period three
Capacity Control
notes
out of the condition called
In the past, absorption water chillers would vary the heat input to the generator as the primary means of maintaining the desired
15 psia
[103.4 kPa]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| re |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| su | |
|
|
|
|
|
| s | 5 psia | |
|
|
|
|
| re |
| ||
|
|
|
| p |
|
|
| |
|
|
| r |
|
|
|
| |
|
| o |
|
|
|
| [34.5 kPa] | |
| p |
|
|
|
|
| ||
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
v |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1psia
[6.9 kPa]
0.1 psia |
|
|
|
|
| crystallization | |
[0.69 kPa] |
|
|
| 123°F |
| line |
|
50°F | 100°F |
|
| [50.6°C] | 150°F | 200°F | |
|
|
|
| ||||
[10°C] | [37.8°C] |
|
|
| [65.6°C] | [93.3°C] | |
| solution temperature |
| |||||
5 | concentration |
0 |
|
0 |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
0 |
|
6 |
|
LiBr solution
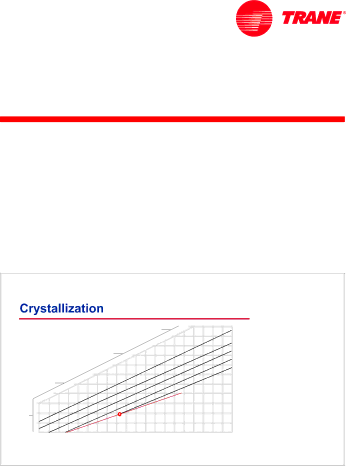
Figure 44
Crystallization
Lithium bromide is chemically classified as a salt. In its solid state, it has a crystalline structure and, like most salts, is soluble in water. With any salt solution, there is a “saturation” temperature for a given concentration, below which the salt begins to leave the solution as a solid. This is called crystallization.
The saturation temperature for various solution concentrations is represented by the crystallization line on the equilibrium chart. For example, consider a lithium bromide solution of 65% concentration. Above 123°F [50.6°C], all salt remains dissolved in the solution. If, however, the solution concentration remains the same and the temperature falls below 123°F [50.6°C], the solution becomes
37 |