i n t e l l i g e n t | w i r e l e s s | p l a t f o r m |
|
|
|
4. Quality of Service (QoS)
The primary goal of QoS is to provide priority for certain applications by dedicating bandwidth, controlling jitter and latency (which are required by some
QoS in 802.11 is defined by the IEEE 802.11e set of standards. Wireless Multimedia Extensions (WME), also known as
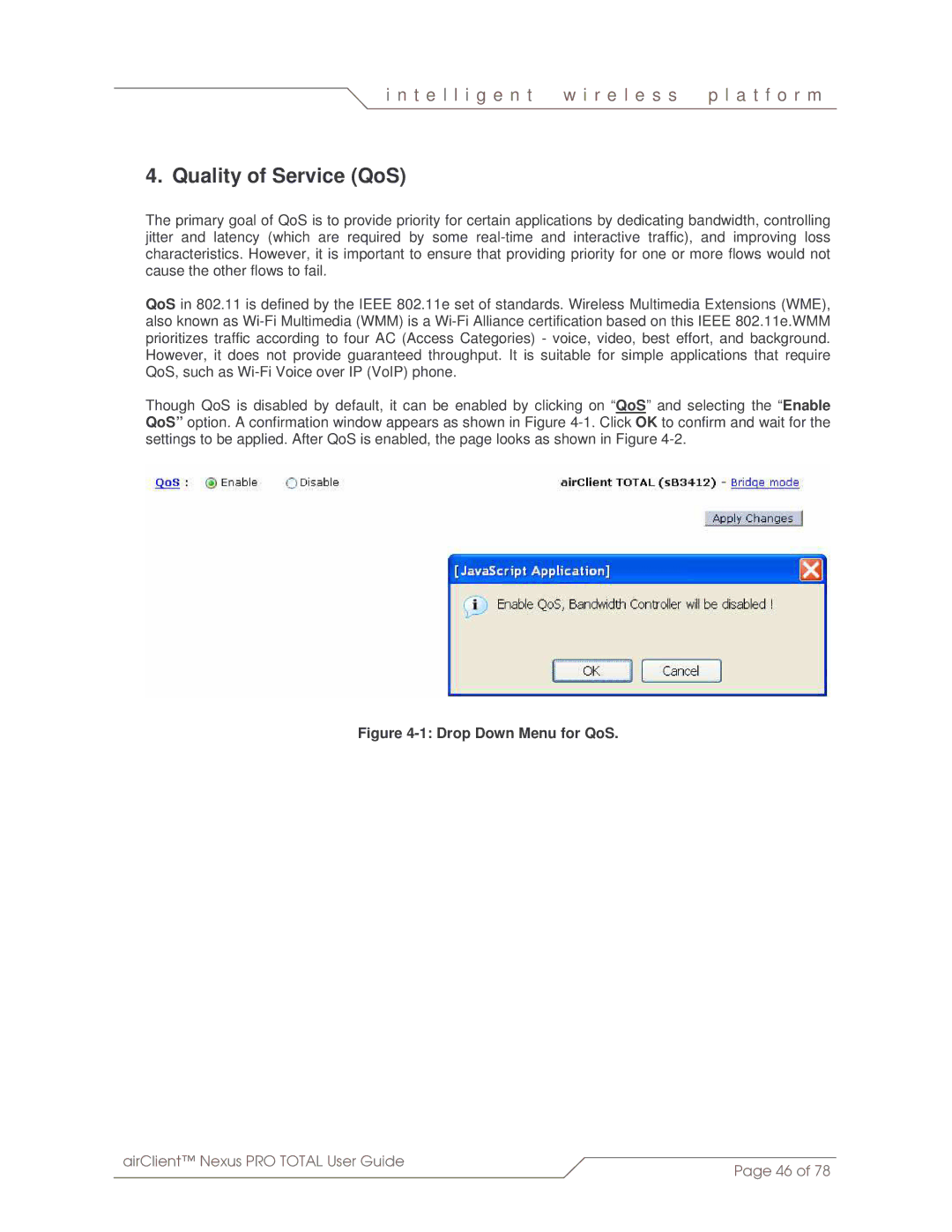
Though QoS is disabled by default, it can be enabled by clicking on “QoS” and selecting the “Enable QoS” option. A confirmation window appears as shown in Figure
Figure 4-1: Drop Down Menu for QoS.
airClient™ Nexus PRO TOTAL User Guide | Page 46 of 78 |
|