2
NETWORK PLANNING
The Mini Broadband Router is designed to be very flexible in its deployment options. It can be used as an Internet gateway for a small network, or as an access point to extend an existing wired network to support wireless users. It also supports use as a wireless bridge to connect up to four wired LANs, or as a wireless client to connect to another wireless network.
This chapter explains some of the basic features of the Mini Broadband Router and shows some network topology examples in which the device is implemented.
INTERNET GATEWAY ROUTER
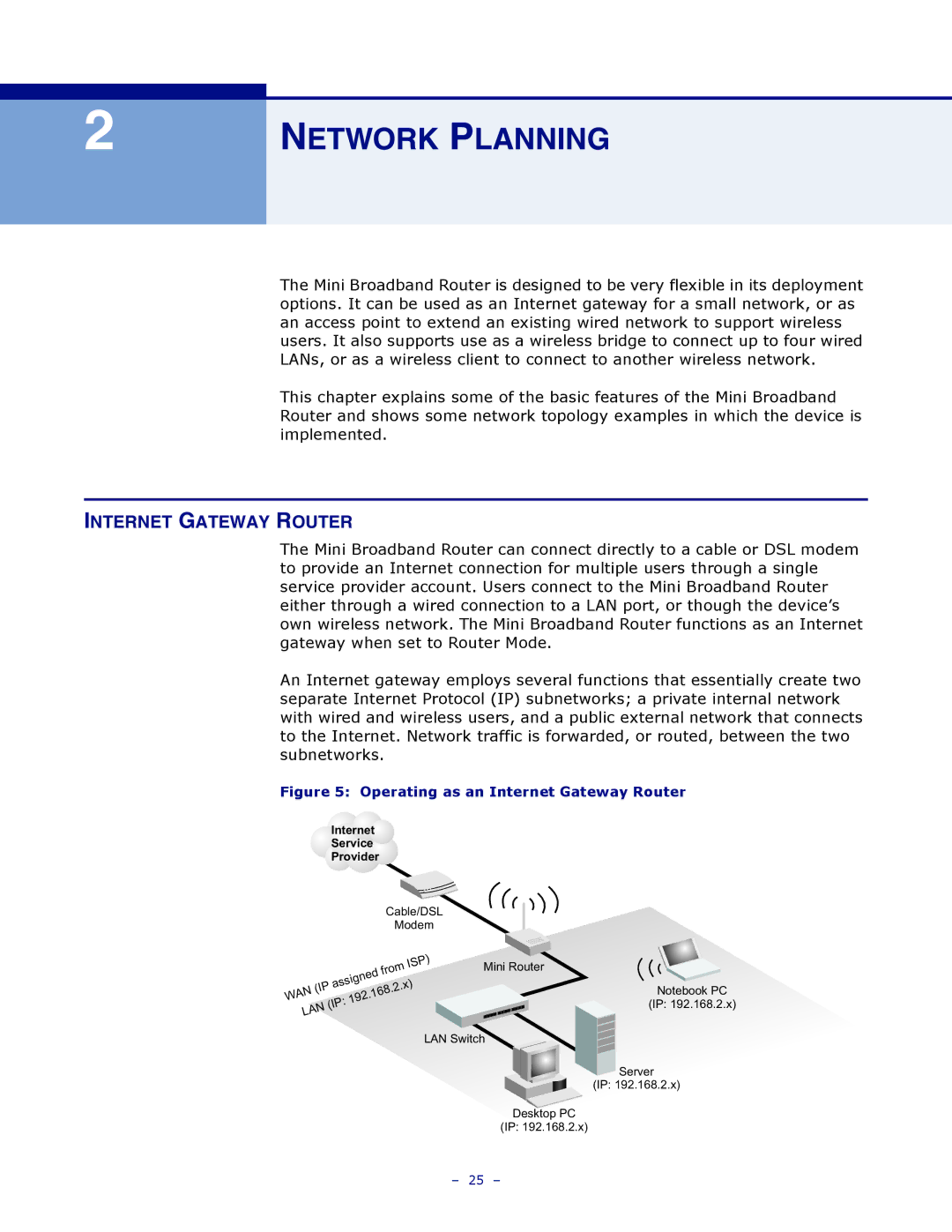
The Mini Broadband Router can connect directly to a cable or DSL modem to provide an Internet connection for multiple users through a single service provider account. Users connect to the Mini Broadband Router either through a wired connection to a LAN port, or though the device’s own wireless network. The Mini Broadband Router functions as an Internet gateway when set to Router Mode.
An Internet gateway employs several functions that essentially create two separate Internet Protocol (IP) subnetworks; a private internal network with wired and wireless users, and a public external network that connects to the Internet. Network traffic is forwarded, or routed, between the two subnetworks.
Figure 5: Operating as an Internet Gateway Router
Internet
Service
Provider
Cable/DSL
Modem
|
|
|
|
| from | ISP) | Mini Router |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| (IP | assigned | .x) |
| |||
|
|
| .2 |
|
| ||
WAN |
|
|
| .168 |
|
| |
| (IP: | 192 |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| |||
LAN |
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
LAN Switch
Notebook PC
(IP: 192.168.2.x)
Server
(IP: 192.168.2.x)
Desktop PC
(IP: 192.168.2.x)
– 25 –