ACCF/SF Module
Page
ATM Terminology
Introduction
Finding Information in This Guide
Conventions
Page
Contents
Contents
Avaya M770 M-ACCF/SF ATM Access Modules User’s Guide Iii
Contents
Contents
Page
Management Submenu
List of Figures
Port Submenu Display Results
ATM Submenu
Snmp Submenu
List of Tables
Page
ATM Benefits
ATM Access Modules
Features and Benefits
Overview
LAN Emulation Lane version
Avaya M770 Frame Switch Domains
ATM Access Module Features
Wire Rate Transmission on ATM port
LAN Emulation Client LEC
Network Layer Concepts LAN Emulation
LAN Emulation Overview
Emulated LAN Components
Broadcast and Unknown Server BUS
LAN Emulation Configuration Server Lecs
LAN Emulation Server LES
Control VCCs
Emulated LAN Connections
Data VCCs
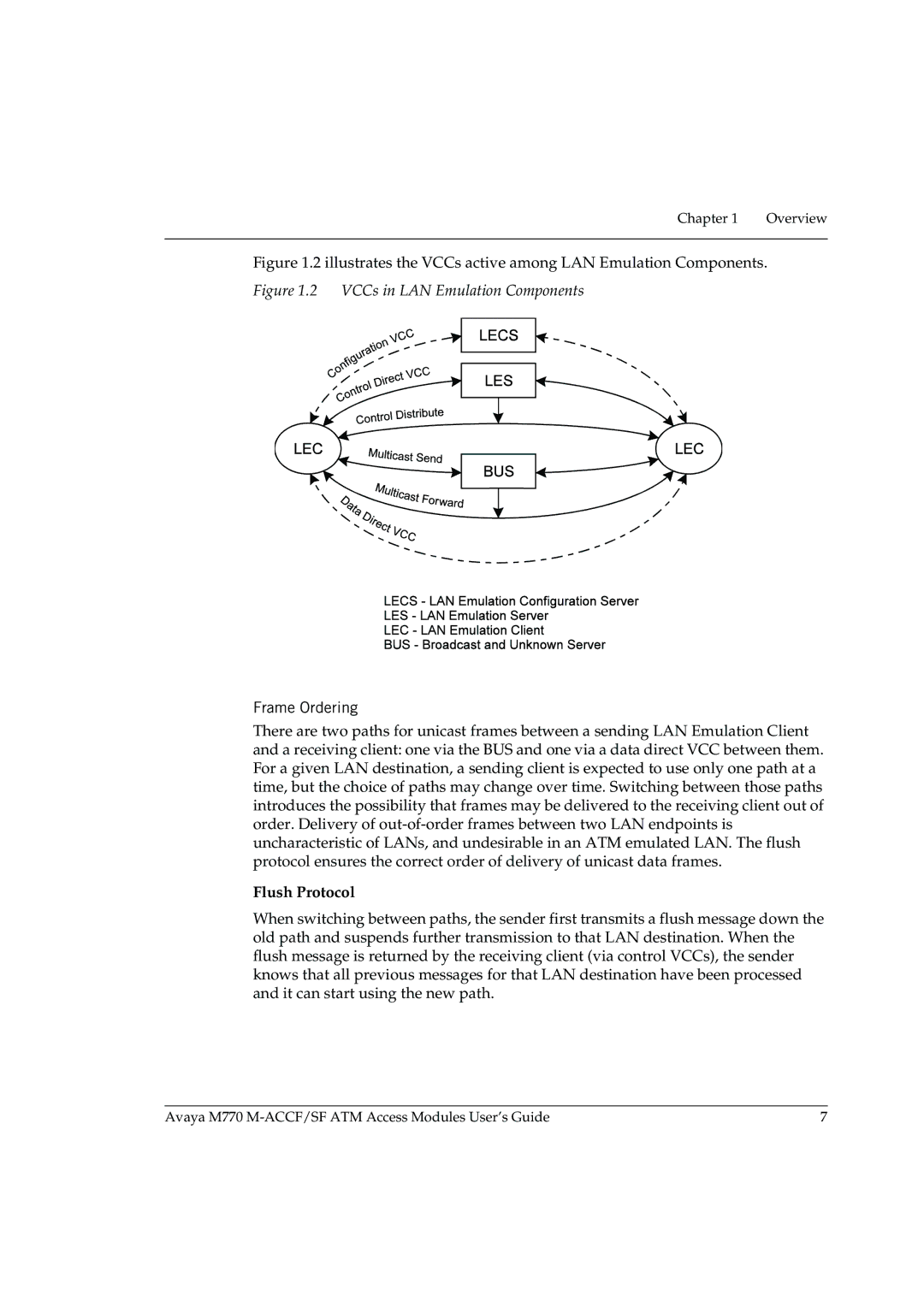
Flush Protocol
Frame Ordering
Operation of the LAN Emulation
Connecting a LEC to an Elan
Registration
Connection Processes of the LEC to Lane Server
LAN Emulation Components in Your Network
Address Resolution
Connection Management
An Example
LAN Emulation and Avaya Devices
Mapping Ethernet and ATM Addresses
Joining the Elan
LEC must know the name of the Elan it is to join
Locating the Lecs
If the destination MAC address is listed in the ARP Table
Address Resolution
What Happens to Broadcast and Multicast Frames?
LAN Emulation Address Resolution Protocol Learp
What Happens to Unicast Frames?
Layered Network Architecture
Network Layer Concepts ATM & ATM Adaptation
ATM Basics
Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM Layer
ATM Adaptation Layer AAL
Service Processing
ATM is Service Transparent
10 Communication Channels
ATM is Connection-Oriented
Virtual Path Identifier VPI Virtual Channel Identifier VCI
11 Connection Terminology
Switched Virtual Circuits SVCs
12 Switching Cells Using VPI and VCI Values
Interim Local Management Interface Ilmi
ATM Interfaces
ATM Layer and Cell Structure
ATM Address Registration
Networkhostidentifier
15 ATM Cell Structure
Extending VLANs into the ATM Network
Physical Layer
16 Vlan to Elan Mapping
17 Extending VLANs into the ATM Network
Planning Your Network
Applications
Putting Your ATM Network Together
Does your network conform to the ATM configuration rules?
ATM Configuration Rules
Will you have sufficient Elan resources?
What logical network domains, VLANs, do you wish to set up?
Are the LAN Emulation services configured correctly?
Extending VLANs Through the ATM Network
ATM Connections Within Your Network
ATM Backbone in the Building
Network Configuration Examples
ATM Backbone in the Building
Avaya M770 Multitechnology Functionality
Avaya M770 Multitechnology Functionality
Routing in the X-Switch Domain
Routing in the X-Switch Domain
Safety Information
Installation
Installing the M-ACC Module
Agency Approval
Pre-installation Procedure
Single-mode Module Laser Classification
Multi-Mode Module LED Warning
Budget Calculation Examples
Domain Usage Considerations
Avaya M770 Module DRU Budget
DRU Budget Information Window
DRU Budget Information Window
Installing the Module
Inserting the Module into the Hub
Connecting a Cable to the ATM Port
Removing an Existing ATM Access Module
Power On Self Test
CAM Contents Addressable Memory tests
M-ACC LEDs Descriptions
Post-Installation Checks
Connecting to the Serial Port
Configuring the M-ACC Module
ACC Module Default Settings
M-ACC Module Default Settings
For example telnet
Establishing a Telnet Session
To connect to the M-SPX/S Console port
Setting up the M-ACC Module
Assigning the M-ACC module IP address, Gateway and Netmask
Module Setup Main Menu
ATM IP Configuration
Setting up the ATM Access Module
There is no need to perform a reset. Configuration Example
MLS Bridging
Accmmls Switch
Introduction
Switch CLI & ATM Terminal Interface
Switch Command Line Interface CLI
ACC ATM Access Module Terminal Menu Interface
Conventions Used
Commands Summary Table
Switch Command Line Interface CLI
Reset the Module
Entering Software Download Parameters
Software Download to the X-Switch CPU
Monitoring the Software Download Process
Starting the Software Download Process
Create Report
Set Defaults to Factory Settings
Set Primary Version
Clear Mac Address Table
Configuration Copy
Assigning the M-ACC module IP address, Gateway and Netmask
Logging On
Commands Tree Chart
Submenus
Managing the ATM Access Module
Logging Off
Menu Structure of the ATM Access Module
System Menu
Configuring System Parameters
Main Menu Options
Initialize Submenu 1,2
Passwords Submenu 1,3
Reset Submenu1,4
Display Submenu 1,1
Operational Meanings of Display Flash Log Submenu Items
System Logger Submenu 1,5
Display Flash Log Messages Submenu 1,5,1
Operational Meanings of Display Memory Submenu Items
Display Memory Log Messages Submenu 1,5,2
System Software Download Submenu 1,6
Configuring an ATM Port
ATM access module Configuration
Operational Meanings of Port Submenu Items
Port Submenu 2,1
VCC Submenu 2,2
ATM Port Physical Submenu 2,1,6
Aging Submenu 2,2,4
VCC Submenu Items and their Operational Meanings
IP Submenu 3,1
Administering IP and Snmp Management
Snmp Configuration Submenu 3,2
Configure Submenu Items and their Operational Meanings
18 updSysAtt Submenu 3,2,6
20 Virtual net Submenu
VN Configuration Menu
LEC ATM
Vlan
Vlan Elan ID
Elan
LES ATM
LEC
Downloading
Setting up an ATM VLAN/ELAN
Upgrading Software
Preliminaries
ATM Port Statistics
Monitoring the ATM Access Module
Port Statistics Display Items and their Meanings
22 ATM Port Statistics Screen
Statistics Display Items and their Meanings
VCC Statistics
Cajun LANEMaster version
Network Management and Monitoring
CajunView M770 Device Manager version
Running M770 Manager from HP Windows NT
CajunView M770 Device Manager
Starting the M770 Manager
Running M770 Manager from HP-OV for Windows
Starting Cajun LANEMaster
LANEMaster
Overview
Overview
Cajun LANEMaster Views
Cajun LANEMaster Window
Page
ATM Cable Specification
Specifications
ACC ATM Access Module Technical Specifications
Environmental, Safety, and EMC Specifications
SDH Standard Supported
Table A.3 Standard Multi-mode Cable Specifications
Optical Standard Supported
ATM Forum
EIA-492CAAA
Table A.4 Standard Multi-mode Cable Specifications
Important Safety Information
Safety Information
ELAN/VLAN
Troubleshooting
Table B.1 Troubleshooting Tips
Page
SAR
Index
Numerics
ATM WAN
Text
ATM VLAN/ELAN
Learp
Luni
LES
VCC
Emea Europe, Middle East and Africa Region
How to Contact Us
United States
UAE
AP Asia Pacific Region
Avaya.com