Chapter 6: Operation
Although there are no operating procedures associated with the DN965X, this chapter shows you how to create a MADI split.
Using a MADI module as a MADI split
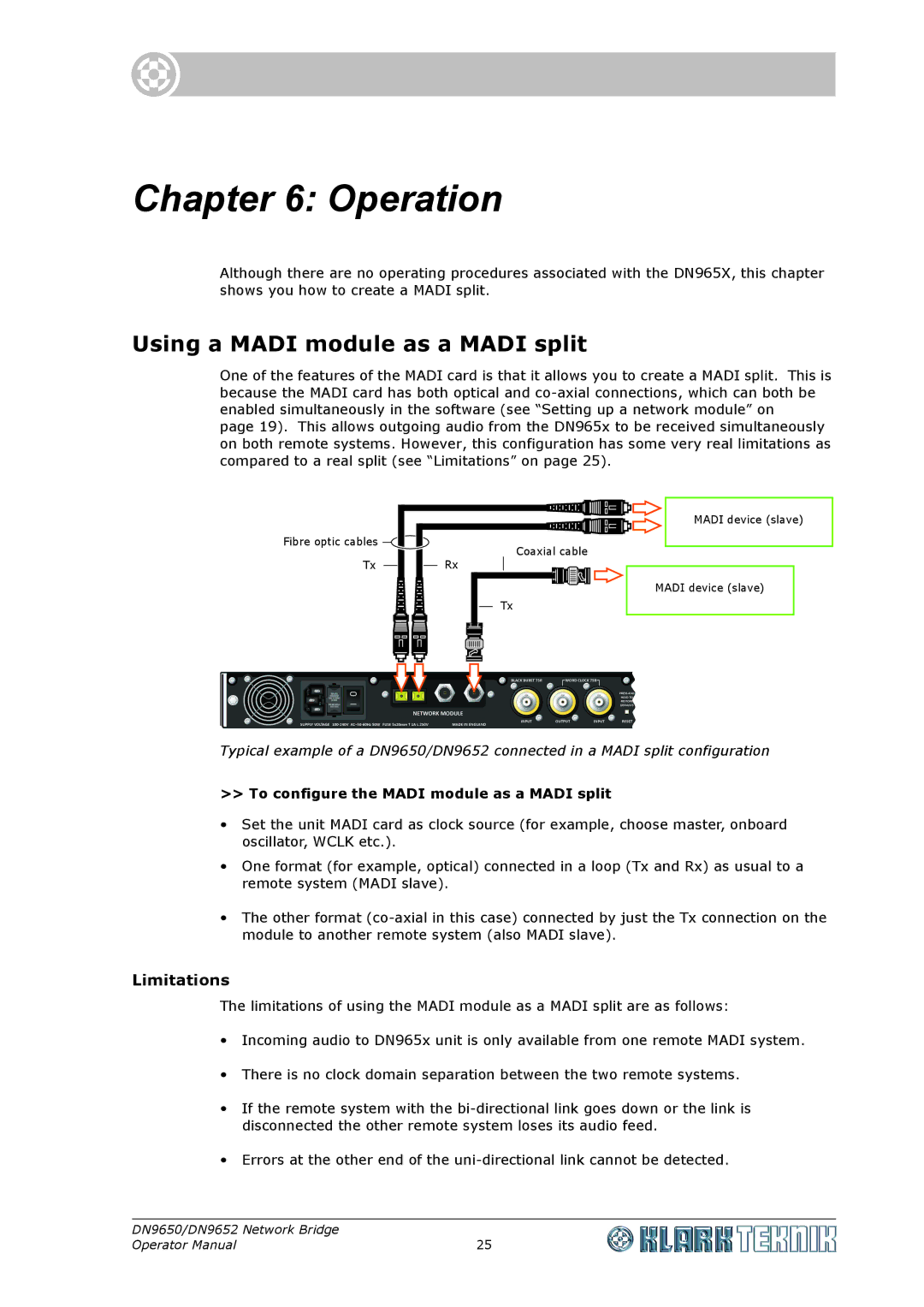
One of the features of the MADI card is that it allows you to create a MADI split. This is because the MADI card has both optical and
page 19). This allows outgoing audio from the DN965x to be received simultaneously on both remote systems. However, this configuration has some very real limitations as compared to a real split (see “Limitations” on page 25).
Fibre optic cables ![]()
![]()
![]()
Coaxial cable
Tx |
|
|
| Rx |
|
|
Tx |
MADI device (slave)
MADI device (slave)
Typical example of a DN9650/DN9652 connected in a MADI split configuration
>>To configure the MADI module as a MADI split
•Set the unit MADI card as clock source (for example, choose master, onboard oscillator, WCLK etc.).
•One format (for example, optical) connected in a loop (Tx and Rx) as usual to a remote system (MADI slave).
•The other format
Limitations
The limitations of using the MADI module as a MADI split are as follows:
•Incoming audio to DN965x unit is only available from one remote MADI system.
•There is no clock domain separation between the two remote systems.
•If the remote system with the
•Errors at the other end of the
DN9650/DN9652 Network Bridge |
|
Operator Manual | 25 |