network. You may enter a single port number or a range of port numbers to be forwarded, and the local IP address of the desired server. The port number identifies a service; for example, web service is on port 80 and FTP on port 21. In some cases, such as for unknown services or where one server can support more than one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might be better to specify a range of port numbers.
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A service request that does not have a server explicitly designated for it is forwarded to the default server. If the default is not defined, the service request is simply discarded.
The most often used port numbers are shown in the following table. Please refer to RFC 1700 for further information about port numbers.
SERVICES | PORT NUMBER |
|
|
ECHO | 7 |
|
|
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) | 21 |
|
|
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) | 25 |
|
|
DNS (Domain Name System) | 53 |
|
|
Finger | 79 |
|
|
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer protocol or WWW, Web) | 80 |
|
|
POP3 (Post Office Protocol) | 110 |
|
|
NNTP (Network News Transport Protocol) | 119 |
|
|
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) | 161 |
|
|
SNMP trap | 162 |
|
|
PPTP | 1723 |
|
|
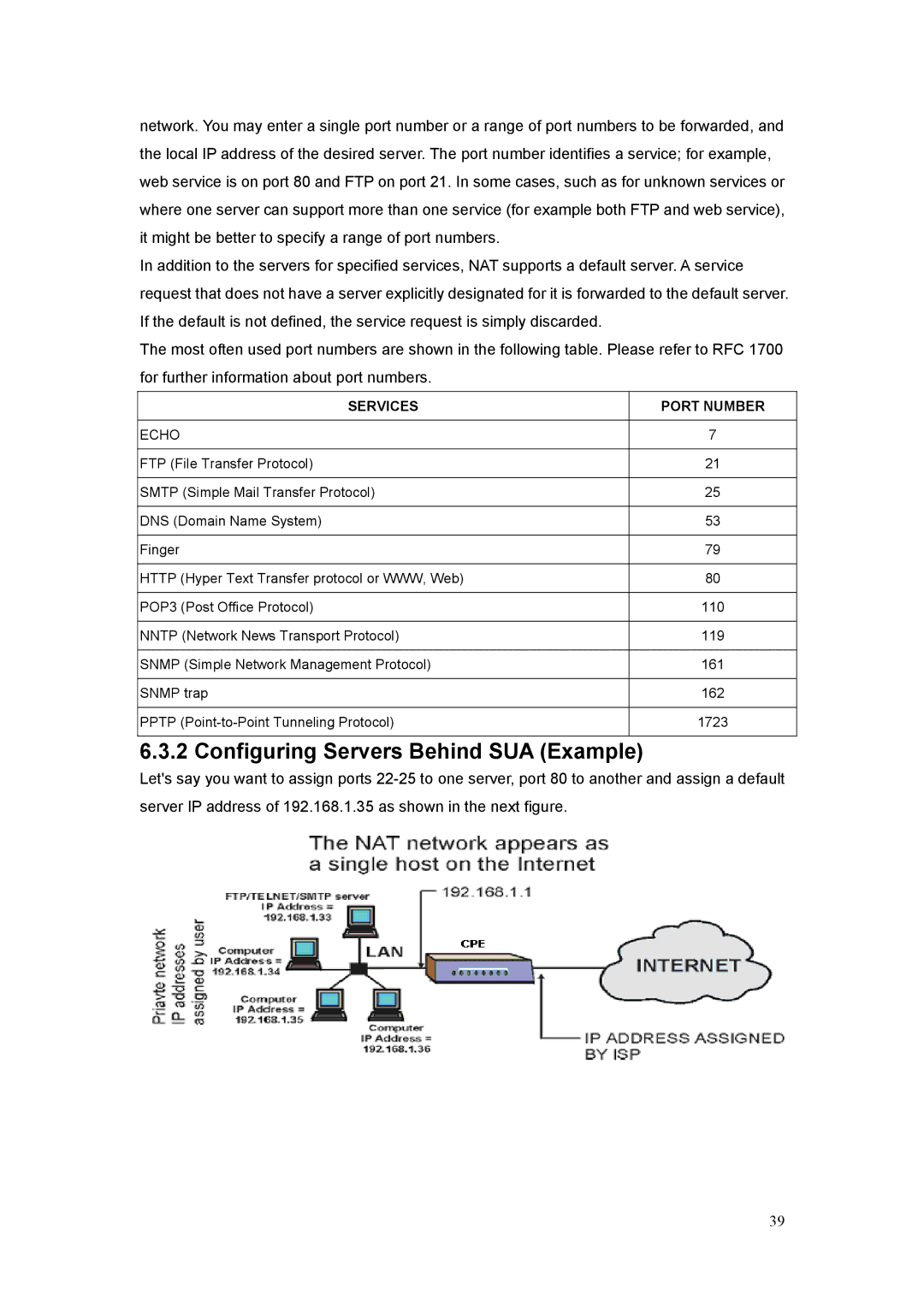
6.3.2 Configuring Servers Behind SUA (Example)
Let's say you want to assign ports
39