![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
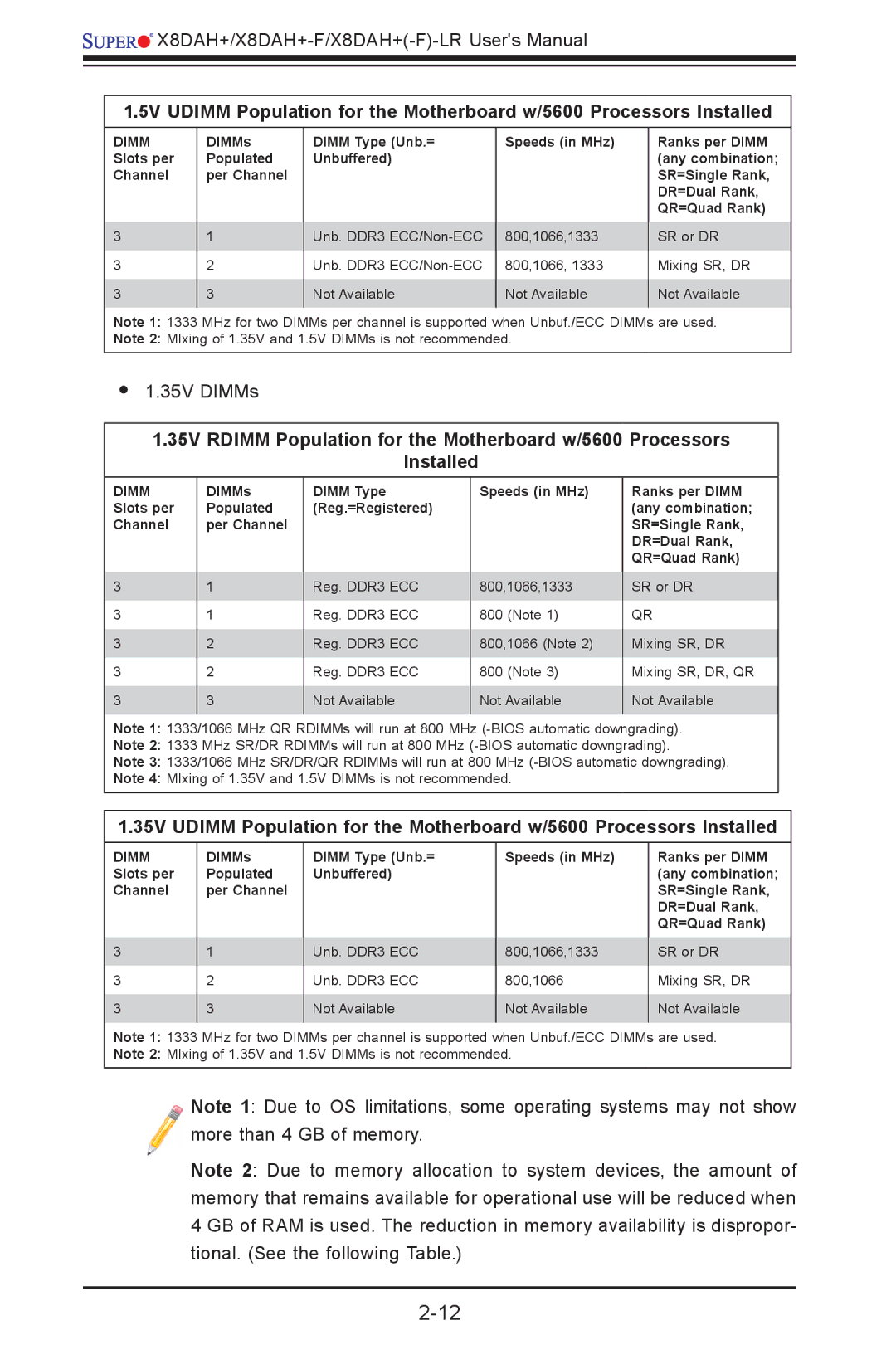
1.5V UDIMM Population for the Motherboard w/5600 Processors Installed
DIMM Slots per Channel
3
3
3
DIMMs Populated per Channel
1
2
3
DIMM Type (Unb.=
Unbuffered)
Unb. DDR3
Unb. DDR3
Not Available
Speeds (in MHz)
800,1066,1333
800,1066, 1333
Not Available
Ranks per DIMM (any combination; SR=Single Rank, DR=Dual Rank, QR=Quad Rank)
SR or DR
Mixing SR, DR
Not Available
Note 1: 1333 MHz for two DIMMs per channel is supported when Unbuf./ECC DIMMs are used.
Note 2: MIxing of 1.35V and 1.5V DIMMs is not recommended.
•1.35V DIMMs
1.35V RDIMM Population for the Motherboard w/5600 Processors
Installed
DIMM Slots per Channel
3
3
3
3
3
DIMMs |
| DIMM Type |
Populated |
| (Reg.=Registered) |
per Channel |
|
|
1 |
| Reg. DDR3 ECC |
|
1Reg. DDR3 ECC
2Reg. DDR3 ECC
2Reg. DDR3 ECC
3Not Available
Speeds (in MHz)
800,1066,1333
800 (Note 1)
800,1066 (Note 2)
800 (Note 3)
Not Available
Ranks per DIMM (any combination; SR=Single Rank, DR=Dual Rank, QR=Quad Rank)
SR or DR
QR
Mixing SR, DR
Mixing SR, DR, QR
Not Available
Note 1: 1333/1066 MHz QR RDIMMs will run at 800 MHz
Note 2: 1333 MHz SR/DR RDIMMs will run at 800 MHz
Note 3: 1333/1066 MHz SR/DR/QR RDIMMs will run at 800 MHz
Note 4: MIxing of 1.35V and 1.5V DIMMs is not recommended.
1.35V UDIMM Population for the Motherboard w/5600 Processors Installed
DIMM Slots per Channel
3
3
3
DIMMs | DIMM Type (Unb.= |
Populated | Unbuffered) |
per Channel |
|
|
|
1Unb. DDR3 ECC
2Unb. DDR3 ECC
3Not Available
Speeds (in MHz)
800,1066,1333
800,1066
Not Available
Ranks per DIMM (any combination; SR=Single Rank, DR=Dual Rank, QR=Quad Rank)
SR or DR
Mixing SR, DR
Not Available
Note 1: 1333 MHz for two DIMMs per channel is supported when Unbuf./ECC DIMMs are used.
Note 2: MIxing of 1.35V and 1.5V DIMMs is not recommended.
Note 1: Due to OS limitations, some operating systems may not show more than 4 GB of memory.
Note 2: Due to memory allocation to system devices, the amount of memory that remains available for operational use will be reduced when 4 GB of RAM is used. The reduction in memory availability is dispropor- tional. (See the following Table.)