Industry Automation and Drive Technologies - SCE
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) makes it possible to automatically identify and localize objects and living beings, and thus considerably facilitates recording and storing data. The RFID system consists of the following: 1) a transponder that is located in the object or in the living being and identifies it, and 2) a reading device for reading out the transponder ID. The reading device includes a software (a micro-program) that controls the actual read process, and an RFID middleware with interfaces to other EDP systems and data bases.
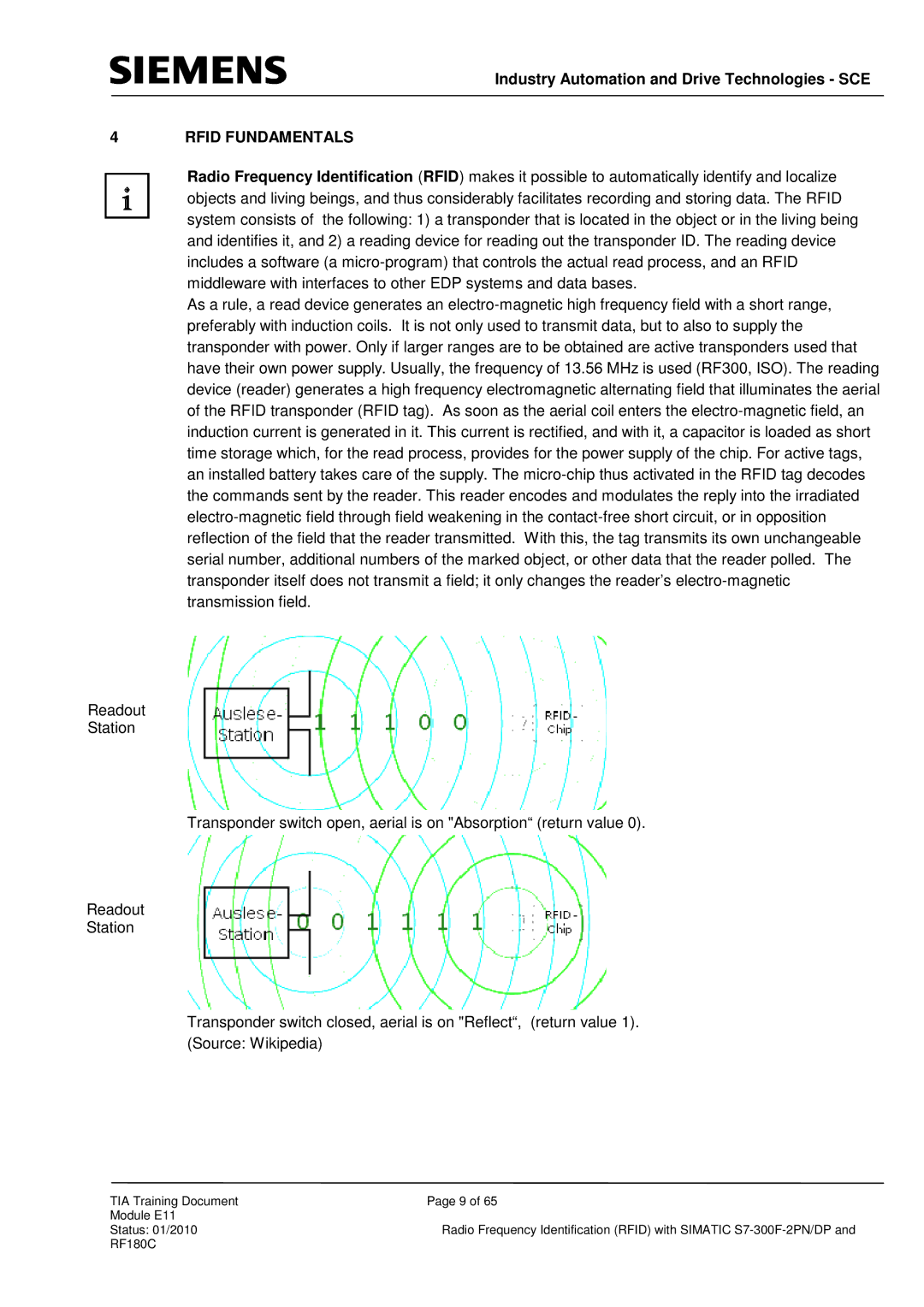
As a rule, a read device generates an electro-magnetic high frequency field with a short range, preferably with induction coils. It is not only used to transmit data, but to also to supply the transponder with power. Only if larger ranges are to be obtained are active transponders used that have their own power supply. Usually, the frequency of 13.56 MHz is used (RF300, ISO). The reading device (reader) generates a high frequency electromagnetic alternating field that illuminates the aerial of the RFID transponder (RFID tag). As soon as the aerial coil enters the electro-magnetic field, an induction current is generated in it. This current is rectified, and with it, a capacitor is loaded as short time storage which, for the read process, provides for the power supply of the chip. For active tags, an installed battery takes care of the supply. The micro-chip thus activated in the RFID tag decodes the commands sent by the reader. This reader encodes and modulates the reply into the irradiated electro-magnetic field through field weakening in the contact-free short circuit, or in opposition reflection of the field that the reader transmitted. With this, the tag transmits its own unchangeable serial number, additional numbers of the marked object, or other data that the reader polled. The transponder itself does not transmit a field; it only changes the reader’s electro-magnetic transmission field.
Readout
Station
Transponder switch open, aerial is on "Absorption“ (return value 0).
Readout
Station
Transponder switch closed, aerial is on "Reflect“, (return value 1). (Source: Wikipedia)
TIA Training Document | Page 9 of 65 |
Module E11 | |
Status: 01/2010 | Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) with SIMATIC S7-300F-2PN/DP and |
RF180C | |