Status Mode
After selecting the LTU from the SCU, the display enters Status mode. It alternately displays loop margin for each HDSL loop, any active alarm condition, and general status conditions.
The HDSL loop margin is displayed for each loop that is active with the messages “1=xx” and “2=xx” where
xxis the HDSL loop margin for that loop. The loop margin is held on the display for 2 seconds. The loop margin will not be displayed if that loop is in
E1 Core Frame Mapping
The function of E1 core frame mapping is to assign 2048 kbps framed E1 data to a 2304 kbps core frame filled with 2048 kbps data. This converts a
4. HDSL SYSTEM TESTING
The ADTRAN HDSL system provides extensive ability to monitor the status and performance of the G.703 signals and HDSL loop signals. Detailed performance monitoring is provided by the V.24 Control Port on the ADTRAN System Controller Unit (SCU). These features are valuable in troubleshooting and isolating any system level problems that may occur at installation or during operation of the HDSL system.
LTU G.703 Bantam Jack
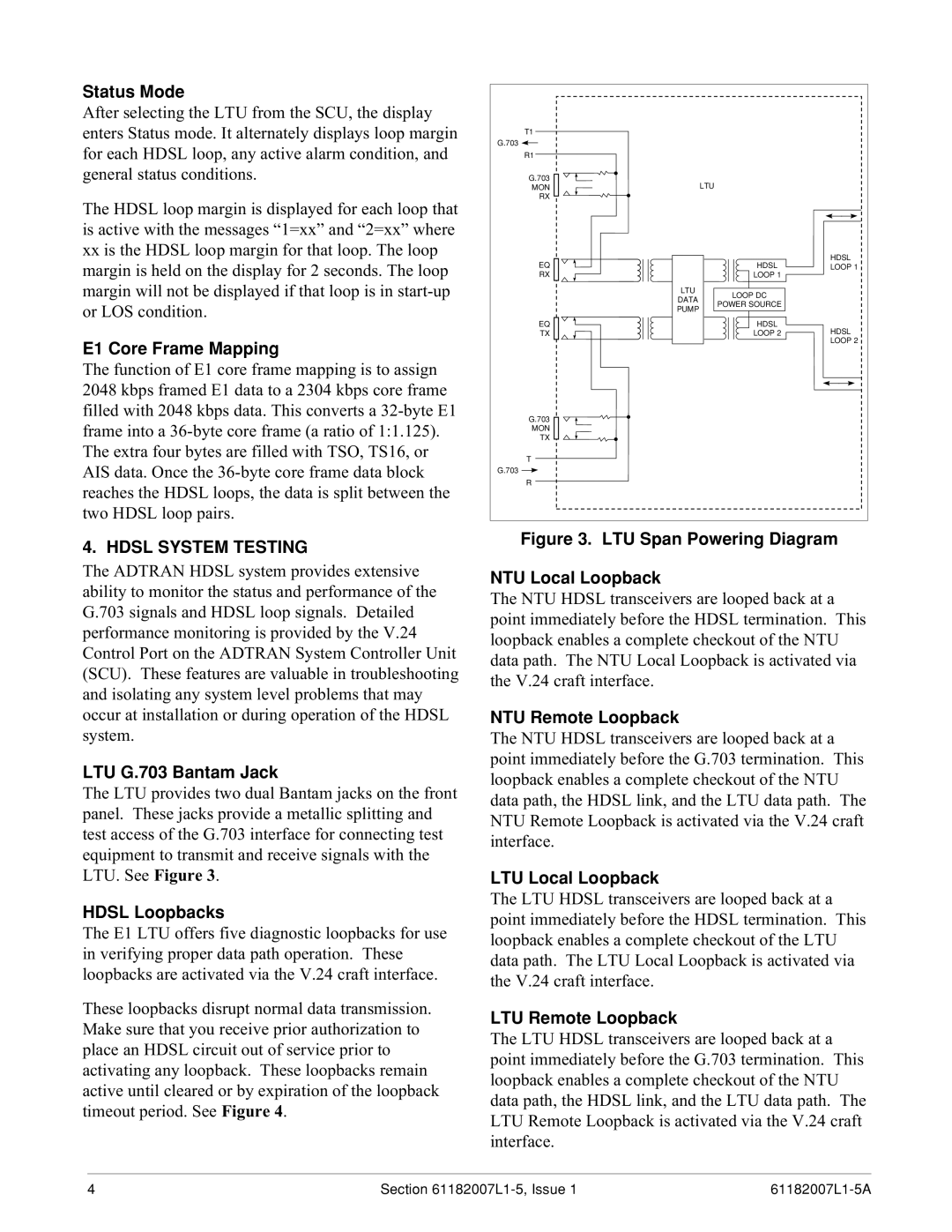
The LTU provides two dual Bantam jacks on the front panel. These jacks provide a metallic splitting and test access of the G.703 interface for connecting test equipment to transmit and receive signals with the LTU. See Figure 3.
HDSL Loopbacks
The E1 LTU offers five diagnostic loopbacks for use in verifying proper data path operation. These loopbacks are activated via the V.24 craft interface.
These loopbacks disrupt normal data transmission. Make sure that you receive prior authorization to place an HDSL circuit out of service prior to activating any loopback. These loopbacks remain active until cleared or by expiration of the loopback timeout period. See Figure 4.
T1 |
|
|
|
G.703 |
|
|
|
R1 |
|
|
|
G.703 |
| LTU |
|
MON |
|
| |
RX |
|
|
|
EQ |
| HDSL | HDSL |
| LOOP 1 | ||
RX |
| LOOP 1 |
|
| LTU | LOOP DC |
|
| DATA |
| |
| POWER SOURCE |
| |
| PUMP |
| |
|
|
| |
EQ |
| HDSL | HDSL |
TX |
| LOOP 2 | |
|
|
| LOOP 2 |
G.703 |
|
|
|
MON |
|
|
|
TX |
|
|
|
T |
|
|
|
G.703 |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
Figure 3. LTU Span Powering Diagram
NTU Local Loopback
The NTU HDSL transceivers are looped back at a point immediately before the HDSL termination. This loopback enables a complete checkout of the NTU data path. The NTU Local Loopback is activated via the V.24 craft interface.
NTU Remote Loopback
The NTU HDSL transceivers are looped back at a point immediately before the G.703 termination. This loopback enables a complete checkout of the NTU data path, the HDSL link, and the LTU data path. The NTU Remote Loopback is activated via the V.24 craft interface.
LTU Local Loopback
The LTU HDSL transceivers are looped back at a point immediately before the HDSL termination. This loopback enables a complete checkout of the LTU data path. The LTU Local Loopback is activated via the V.24 craft interface.
LTU Remote Loopback
The LTU HDSL transceivers are looped back at a point immediately before the G.703 termination. This loopback enables a complete checkout of the NTU data path, the HDSL link, and the LTU data path. The LTU Remote Loopback is activated via the V.24 craft interface.
4 | Section |