Rev. A.3, 5/00 | Page- 10 |
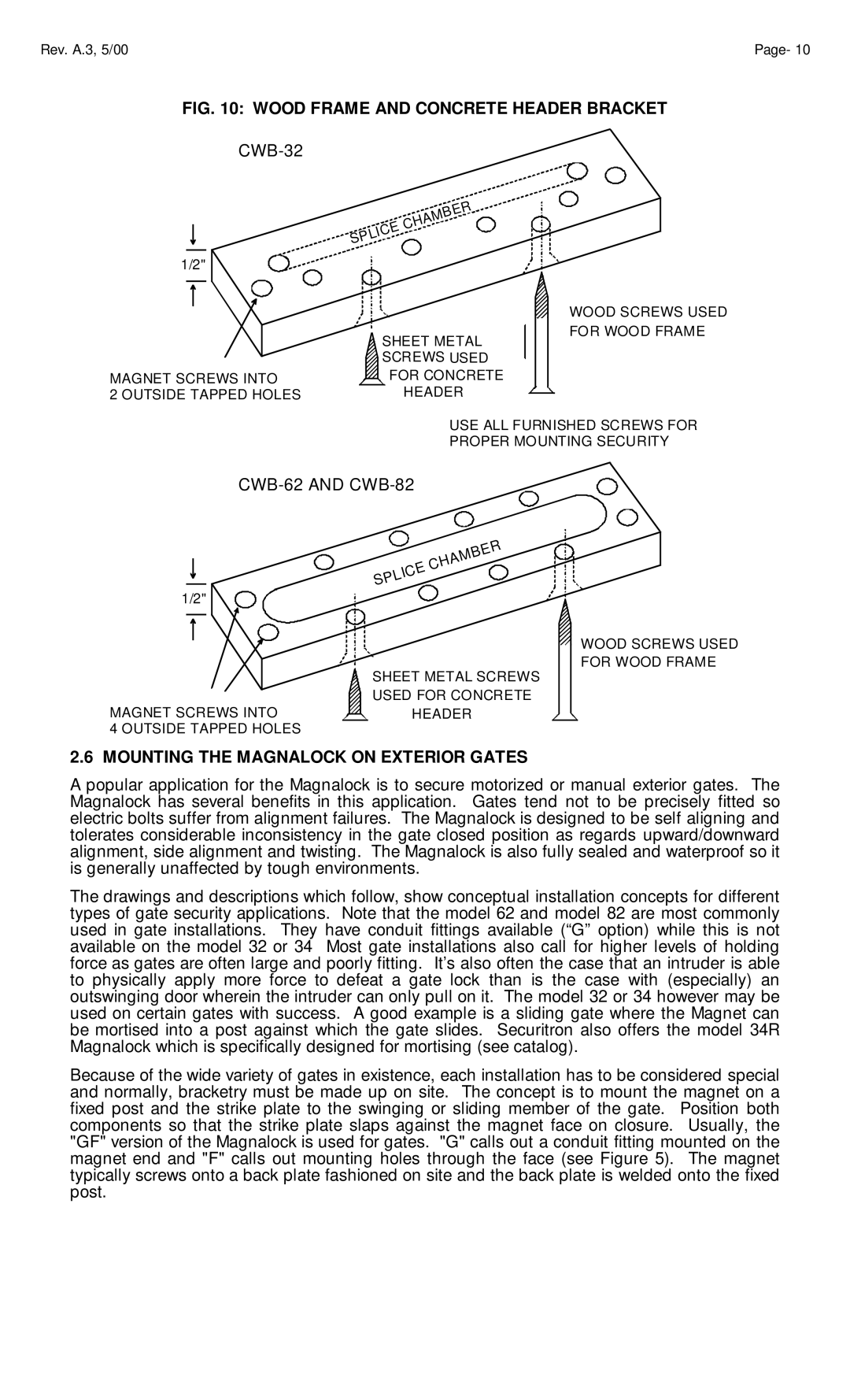
FIG. 10: WOOD FRAME AND CONCRETE HEADER BRACKET
CWB-32
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| M |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| H |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| EC |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1/2" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| WOOD SCREWS USED |
|
|
|
|
| SHEET METAL | FOR WOOD FRAME | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
| SCREWS USED |
| ||||||
MAGNET SCREWS INTO |
|
|
|
| FOR CONCRETE |
| ||||||
2 OUTSIDE TAPPED HOLES |
|
|
|
|
| HEADER |
| |||||
USE ALL FURNISHED SCREWS FOR
PROPER MOUNTING SECURITY
CWB-62 AND CWB-82
1/2" ![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| M |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| H |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| EC |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| IC |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WOOD SCREWS USED
FOR WOOD FRAME
SHEET METAL SCREWS
USED FOR CONCRETE
MAGNET SCREWS INTO ![]()
![]()
![]() HEADER 4 OUTSIDE TAPPED HOLES
HEADER 4 OUTSIDE TAPPED HOLES
2.6 MOUNTING THE MAGNALOCK ON EXTERIOR GATES
A popular application for the Magnalock is to secure motorized or manual exterior gates. The Magnalock has several benefits in this application. Gates tend not to be precisely fitted so electric bolts suffer from alignment failures. The Magnalock is designed to be self aligning and tolerates considerable inconsistency in the gate closed position as regards upward/downward alignment, side alignment and twisting. The Magnalock is also fully sealed and waterproof so it is generally unaffected by tough environments.
The drawings and descriptions which follow, show conceptual installation concepts for different types of gate security applications. Note that the model 62 and model 82 are most commonly used in gate installations. They have conduit fittings available (“G” option) while this is not available on the model 32 or 34 Most gate installations also call for higher levels of holding force as gates are often large and poorly fitting. It’s also often the case that an intruder is able to physically apply more force to defeat a gate lock than is the case with (especially) an outswinging door wherein the intruder can only pull on it. The model 32 or 34 however may be used on certain gates with success. A good example is a sliding gate where the Magnet can be mortised into a post against which the gate slides. Securitron also offers the model 34R Magnalock which is specifically designed for mortising (see catalog).
Because of the wide variety of gates in existence, each installation has to be considered special and normally, bracketry must be made up on site. The concept is to mount the magnet on a fixed post and the strike plate to the swinging or sliding member of the gate. Position both components so that the strike plate slaps against the magnet face on closure. Usually, the "GF" version of the Magnalock is used for gates. "G" calls out a conduit fitting mounted on the magnet end and "F" calls out mounting holes through the face (see Figure 5). The magnet typically screws onto a back plate fashioned on site and the back plate is welded onto the fixed post.