Wire Feed Arc Welder | Models WG2060 and WG2064 |
Modelos WG2060 y WG2064
Glossary of Welding Terms
AC or Alternating Current - electric current that reverses direction periodically. Sixty cycle current travels in both directions sixty times per second.
Arc Length - the distance from the end of the electrode to the point where the arc makes contact with the work surface.
Base Metal - the material to be welded.
Butt Joint - a joint between two members aligned approximately in the same plane.
Crater - a pool, or pocket, that is formed as the arc comes in contact with the base metal.
DC or Direct Current - electric current which flows only in one direction. The polarity (+ or
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) - also called MIG, is a welding process used with a wire feed welding machine. The wire is solid and an inert gas is used for shielding.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
-also called TIG, is a welding process used with welding equipment with a high frequency generator. The arc is created between a
Lap Joint - a joint between two overlapping members in parallel planes.
Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) - the voltage between the electrode and the work clamp of the welding machine when no current is flowing (not
Spatter - metal particles thrown from the weld which cool and harden on the work surface. Spatter can be minimized by using a spatter resistant spray on the work piece before welding.
Tack Weld - weld made to hold parts in proper alignment until final welds are made.
Travel Angle - the angle of the electrode in the line of welding. It varies from 5º to 45º depending on welding conditions.
T Joint - made by placing the edge of one piece of metal on the surface of the other piece at approximately a 90º angle.
Undercut - a condition that results when welding amperage is too high. The excessive amperage leaves a
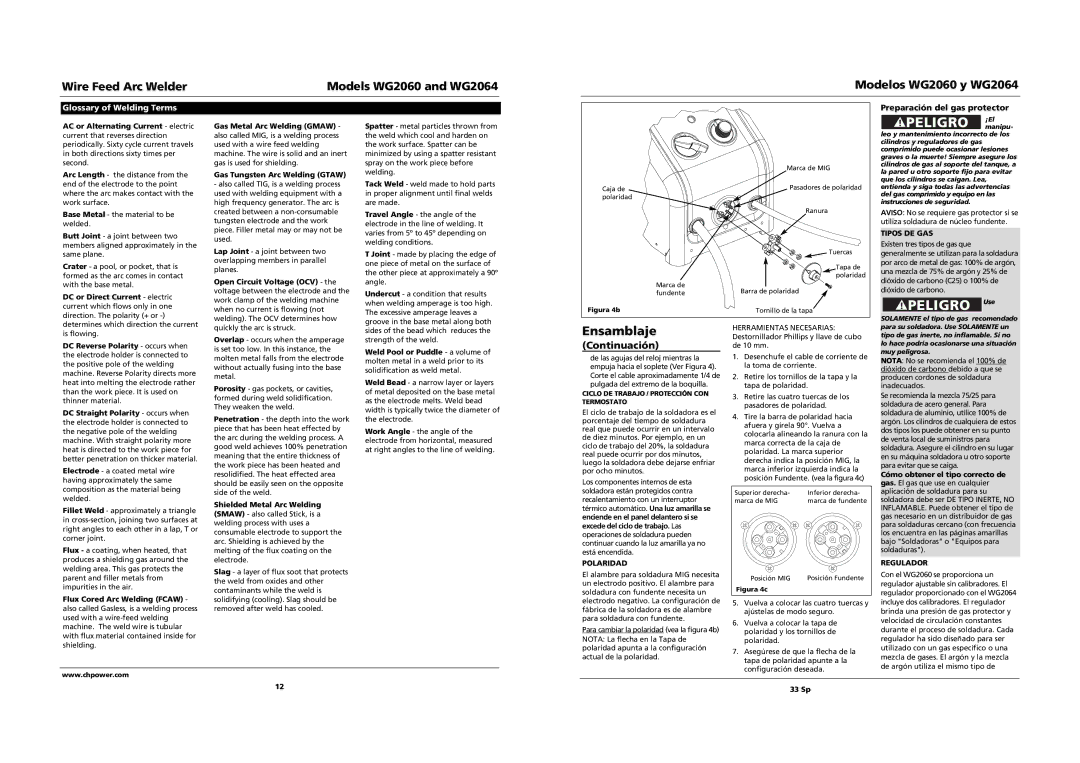
| Marca de MIG |
Caja de | Pasadores de polaridad |
polaridad |
|
| Ranura |
Tuercas
Tapa de polaridad
Marca de | Barra de polaridad |
fundente | |
Figura 4b | Tornillo de la tapa |
Preparación del gas protector
! PELIGRO ¡El
manipu- leo y mantenimiento incorrecto de los cilindros y reguladores de gas comprimido puede ocasionar lesiones graves o la muerte! Siempre asegure los cilindros de gas al soporte del tanque, a la pared u otro soporte fijo para evitar que los cilindros se caigan. Lea, entienda y siga todas las advertencias del gas comprimido y equipo en las instrucciones de seguridad.
AVISO: No se requiere gas protector si se utiliza soldadura de núcleo fundente.
TIPOS DE GAS
Existen tres tipos de gas que generalmente se utilizan para la soldadura por arco de metal de gas: 100% de argón, una mezcla de 75% de argón y 25% de dióxido de carbono (C25) o 100% de dióxido de carbono.
!PELIGRO Use
determines which direction the current is flowing.
DC Reverse Polarity - occurs when the electrode holder is connected to the positive pole of the welding machine. Reverse Polarity directs more heat into melting the electrode rather than the work piece. It is used on thinner material.
DC Straight Polarity - occurs when the electrode holder is connected to the negative pole of the welding machine. With straight polarity more heat is directed to the work piece for better penetration on thicker material.
Electrode - a coated metal wire having approximately the same composition as the material being welded.
Fillet Weld - approximately a triangle in
Flux - a coating, when heated, that produces a shielding gas around the welding area. This gas protects the parent and filler metals from impurities in the air.
Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) - also called Gasless, is a welding process used with a
welding). The OCV determines how quickly the arc is struck.
Overlap - occurs when the amperage is set too low. In this instance, the molten metal falls from the electrode without actually fusing into the base metal.
Porosity - gas pockets, or cavities, formed during weld solidification. They weaken the weld.
Penetration - the depth into the work piece that has been heat effected by the arc during the welding process. A good weld achieves 100% penetration meaning that the entire thickness of the work piece has been heated and resolidified. The heat effected area should be easily seen on the opposite side of the weld.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) - also called Stick, is a welding process with uses a consumable electrode to support the arc. Shielding is achieved by the melting of the flux coating on the electrode.
Slag - a layer of flux soot that protects the weld from oxides and other contaminants while the weld is solidifying (cooling). Slag should be removed after weld has cooled.
groove in the base metal along both sides of the bead which reduces the strength of the weld.
Weld Pool or Puddle - a volume of molten metal in a weld prior to its solidification as weld metal.
Weld Bead - a narrow layer or layers of metal deposited on the base metal as the electrode melts. Weld bead width is typically twice the diameter of the electrode.
Work Angle - the angle of the electrode from horizontal, measured at right angles to the line of welding.
Ensamblaje
(Continuación)
de las agujas del reloj mientras la empuja hacia el soplete (Ver Figura 4). Corte el cable aproximadamente 1/4 de pulgada del extremo de la boquilla.
CICLO DE TRABAJO / PROTECCIÓN CON TERMOSTATO
El ciclo de trabajo de la soldadora es el porcentaje del tiempo de soldadura real que puede ocurrir en un intervalo de diez minutos. Por ejemplo, en un ciclo de trabajo del 20%, la soldadura real puede ocurrir por dos minutos, luego la soldadora debe dejarse enfriar por ocho minutos.
Los componentes internos de esta soldadora están protegidos contra recalentamiento con un interruptor térmico automático. Una luz amarilla se enciende en el panel delantero si se excede del ciclo de trabajo. Las operaciones de soldadura pueden continuar cuando la luz amarilla ya no está encendida.
POLARIDAD
El alambre para soldadura MIG necesita un electrodo positivo. El alambre para soldadura con fundente necesita un electrodo negativo. La configuración de fábrica de la soldadora es de alambre para soldadura con fundente.
Para cambiar la polaridad (vea la figura 4b)
NOTA: La flecha en la Tapa de polaridad apunta a la configuración actual de la polaridad.
HERRAMIENTAS NECESARIAS: Destornillador Phillips y llave de cubo de 10 mm.
1.Desenchufe el cable de corriente de la toma de corriente.
2.Retire los tornillos de la tapa y la tapa de polaridad.
3.Retire las cuatro tuercas de los pasadores de polaridad.
4.Tire la barra de polaridad hacia afuera y gírela 90°. Vuelva a colocarla alineando la ranura con la marca correcta de la caja de polaridad. La marca superior derecha indica la posición MIG, la marca inferior izquierda indica la posición Fundente. (vea la figura 4c)
Superior derecha- | Inferior derecha- |
marca de MIG | marca de fundente |
Posición MIG | Posición Fundente |
Figura 4c
5.Vuelva a colocar las cuatro tuercas y ajústelas de modo seguro.
6.Vuelva a colocar la tapa de polaridad y los tornillos de polaridad.
7.Asegúrese de que la flecha de la tapa de polaridad apunte a la configuración deseada.
SOLAMENTE el tipo de gas recomendado para su soldadora. Use SOLAMENTE un tipo de gas inerte, no inflamable. Si no lo hace podría ocasionarse una situación muy peligrosa.
NOTA: No se recomienda el 100% de dióxido de carbono debido a que se producen cordones de soldadura inadecuados.
Se recomienda la mezcla 75/25 para soldadura de acero general. Para soldadura de aluminio, utilice 100% de argón. Los cilindros de cualquiera de estos dos tipos los puede obtener en su punto de venta local de suministros para soldadura. Asegure el cilindro en su lugar en su máquina soldadora u otro soporte para evitar que se caiga.
Cómo obtener el tipo correcto de gas. El gas que use en cualquier aplicación de soldadura para su soldadora debe ser DE TIPO INERTE, NO INFLAMABLE. Puede obtener el tipo de gas necesario en un distribuidor de gas para soldaduras cercano (con frecuencia los encuentra en las páginas amarillas bajo "Soldadoras" o "Equipos para soldaduras").
REGULADOR
Con el WG2060 se proporciona un regulador ajustable sin calibradores. El regulador proporcionado con el WG2064 incluye dos calibradores. El regulador brinda una presión de gas protector y velocidad de circulación constantes durante el proceso de soldadura. Cada regulador ha sido diseñado para ser utilizado con un gas específico o una mezcla de gases. El argón y la mezcla de argón utiliza el mismo tipo de
www.chpower.com
12 | 33 Sp |
|