GLOSSARY OF TERMS
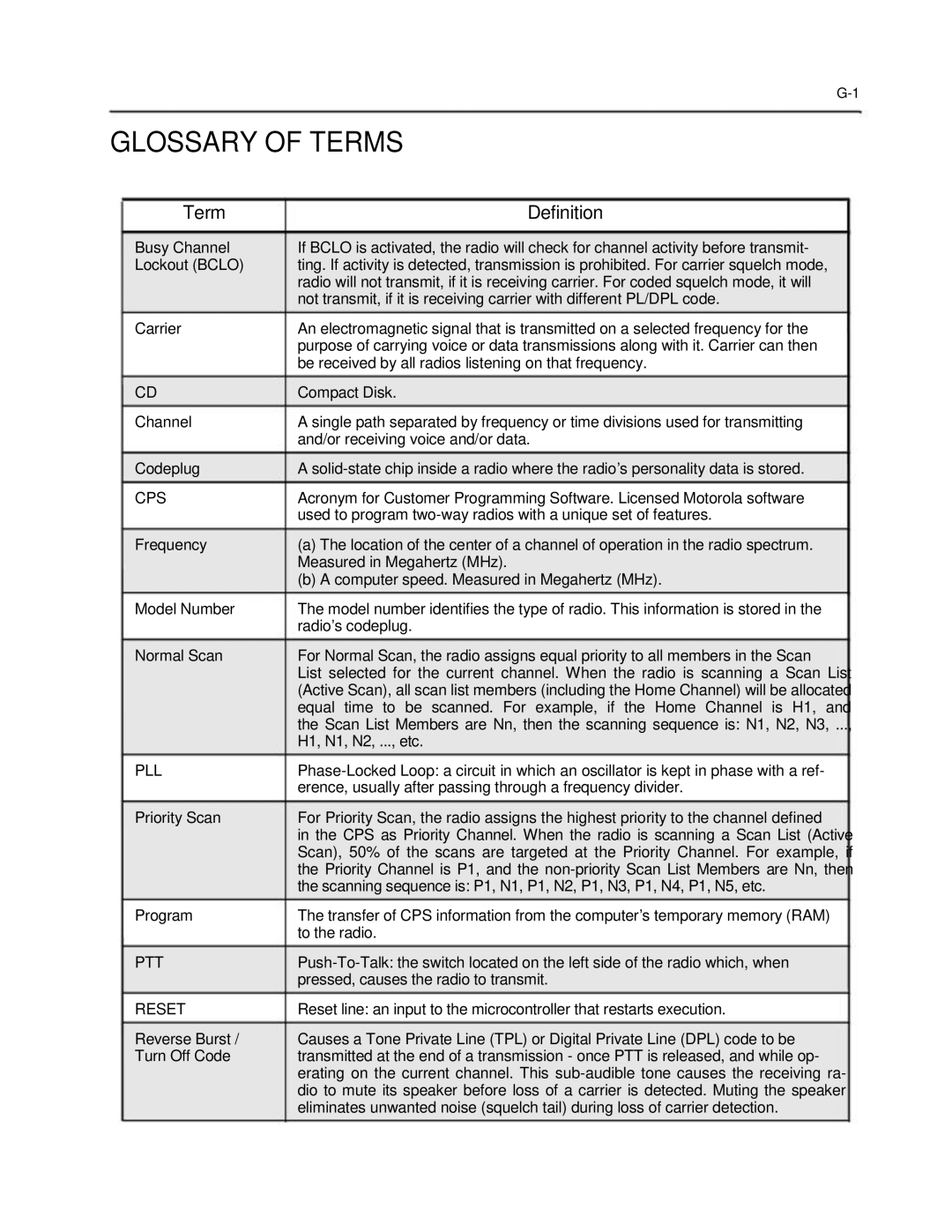
Term | Definition |
Busy Channel | If BCLO is activated, the radio will check for channel activity before transmit- |
Lockout (BCLO) | ting. If activity is detected, transmission is prohibited. For carrier squelch mode, |
| radio will not transmit, if it is receiving carrier. For coded squelch mode, it will |
| not transmit, if it is receiving carrier with different PL/DPL code. |
Carrier | An electromagnetic signal that is transmitted on a selected frequency for the |
| purpose of carrying voice or data transmissions along with it. Carrier can then |
| be received by all radios listening on that frequency. |
CD | Compact Disk. |
Channel | A single path separated by frequency or time divisions used for transmitting |
| and/or receiving voice and/or data. |
Codeplug | A |
CPS | Acronym for Customer Programming Software. Licensed Motorola software |
| used to program |
Frequency | (a) The location of the center of a channel of operation in the radio spectrum. |
| Measured in Megahertz (MHz). |
| (b) A computer speed. Measured in Megahertz (MHz). |
Model Number | The model number identifies the type of radio. This information is stored in the |
| radio‟s codeplug. |
Normal Scan | For Normal Scan, the radio assigns equal priority to all members in the Scan |
| List selected for the current channel. When the radio is scanning a Scan List |
| (Active Scan), all scan list members (including the Home Channel) will be allocated |
| equal time to be scanned. For example, if the Home Channel is H1, and |
| the Scan List Members are Nn, then the scanning sequence is: N1, N2, N3, ..., |
| H1, N1, N2, ..., etc. |
PLL | |
| erence, usually after passing through a frequency divider. |
Priority Scan | For Priority Scan, the radio assigns the highest priority to the channel defined |
| in the CPS as Priority Channel. When the radio is scanning a Scan List (Active |
| Scan), 50% of the scans are targeted at the Priority Channel. For example, if |
| the Priority Channel is P1, and the |
| the scanning sequence is: P1, N1, P1, N2, P1, N3, P1, N4, P1, N5, etc. |
Program | The transfer of CPS information from the computer‟s temporary memory (RAM) |
| to the radio. |
PTT | |
| pressed, causes the radio to transmit. |
RESET | Reset line: an input to the microcontroller that restarts execution. |
Reverse Burst / | Causes a Tone Private Line (TPL) or Digital Private Line (DPL) code to be |
Turn Off Code | transmitted at the end of a transmission - once PTT is released, and while op- |
| erating on the current channel. This |
| dio to mute its speaker before loss of a carrier is detected. Muting the speaker |
| eliminates unwanted noise (squelch tail) during loss of carrier detection. |