Health Benefits of Plant Foods A to Z
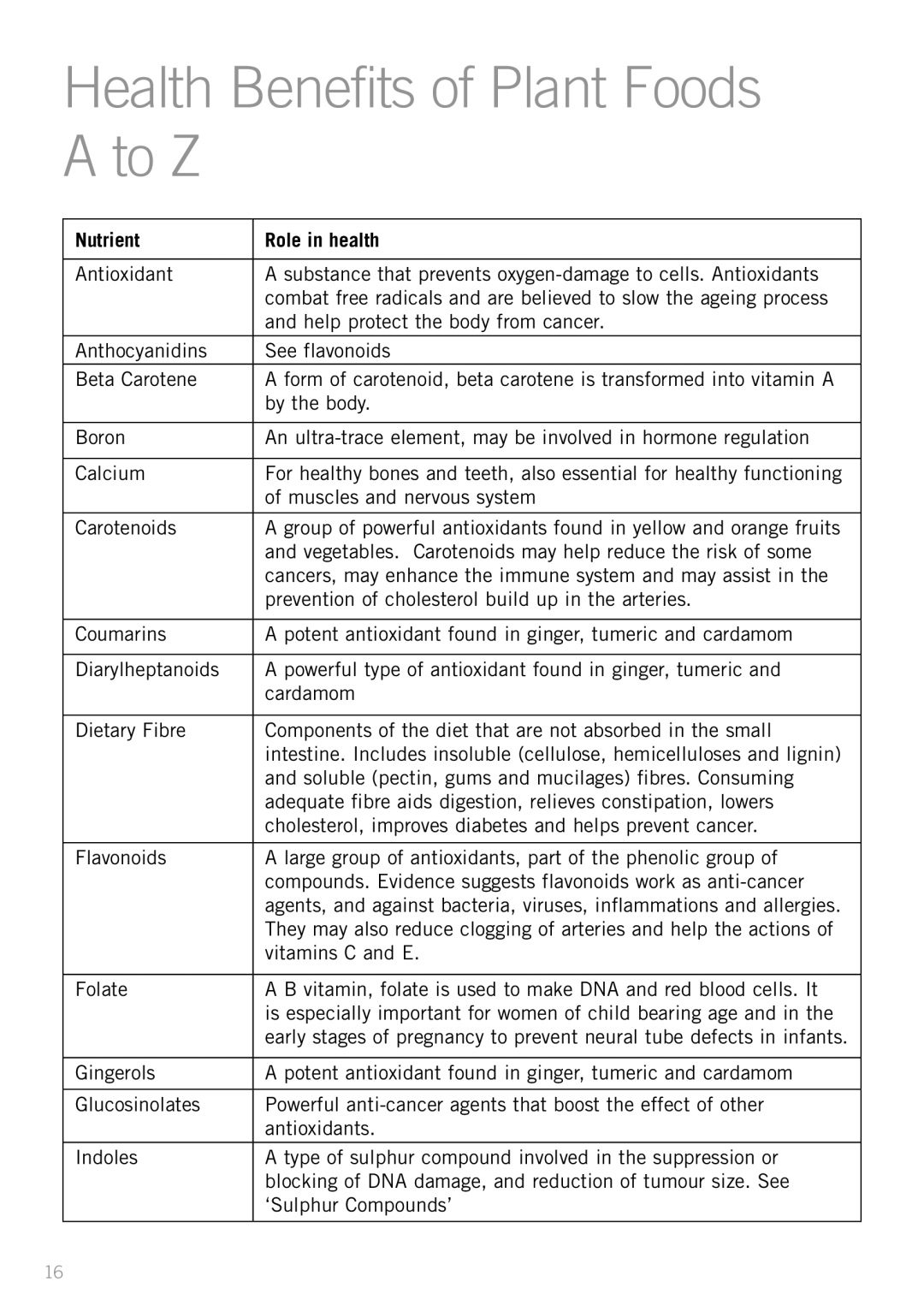
Nutrient | Role in health |
|
|
Antioxidant | A substance that prevents |
| combat free radicals and are believed to slow the ageing process |
| and help protect the body from cancer. |
Anthocyanidins | See flavonoids |
Beta Carotene | A form of carotenoid, beta carotene is transformed into vitamin A |
| by the body. |
|
|
Boron | An |
|
|
Calcium | For healthy bones and teeth, also essential for healthy functioning |
| of muscles and nervous system |
|
|
Carotenoids | A group of powerful antioxidants found in yellow and orange fruits |
| and vegetables. Carotenoids may help reduce the risk of some |
| cancers, may enhance the immune system and may assist in the |
| prevention of cholesterol build up in the arteries. |
|
|
Coumarins | A potent antioxidant found in ginger, tumeric and cardamom |
|
|
Diarylheptanoids | A powerful type of antioxidant found in ginger, tumeric and |
| cardamom |
|
|
Dietary Fibre | Components of the diet that are not absorbed in the small |
| intestine. Includes insoluble (cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin) |
| and soluble (pectin, gums and mucilages) fibres. Consuming |
| adequate fibre aids digestion, relieves constipation, lowers |
| cholesterol, improves diabetes and helps prevent cancer. |
|
|
Flavonoids | A large group of antioxidants, part of the phenolic group of |
| compounds. Evidence suggests flavonoids work as |
| agents, and against bacteria, viruses, inflammations and allergies. |
| They may also reduce clogging of arteries and help the actions of |
| vitamins C and E. |
|
|
Folate | A B vitamin, folate is used to make DNA and red blood cells. It |
| is especially important for women of child bearing age and in the |
| early stages of pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects in infants. |
|
|
Gingerols | A potent antioxidant found in ginger, tumeric and cardamom |
|
|
Glucosinolates | Powerful |
| antioxidants. |
|
|
Indoles | A type of sulphur compound involved in the suppression or |
| blocking of DNA damage, and reduction of tumour size. See |
| ‘Sulphur Compounds’ |
|
|
16