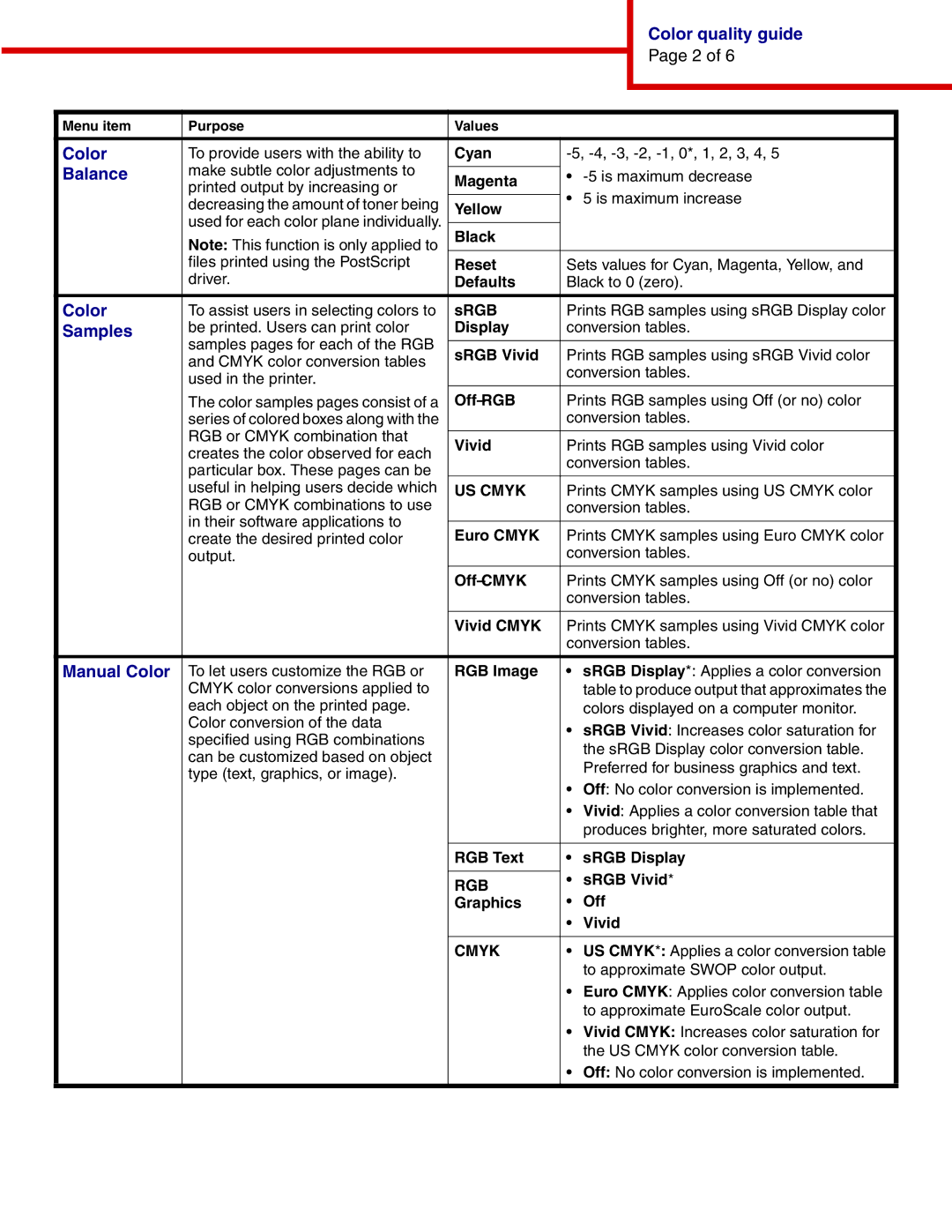
1454, 1464 specifications
The IBM 1454 and 1464 are notable computing systems that have played a significant role in the evolution of technology. Introduced in the 1960s, these systems were part of IBM's early foray into mini-computers, which aimed to provide more accessible computing power compared to their larger mainframe counterparts.The IBM 1454, which was designed with an emphasis on flexibility and adaptability, featured a modular architecture that allowed for various configurations based on user needs. It supported multiple programming languages, which made it versatile for a range of applications, from scientific calculations to business data processing. One of its main features was the capability to interface with peripheral devices, showcasing an early attempt at creating a more interconnected computing environment.
On the other hand, the IBM 1464 was an advancement over the 1454, boasting enhanced processing capabilities and memory management. It was specifically engineered for real-time applications, which was becoming increasingly important in industries such as telecommunications and manufacturing. The 1464 incorporated improved input/output operations, enabling faster data processing and more efficient use of hardware resources. This made it suitable for complex tasks that required immediate processing and feedback.
Both models utilized IBM’s proprietary technologies, including a unique assembly language and input/output channels that optimized data flow between the CPU and peripherals. They were also equipped with magnetic core memory, which, while basic by today's standards, was a cutting-edge feature at the time, providing both speed and reliability.
In terms of characteristics, the IBM 1454 and 1464 were compact for their time, designed to fit into space-constrained environments such as laboratories and business offices. They also came with comprehensive documentation and support, reflecting IBM's commitment to customer service and user education.
In summary, the IBM 1454 and 1464 were pivotal in defining the landscape of mini-computing during their era. With their modular designs, robust processing capabilities, and support for real-time applications, they laid the groundwork for future advancements in computer technology. Their legacy continues to influence modern computing systems, making them critical milestones in the history of information technology.