Xerox
Page
Table of contents
Using Hfdl commands
Messages
Creating a sample form
Managing and printing sample forms
Appendices
INDEX±1
Glossary
Index
About this manual
Contents
Introduction
Xerox publications
Related publications
Conventions
LPI
IBM publications
Publication Number
Page
Hfdl features
Overview
Hardware requirements
Prerequisites
Operating environment
Software requirements
Centralized printers OSS version
Contrasting Hfdl with a typical forms application
Supported centralized printers
Decentralized printers
Forms you can create with Hfdl
Orientation
Planning your forms
Determining format
Frames
System
Virtual
Form origin
Physical
Positioning form elements
Form element Element origin
Grids
Y coordinates
Unit value
Data types
Negative coordinates
Forms data
Font orientation
Fonts
Fixed and proportionally spaced fonts
Font orientation when using short±edge paper feed
±6 shows the font orientations relative to the physical
Virtual keyboard and font character maps
Character Code point Identifier That prints 000/042
Virtual keyboard character maps
Ascii
Ink color availability and control
Adding color to forms
Font character maps
Ruler scales
Choosing paper size
Forms design ruler
Suggested uses
±14
Available specifications
Using Hfdl commands
Creating forms with Hfdl commands
Special characters
Command format
Reserved words
Setting up your form
Understanding the command syntax flow charts
Form command syntax
Form command
Paper command
Default
Examples Long form
LANDSCAPE/PORTRAIT command
Paper Usletter Size Uslegal
Paper Usletter
Parameters
Wide
High
Portrait page Size is 8.5 Inches Wide by 11 Inches High
CPI LPI
Grid command
Grid Unit
Origin
Grid Unit is 12 CPI by 8 LPI Origin 0.18 Inch 0.66 Inch
Font command
LANDSCAPE/PORTRAIT commands
Grid FMT1
Defaults
Icatalog command
Palette command
Icatalog
Palette PAL1
INK command
Palette is PAL1
INK
Inkname format
Example Long form
Inks RED, Pink
Inkname syntax
Or Color
Description commands
Iresult command
Line command
AT 3 Inches Draw 5 Horizontal Lines in Inches from
BOX command
Inches to 10 Inches Using Solid 1 Using INK 3
Repeat Horizontally Every 0.50 Inches
High Hairline Using Solid INK
Using Dotted INK Fill Shading Light
AT 4,6 BOX 14 Wide by 4 High
AT 4,6 Draw 4 Boxes 14 Wide by 4 High Using Solid
Hairline INK 2 and Repeat Every
Text AT command
Text Horizontal Vertical Spaced
Font INK Using
DOT Using Line
PER Line
CENTER, TOP, BOTTOM, JUSTIFIED. See the Xerox Laser
When you use Text Aligned in Column or Text Justified
INCHES, CENTIMETERS, CPI, LPI, DOTS, and XDOTS. You can
Example
Column 1 Inch Wide
Used with DOT Leader or Font n
Text in BOX command
Text AT 1,1 John Doe DOT Leader 987±6543
Bottom Right
Font INK Using BOX TOP
Leader Font NEW DOT Using Line BOX Next Horizontal
Right Bottom
Use Justified in COLUMN, refer to the ªTEXT AT commandº
Units are INCHES, CENTIMETERS, DOTS, and XDOTS. You can
For the in TOP, .......BOTTOM BOX.... for text placement
Same applies for in Next HORIZONTAL/VERTICAL BOX
Logo command
INK Using
Logo NEW1 AT 1,1 Using INK
Graphic command
Default None Examples Long form
Scale INK Using
Section command
Graphic Symbol AT 1,1 Scale is 4 Using INK
Section definitions
Do Section command
Section command
Section invocation
Do Nusec 3 AT 1,1 Repeat Horizontally Every
Section Times
Repeat Horizontally
Interword gap formula
Column command
Interword command
Specifying the interword multiplier
Using Spacing and Interword together
Specifying the base gap
Interword Spaceis
Gap, specified by Interword gap
DOT Leader command
DOT Leader Using Font
LET command
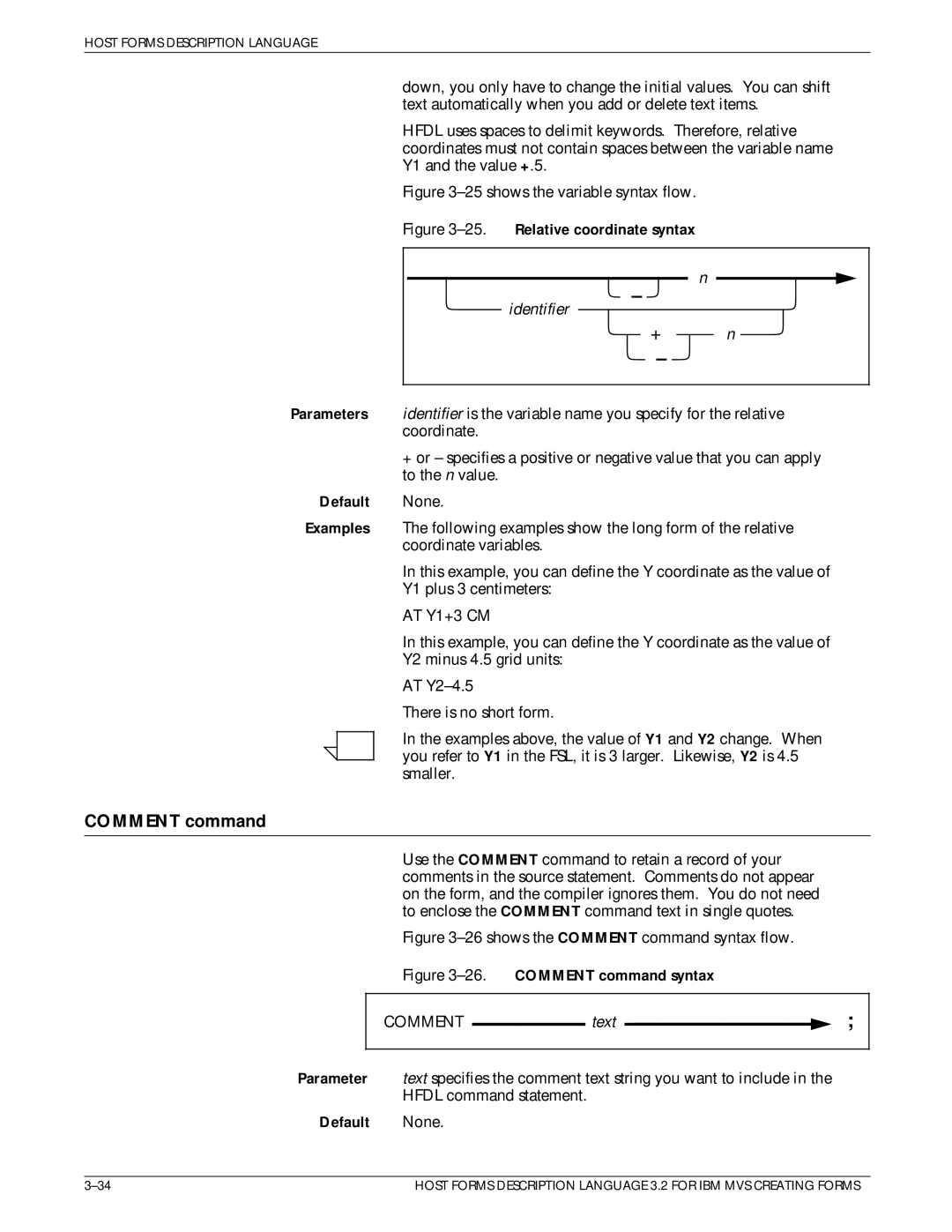
Relative coordinate
Comment command
Comment
Comment ***HFDL is Able to Describe Many Types Forms
END command
END command syntax
±36
Creating a sample form
Comment Define Titles
Form XEROX2 Resolution is 300 SPI Paper Size is Usletter
Setting up the form
Form XEROX2, Resolution is 300 SPI
Paper Size is Usletter
Using the sample description command
Form XEROX2
AT 2, ±1 Draw 1 BOX 133 Wide by 5 High Using Solid
Creating a Sample Form
Horizontal Text Using Font 3 AT 61, ±1 XEROX2 5/93
AT 11, ±1 6 Boxes 133, 4 Shading Vertically Every
Command syntax
Using the Compile command
Command coding conventions
Managing and printing sample forms
FSL=DDnamePDS member name where DDname = Xffsl
Operands
Gap, specified by
Coding alternative literal introduction
Characters To print When literal intro is
To print When shift
Key
COM FSL=XFFSL VER=XC MEM=MMBR?? FOR=FORM
Command syntax examples
Batch processing Compile commands
Compile FSL=XFFSL VER=X1 LITERAL=$ SHIFT=@ Object
Hfdl compiler JCL
±4. Resource DDnames for centralized printers Description
Hfdl execution DDnames for centralized
Resource DDnames for decentralized printers
DDname Description
Printers
Hfdl execution DDnames for decentralized
Xfifo
Xsuin
Data sets required to download and print
DDnames Description
Xsuactl
Downloading and printing a sample
Invoking the Hfdl compiler
Downloading and printing a sample
Xsuin
Specifying monochrome forms
Accessing compiled forms
Editing an existing form
Message indicators
Messages
XFG6007F DDname name is not defined
XFG6005W Group name too long, using name
XFG6006W Member/Form name name is too long
XFG6008F Dsname name does not exist
XFG6020I There are N forms compiled
XFG6013F Cannot open FSL
XFG6014F Cannot open scratch file file name
XFM8nnn Internal Failure
XFP1001W Discarding excess FDL
XFP1002W Semicolon expected
XFP1006W Invalid line weight, using Hairline
XFP1004W Draw N and Repeat Every disagree, using
XFP1005W Undefined Section Name name, command ignorned
XFP1007W Invalid border weight, using Hairline
XFP1010W Box not found
XFP1012W Unexpected fraction, using integer
XFP1014W Invalid resolution, using 300 spi
XFP1015W Unexpected end of text terminating code expected
XFP1024W Section name too long, using name
XFP1021W Setup command out of sequence
XFP1022W Identifier name too long, using name
XFP1025W Logos not supported for XES forms
XFP1030W Can not close data base
XFP3001E Syntax error on command segment
XFP1029W No substitution allowed for Logo logo name
XFP1032W Column off right of physical
XFP3006E
XFP3008E Setup command not allowed within section
XFP3005E Vertical text inconsistent with left/right
XFP3007E Stacked text and justify conflict
XFP3014E Value out of range
XFP3016E Font command not defined
XFP3018E INK command not defined
XFP3015E Keyword out of context/sequence
XFP3030E Box off top/bottom/left/right of physical
XFP3021E Font name font name exceeds 20 characters
XFP3024E Line end coordinate = start coordinate
XFP3034E Box width is zero
XFP4010F Grid format not defined format name
XFP4006F Cannot open FSL
XFP4009F Cannot open IFF
XFP4012F Too many fonts specified
XFP4030F Database access fault mode =return code
Return Description Code
±14
±15
±16
XFP4034F Invalid graphic scale factor
XFP4040F Text string exceeds buffer limits
XFP4051F Keyboard map error rc= return code
XFP4063F Data List Error
XFP4050F Keyboard map not found
XFP4067F Attribute data list Error
XFP4064F Query List Error
XFP4066F Delete old Attribute Error
XFP4068F ADD Attribute Error
XFP4081F Can not open Database. Check DB reference
XFP4082F DB security fault. No access privilege for user
XFP5000F Memory allocation fault rc=
XFP4084F Invalid virtual keyboard character map name
XFU4064F Query List Error
XFU4030F Database access fault mode=return code
XFU4063F Data List Error
XFU4060F Can not open FRM
XFU4069F Blob Data List Error
XFU4067F Attribute data list Error
XFU4068F ADD Attribute Error
XFU4070F Can not add 1st Blob
XFX0007F Invalid resolution record format
XFX0002F Memory allocation error
XFX0003F Open file error
XFX0004F Invalid IFF version record format
XFX0012F Invalid grid record format
XFX0022F Error opening IFF file
XFX0011F Invalid origin record format
XFX0013F Invalid line record format
XFX0025F Unexpected IFF command sequence
XFX0023F Error opening XES file
XFX0024F Error writing XES file
XFX0026F Error sorting IFF File
XFX0036W Error terminating Xprm
XFX0034F Error initializing to Xprm databases
XFX0035F Fatal error return from Xprm API
XFX0038F Error reading ink header record
Terminating due to internal error
Exit
±28
Line density limits
Local density and page setup errors
System considerations
Text in boxes
Using lines within sections
Boxes and their image
FMT properties for 8.5 by 11±inch paper
Specification Substitution
FMT grid format properties
FMT properties for 8.5 by 14±inch paper
FMT properties for A4 paper
Approved abbreviations for reserved words
Page
Extension
Table D±1. Command comparison matrix Command/Feature
Comparison of Hfdl and FDL
Page
Paper size inches Hfdl designation
Supported paper sizes
Paper sizes available for Hfdl
Page
Glossary
Host Forms Description Language
Glossary
Host Forms Description Language
GLOSSARY±5
Host Forms Description Language
GLOSSARY±7
Line feed
Library
Line
Line printer
GLOSSARY±9
Host Forms Description Language
GLOSSARY±11
Host Forms Description Language
GLOSSARY±13
Page
Barr SNA, 1±2
Index
Numerals
IBM
Operating
XES
Page
Sig & Bld Ex tertiary entry
IBM
JCL
XES1
FDL
Palette, see Palette command
Elated publi
Public
Asting H
Ng envir
Feat
Ardwa
Onm
Rereq
Er map
Map
Ddi
Ter map
Nt cha
Ms des
Ining forma
Or to f
Ori
Gri
Ning your f
Ge fra
Color av
Age o
Ortiona
Osing pa
Ienta
Uler sca
Rtual ke
Siz
Irtual k
Xerox 4700 Color Document Ment Printer h Nter uses full co
Ecia
Rved w
Com
MN com
Escr
Pro
Ettin
Nd for
Reati
Font card Ard. Us Decentralized1
NT n k
Ipt
1 Jo
LE n sp
ND comm
FDL comma
Ader co
ONT com
Aphic co
Up y
RM com
RID co
Hfdl com
Ax DOT LE
Sult com
OG com
NK comma
Rait com
Ette com
INE com
GO com
Aper com
On You
Ction com
Coordi
Ection comman
XT in BOX com
Flow ch
XT AT com
St NEW L
Mple description com
Sam
Up the fo
Ssing Compile co
Essing compiled f
Sing the C
Oding conve
Diting an ex
Acc
Wnlo
Fying monoc
Ding a
CL requireme
FDL compi
Atch pr
Aging and prin
Printing a sa
EMber=sele
Mpile com
Oup=nam
Essa
FP4034F FP4051F FP4066F FP4084F
Age indi
Em conside
Cape GR
MT grid f
MT prope
Ortrait and G
Oved abb
Eserved wo
Arison of HF
Nd FD
Orted paper si
Reader Satisfaction Survey
Please fold here