Learning About the User Interfaces | 33 |
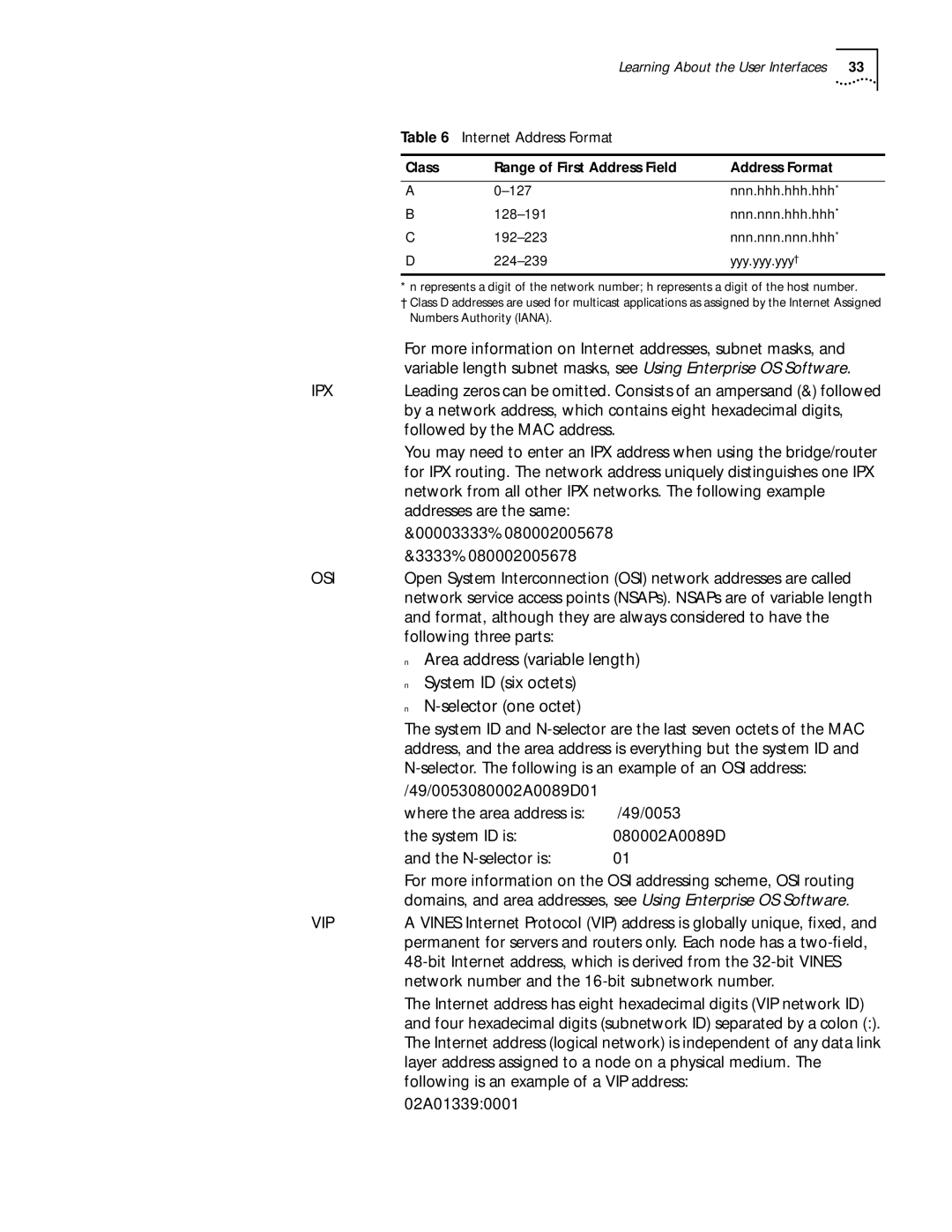
Table 6 Internet Address Format
Class | Range of First Address Field | Address Format |
|
|
|
A | nnn.hhh.hhh.hhh* | |
B | nnn.nnn.hhh.hhh* | |
C | nnn.nnn.nnn.hhh* | |
D | yyy.yyy.yyy† |
* n represents a digit of the network number; h represents a digit of the host number.
†Class D addresses are used for multicast applications as assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
| For more information on Internet addresses, subnet masks, and | |
| variable length subnet masks, see Using Enterprise OS Software. | |
IPX | Leading zeros can be omitted. Consists of an ampersand (&) followed | |
| by a network address, which contains eight hexadecimal digits, | |
| followed by the MAC address. | |
| You may need to enter an IPX address when using the bridge/router | |
| for IPX routing. The network address uniquely distinguishes one IPX | |
| network from all other IPX networks. The following example | |
| addresses are the same: |
|
| &00003333%080002005678 | |
| &3333%080002005678 |
|
OSI | Open System Interconnection (OSI) network addresses are called | |
| network service access points (NSAPs). NSAPs are of variable length | |
| and format, although they are always considered to have the | |
| following three parts: |
|
| ■ Area address (variable length) | |
| ■ System ID (six octets) |
|
| ■ |
|
| The system ID and | |
| address, and the area address is everything but the system ID and | |
|
| |
| /49/0053080002A0089D01 |
|
| where the area address is: | /49/0053 |
| the system ID is: | 080002A0089D |
| and the | 01 |
| For more information on the OSI addressing scheme, OSI routing | |
| domains, and area addresses, see Using Enterprise OS Software. | |
VIP | A VINES Internet Protocol (VIP) address is globally unique, fixed, and | |
| permanent for servers and routers only. Each node has a | |
| ||
| network number and the | |
The Internet address has eight hexadecimal digits (VIP network ID) and four hexadecimal digits (subnetwork ID) separated by a colon (:). The Internet address (logical network) is independent of any data link layer address assigned to a node on a physical medium. The following is an example of a VIP address:
02A01339:0001