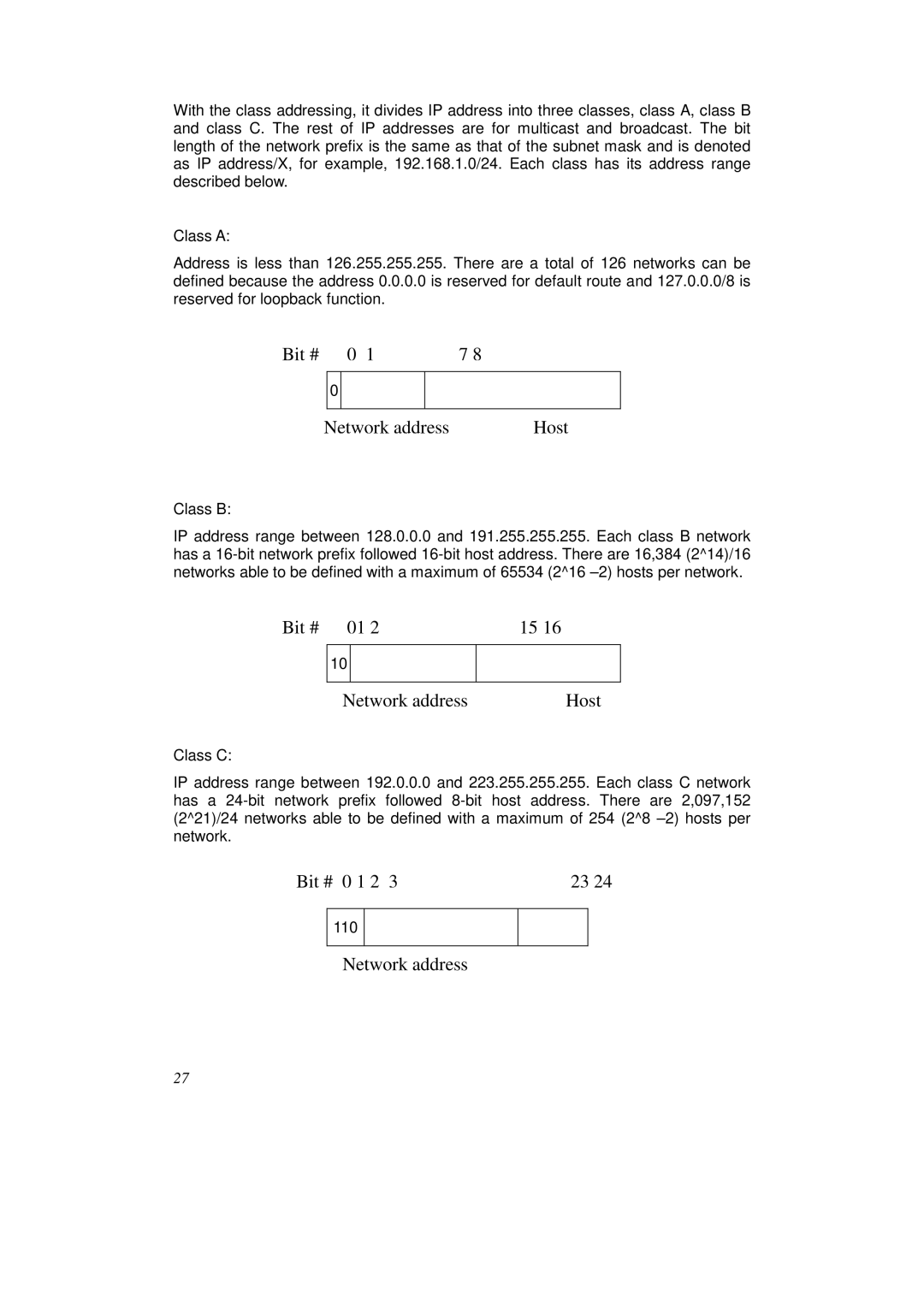
With the class addressing, it divides IP address into three classes, class A, class B and class C. The rest of IP addresses are for multicast and broadcast. The bit length of the network prefix is the same as that of the subnet mask and is denoted as IP address/X, for example, 192.168.1.0/24. Each class has its address range described below.
Class A:
Address is less than 126.255.255.255. There are a total of 126 networks can be defined because the address 0.0.0.0 is reserved for default route and 127.0.0.0/8 is reserved for loopback function.
Bit # | 0 1 |
| 7 8 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Network address | Host | |||
Class B:
IP address range between 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.255.255. Each class B network has a
Bit # | 01 2 | 15 16 | |
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Network address | Host | |
Class C:
IP address range between 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255. Each class C network has a
Bit # 0 1 2 3 | 23 24 |
110
Network address
27