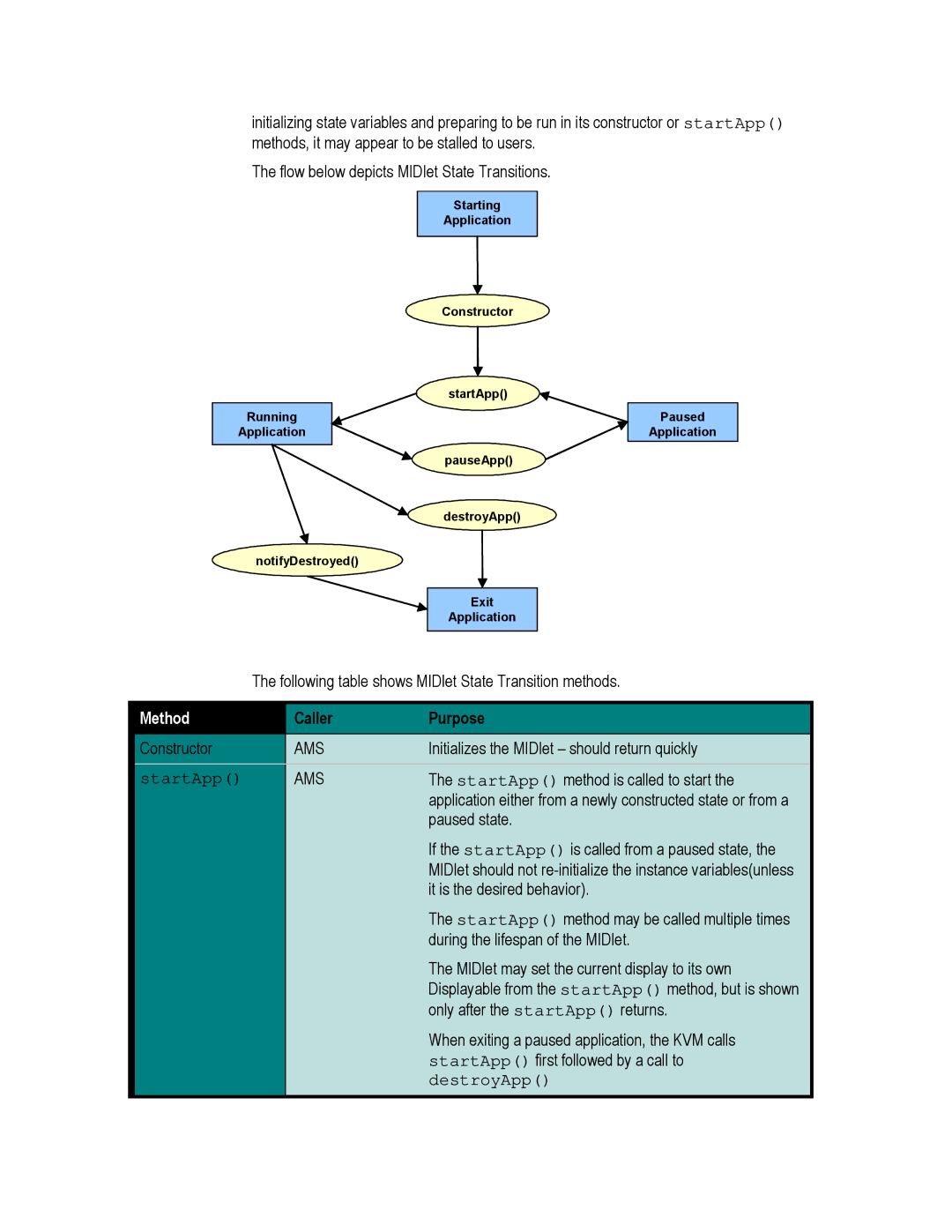
initializing state variables and preparing to be run in its constructor or startApp() methods, it may appear to be stalled to users.
The flow below depicts MIDlet State Transitions.
Starting
Application
Constructor
startApp()
Running
Application
pauseApp()
destroyApp()
notifyDestroyed()
Exit
Application
Paused
Application
The following table shows MIDlet State Transition methods.
| Method | Caller | Purpose |
| Constructor | AMS | Initializes the MIDlet – should return quickly |
| startApp() | AMS | The startApp() method is called to start the |
|
|
| application either from a newly constructed state or from a |
|
|
| paused state. |
|
|
| If the startApp() is called from a paused state, the |
|
|
| MIDlet should not |
|
|
| it is the desired behavior). |
|
|
| The startApp() method may be called multiple times |
|
|
| during the lifespan of the MIDlet. |
|
|
| The MIDlet may set the current display to its own |
|
|
| Displayable from the startApp() method, but is shown |
|
|
| only after the startApp() returns. |
|
|
| When exiting a paused application, the KVM calls |
|
|
| startApp() first followed by a call to |
|
|
| destroyApp() |
|
|
|
|