2
J2ME Introduction
OEM | Native | |
Apps | Apps | Apps |
MIDP | OEM |
|
Classes |
| |
|
| |
CLDC |
|
|
Native System Software |
|
|
Mobile Information Device |
|
|
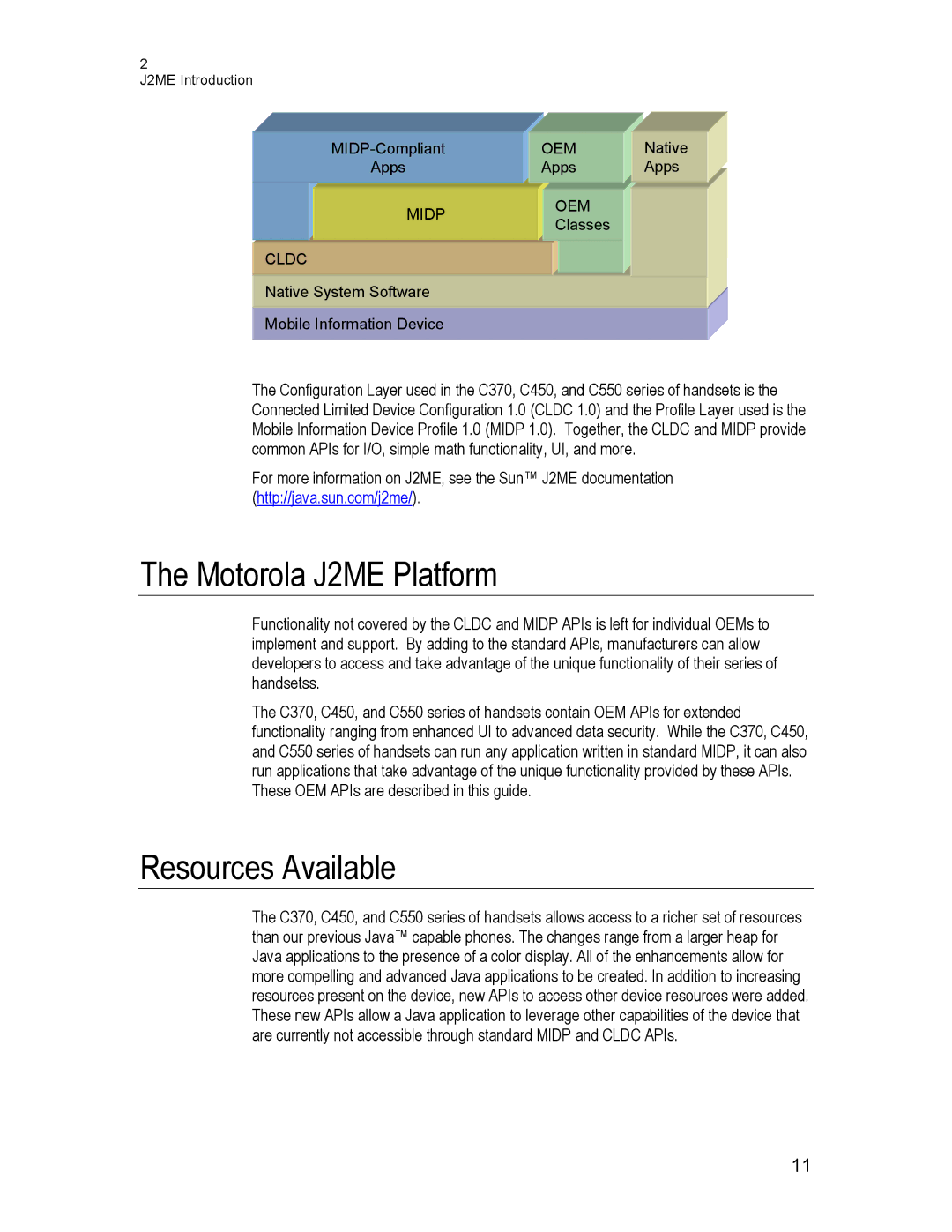
The Configuration Layer used in the C370, C450, and C550 series of handsets is the Connected Limited Device Configuration 1.0 (CLDC 1.0) and the Profile Layer used is the Mobile Information Device Profile 1.0 (MIDP 1.0). Together, the CLDC and MIDP provide common APIs for I/O, simple math functionality, UI, and more.
For more information on J2ME, see the Sun™ J2ME documentation (http://java.sun.com/j2me/).
The Motorola J2ME Platform
Functionality not covered by the CLDC and MIDP APIs is left for individual OEMs to implement and support. By adding to the standard APIs, manufacturers can allow developers to access and take advantage of the unique functionality of their series of handsetss.
The C370, C450, and C550 series of handsets contain OEM APIs for extended functionality ranging from enhanced UI to advanced data security. While the C370, C450, and C550 series of handsets can run any application written in standard MIDP, it can also run applications that take advantage of the unique functionality provided by these APIs. These OEM APIs are described in this guide.
Resources Available
The C370, C450, and C550 series of handsets allows access to a richer set of resources than our previous Java™ capable phones. The changes range from a larger heap for Java applications to the presence of a color display. All of the enhancements allow for more compelling and advanced Java applications to be created. In addition to increasing resources present on the device, new APIs to access other device resources were added. These new APIs allow a Java application to leverage other capabilities of the device that are currently not accessible through standard MIDP and CLDC APIs.
11