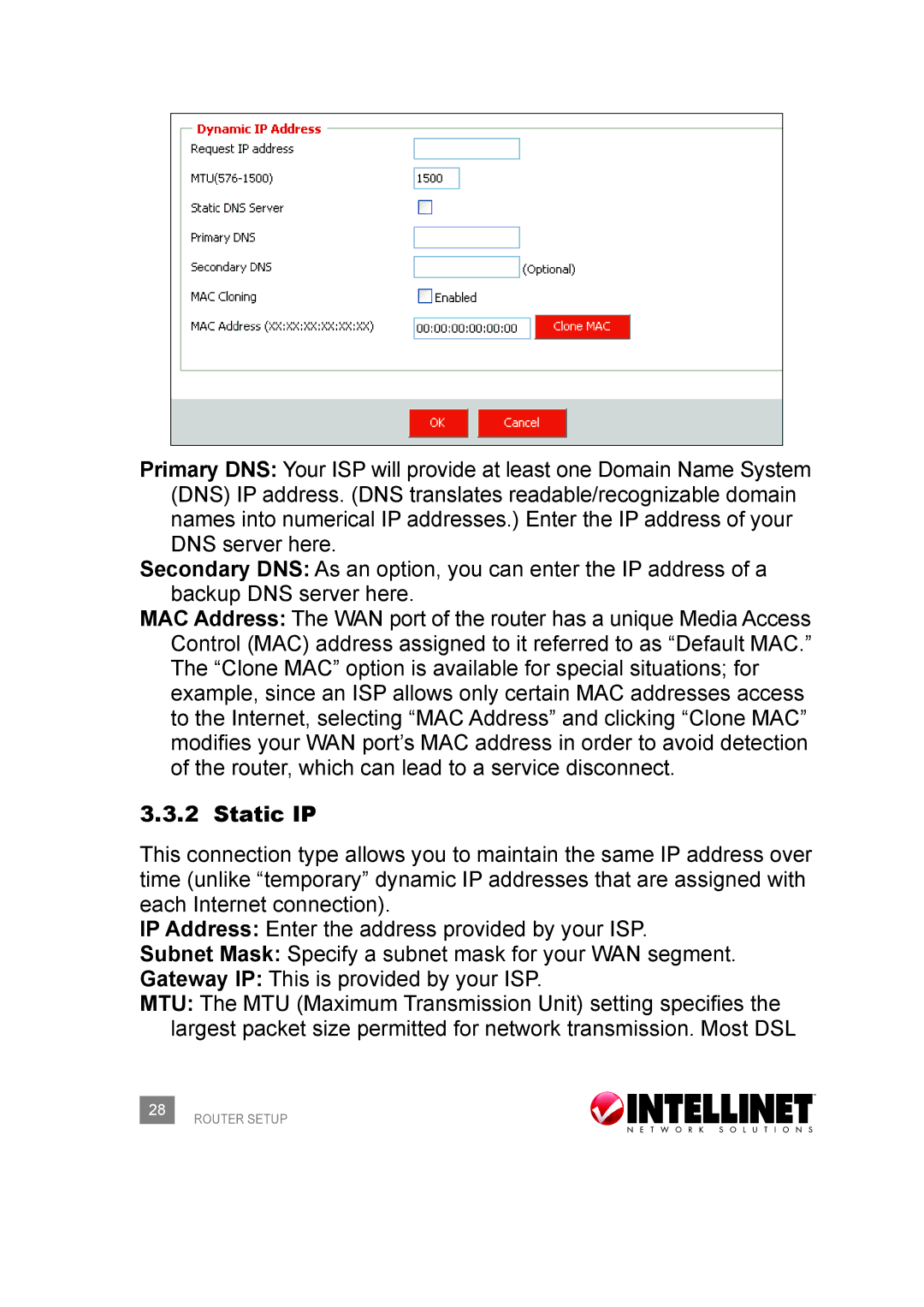
Primary DNS: Your ISP will provide at least one Domain Name System (DNS) IP address. (DNS translates readable/recognizable domain names into numerical IP addresses.) Enter the IP address of your DNS server here.
Secondary DNS: As an option, you can enter the IP address of a backup DNS server here.
MAC Address: The WAN port of the router has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address assigned to it referred to as “Default MAC.” The “Clone MAC” option is available for special situations; for example, since an ISP allows only certain MAC addresses access to the Internet, selecting “MAC Address” and clicking “Clone MAC” modifies your WAN port’s MAC address in order to avoid detection of the router, which can lead to a service disconnect.
3.3.2 Static IP
This connection type allows you to maintain the same IP address over time (unlike “temporary” dynamic IP addresses that are assigned with each Internet connection).
IP Address: Enter the address provided by your ISP.
Subnet Mask: Specify a subnet mask for your WAN segment.
Gateway IP: This is provided by your ISP.
MTU: The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) setting specifies the largest packet size permitted for network transmission. Most DSL