Condensation
Bake
Specify which high altitude food preparation guide you prefer: general information, cakes, cookies, breads, etc.
•It is normal for certain amount of moisture to evaporate from the food during any cooking process. The amount depends on the moisture content of the food. The moisture may condense on any surface cooler than the inside of the oven, such as the control panel.
Bake is cooking with dry, heated air. Both the upper and lower elements cycle to maintain the oven temperature.
The Bake mode can be used to prepare a variety of food items, from pastries to casseroles. Refer to recipe or package directions for oven temperature and baking time.
Tips: • Preheat the oven if the recipe recommends it.
•Baking time will vary with the size, shape and finish of the bakeware. Dark metal pans or nonstick coatings will cook faster with darker results. Insulated bakeware will lengthen the cook time for most foods.
•For best results, bake food on a single rack with at least
•Eliminate heat loss from the oven by using the window to periodically check food for doneness instead of opening the door.
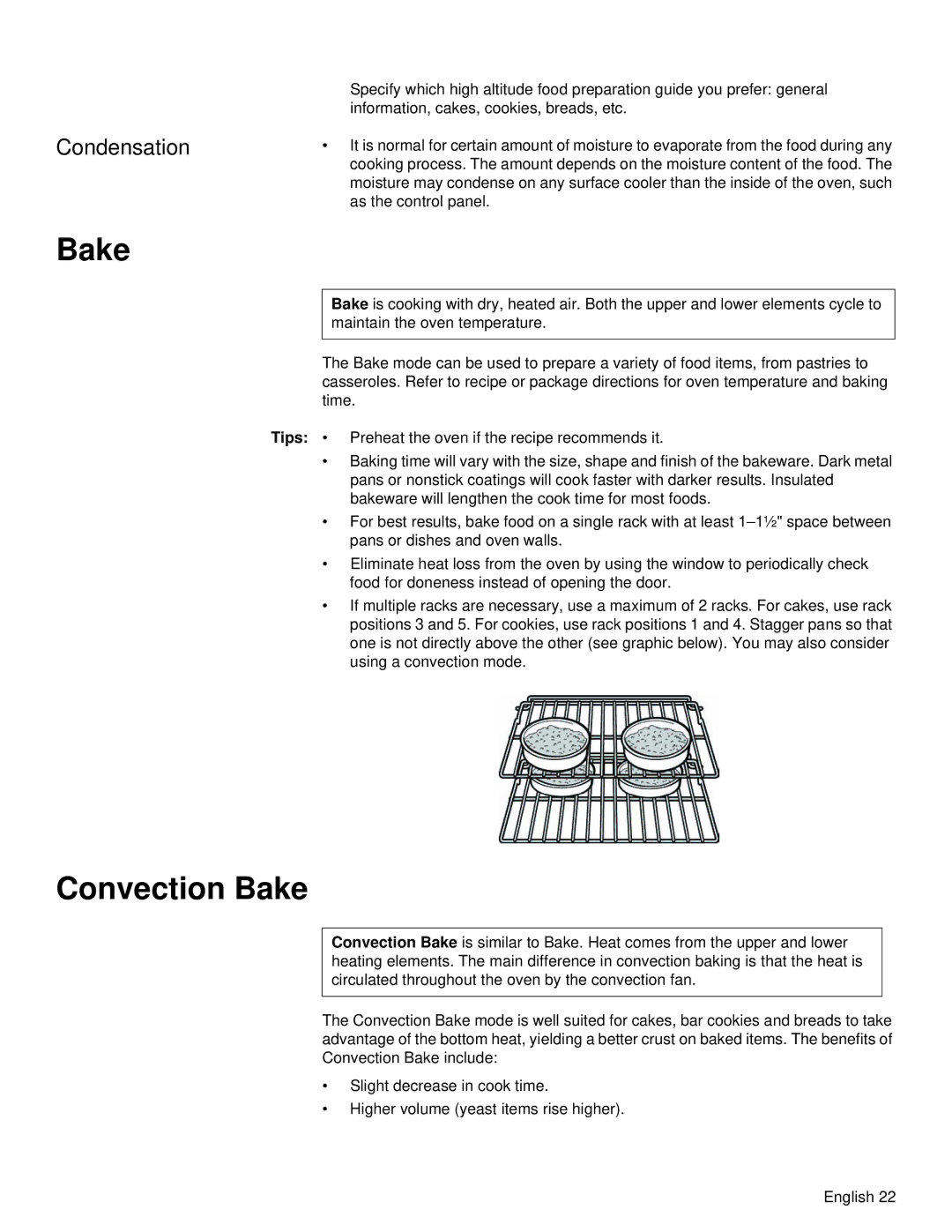
•If multiple racks are necessary, use a maximum of 2 racks. For cakes, use rack positions 3 and 5. For cookies, use rack positions 1 and 4. Stagger pans so that one is not directly above the other (see graphic below). You may also consider using a convection mode.
Convection Bake
Convection Bake is similar to Bake. Heat comes from the upper and lower heating elements. The main difference in convection baking is that the heat is circulated throughout the oven by the convection fan.
The Convection Bake mode is well suited for cakes, bar cookies and breads to take advantage of the bottom heat, yielding a better crust on baked items. The benefits of Convection Bake include:
•Slight decrease in cook time.
•Higher volume (yeast items rise higher).
English 22