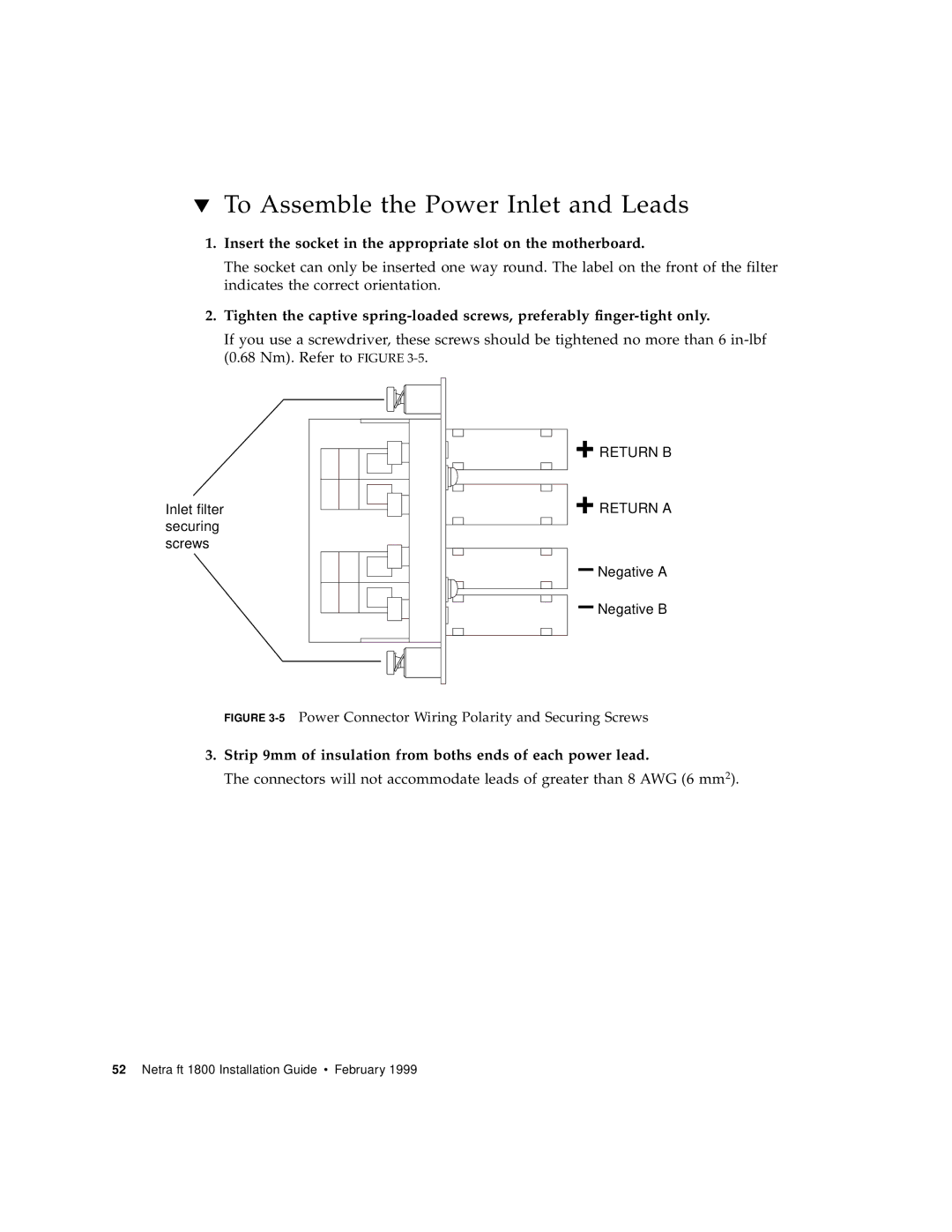
1800 specifications
Sun Microsystems, founded in 1982, unveiled an array of innovative products over the years, among which the Sun-1 workstation and later the Sun-1800 series were significant contributions to the technology landscape. Designed specifically for engineering, graphics, and computing tasks, the Sun-1800 series emerged during a period when workstations were essential for high-performance computing applications.The Sun-1800 series was powered by the SPARC architecture, which became a hallmark of Sun Microsystems' technological advancement. SPARC, an acronym for Scalable Processor Architecture, allowed the system to achieve high levels of performance and efficiency, positioning it well against competitors in the workstation market. The SPARC processors used in the Sun-1800 series enabled faster computation and multitasking, making it well-suited for scientific applications, computer-aided design (CAD), and complex data analyses.
One of the standout features of the Sun-1800 series was its expansive memory capabilities. Supporting configurations that could house up to 128 megabytes of RAM, the workstations were excellent for handling large datasets that were prevalent in research and corporate environments. This high memory capacity, combined with the efficient use of the SPARC architecture, granted users access to significant computational power, which was crucial for multitasking in complex job environments.
The Sun-1800 series also emphasized networking capabilities, with integrated Ethernet support. This allowed users to seamlessly connect their workstations into local area networks, facilitating collaborative projects and data sharing among teams. The use of the Solaris operating system, which was based on UNIX, also provided a robust and stable environment for enterprise applications, making the Sun-1800 ideal for business-critical applications.
Moreover, the system was designed to support various programming languages and development tools, attracting engineers, scientists, and software developers alike. Sun Microsystems also focused on providing high-quality graphics support, with advanced graphical capabilities that enabled users to engage in advanced visualization tasks, such as 3D modeling.
In summary, the Sun Microsystems 1800 series stands out for its powerful SPARC architecture, impressive memory capacity, integrated networking, and robust graphic capabilities. These characteristics, combined with the reliability of the Solaris operating system, positioned the Sun-1800 as a favored choice among professionals in engineering and scientific fields, shaping the future of workstation computing.