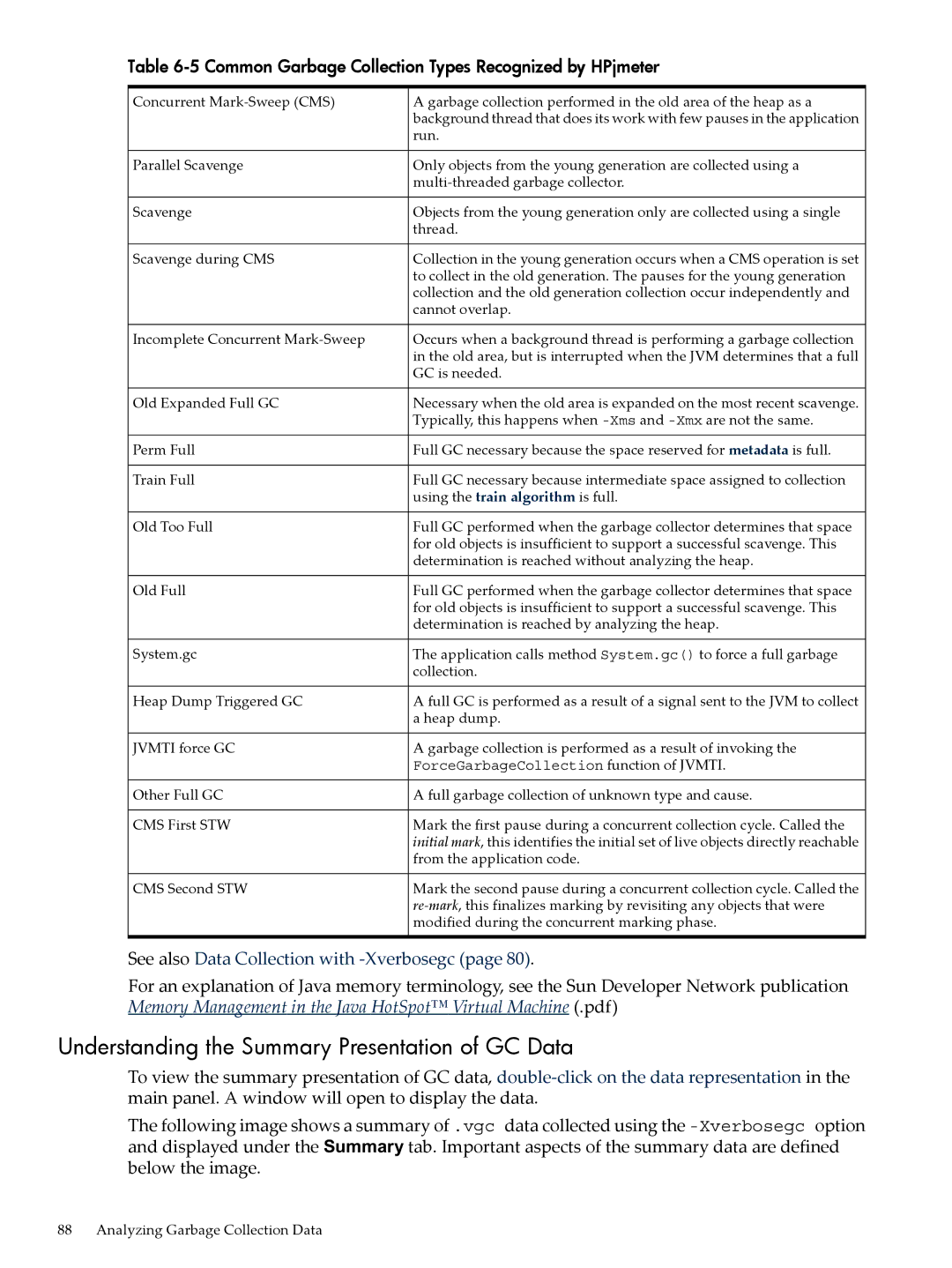
Key to Garbage Collection Types Recognized by HPjmeter
Understanding the Summary Presentation of GC Data
Common Garbage Collection Types Recognized by HPjmeter
Summary Panel Showing Garbage Collection Statistics
Understanding the System Details Captured with GC Data
Basic Garbage Collection Concepts
Analyzing Garbage Collection Data
Using the Main Window Functions
Using the Console
Starting the Console
Data Representation
Main Console Window
Node Agent
Icons and Their Meaning
JVM Agent
Time Slice Entries
Open and Cached Sessions
Saving Data
Console Tool Bar Buttons
Console Menu Choices
Monitor Menu
Remember Main Window Location
Console Guide
Console Guide Location and First Screen
Status Bar
Setting Monitoring Session Preferences
Specifying Metrics to Collect for Monitoring
Enabling Monitoring Alerts
Editing Filters
Specifying Filters for Monitoring
Adding Filters
Viewing Monitoring Data in HPjmeter
Using Alerts
Specifying Filter Sets
Appearance of Alert Threshold in GC Duration Visualizer
Using the Alert Controller
Appearance of Alert Notices in the Main Console Pane
Alert Controller Window
Editing E-mail Notification Attributes
Viewing a Log of the Alert History
Responding to Alerts
Abnormal Thread Termination Alert
Identifying Abnormal Thread Termination Thread Histogram
Excessive Compilation Alert
Expected Out Of Memory Error Alert
GC Duration Notification
Heap Usage Notification
Java Collection Leak Locations Alert
Array Leak Locations Alert
13 Java Collection Leak Locations Visualizer
Process CPU Usage Alert
14 Array Leak Locations Visualizer
System CPU Usage Alert
Thread Deadlock Alert
Unfinalized Queue Growth
Using Visualizer Functions
Profiling Data Viewer
Using Monitoring Displays
Locating Information About a JVM and its Environment
Monitor Code and/or CPU Activity Menu
Java Method HotSpots
Details
Thrown Exceptions
Thrown Exceptions with Stack Traces
Monitoring Metric Thrown Exceptions with Stack Traces
Monitor Memory and/or Heap Activity Menu
Heap Monitor
Garbage Collections
Monitoring Metric Garbage Collections
GC Duration
Percentage of Time Spent in Garbage Collection
Unfinalized Objects
Allocated Object Statistics by Class
Allocating Method Statistics
Current Live Heap Objects
Name of class to which object belongs
Monitor Threads and/or Locks Menu
Thread Histogram
Already acquired by another thread
Lock Contention
14 Monitoring Metric Lock Contention
Monitor JVM and/or System Activity Menu
Method Compilation Count
Method Compilation Frequency
Loaded Classes
Percent % CPU Utilization
17 Monitoring Metric Loaded Classes Related Topics
Using Profile Displays
Viewing Profiling or GC Data in HPjmeter
Using Visualizer Functions
Inline Candidates Exceptions Thrown Memory Leaks
Profile Code and/or CPU Activity
Menu Choices
Method Call Count
Exclusive Method Clock Times
Exclusive Method Times CPU
Call Graph Tree with Call Count
Call Graph Tree with CPU
Call Graph Tree with Clock Time
Inclusive Method CPU Times
Inclusive Method Clock Times
Average Exclusive Method Clock Times
Average Inclusive Method CPU Times
Average Inclusive Method Clock Times
Starvation by Method
Profile Memory and/or Heap Activity
Starvation Ratio
Methods with Loops
Exclusive Class CPU Times
Objects Created by Method
Created Objects Count
Created Objects Bytes
Live Objects Count
Reference Graph Tree
Reference Sub-Trees by Size
Using Profile Displays
For string and char arrays, see String and char arrays
21 Long String Pop-up Box
Class Loaders
23 Class Loaders Visualizer
24 Class Types Pop-up Window Guidelines
Profile by Threads
Residual Objects Count
Residual Objects Bytes
Threads Histogram
Profile by Locks
Thread Groups Histogram
Lock Delay Method Exclusive
Lock Delay Call Graph Tree
Contested Lock Claims by Method
All Lock Claims by Method
Lock Delay Method Inclusive
Lock Contention Ratio by Method
Average Exclusive Method Lock Delay
Exclusive Method Lock Delay / Clock Time
Using Heuristic Metrics from the Estimate Menu
Exclusive Class Lock Delay
Inline Candidates
Exceptions Thrown
Using Specialized Garbage Collection Displays
Heap Usage After GC
Duration Stop the World
27 GC Metric Heap Usage After GC Related Topics
Cumulative Allocation
28 GC Metric Duration Related Topics
Creation Rate
29 GC Metric Cumulative Allocation Related Topics
Allocation Site Statistics
30 GC Metric Creation Rate Related Topics
31 GC Metric Combined Sets of Allocation Site Statistics
32 GC Metric Separated Sets of Allocation Site Statistics
Using Visualizer Functions
Filter Field Descriptions
Using Visualizer Functions
User-Defined X-Y Axes
Multiple User-Defined
37 User-Defined Comparisons of GC Metrics Related Topics
38 Multiple User-Defined Metrics
Glance Data
40 GC Metric Glance Data
41 Glance Data Metric Configuration Box
Run Queue Average
Glance System Call Data
Are private
42 GC Metric Glance System Call Data
Using Visualizer Tool Bars
Common Tool Bar Buttons
Tool Bar Buttons for Manipulating Graphical Data
Tool Bar Buttons for Manipulating Tabular Data
Tool Bar Buttons for Manipulating Garbage Collection Data
Special Button or Other Gadget Functions
Mark an Item for Search
Find a Search Pattern
44 Locating an Item
Pause or Resume Graphical Time-based Scrolling
Changing Time Interval in GC Data Visualizers
46 The View Menu Selections in the GC Viewer
Using Visualizer Tool Bars
Changing Time Interval in Monitoring Visualizers
Change Color Selection for Histogram Display
50 Time Interval Use in a Monitoring Visualizer
Thread Histogram Profile by Threads
Understanding How HPjmeter Works
Performance Overhead on Running Applications
Data Sampling Considerations
Using Confidence Interval to Indicate Sample Validity
Console Overhead
How Memory Leak Detection Works
Related Topics
Page
Troubleshooting
Installation
Documentation and Support
Identifying Version Numbers
Console
See also To Take Advantage of Dynamic Attach
If you see this JVM agent error on startup
JVM agent
Node agent
Zero Preparation Profiling
Unexpected Behavior in Visualizers
Connecting to the HPjmeter Node Agent
Quick References
Start and stop verbose GC data 0.14 0.02
Active mode
Glossary
Jvmpi
SSL
Symbols
Index
Alert Notification Editor, 107 alerts
Restore Roots
Alert Notification Editor, 108 count
Collecting with zero preparation, 83 GC event
Glance system call data, 174 graphical scrolling
JVM
Duration Stop the World, 158 enable, 99
User-Defined X-Y Axes for GC analysis, 167 viewing, 29
Program termination, 47 overhead
Scale Special, 72 scaling data
Xeprofoptions
Xbootclasspath