CRADLEPOINT MBR1400 USER MANUAL Firmware ver. 3.4.1
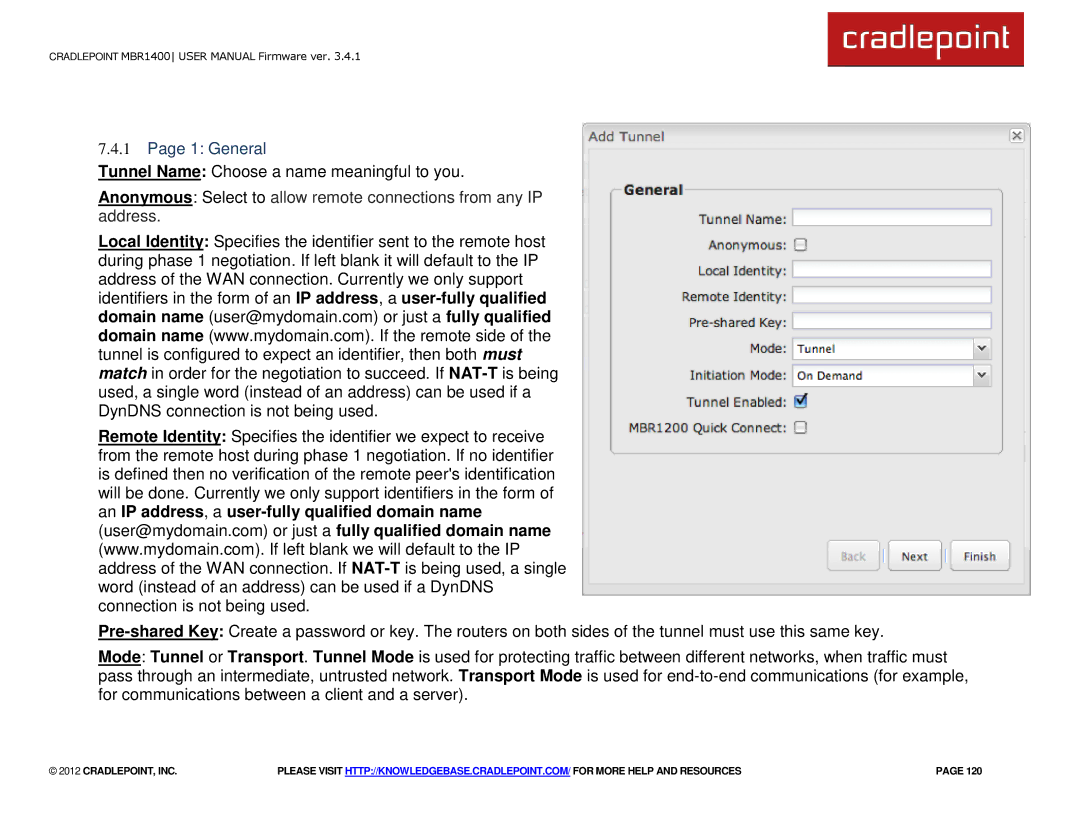
7.4.1Page 1: General
Tunnel Name: Choose a name meaningful to you.
Anonymous: Select to allow remote connections from any IP address.
Local Identity: Specifies the identifier sent to the remote host during phase 1 negotiation. If left blank it will default to the IP address of the WAN connection. Currently we only support identifiers in the form of an IP address, a
Remote Identity: Specifies the identifier we expect to receive from the remote host during phase 1 negotiation. If no identifier is defined then no verification of the remote peer's identification will be done. Currently we only support identifiers in the form of an IP address, a
Mode: Tunnel or Transport. Tunnel Mode is used for protecting traffic between different networks, when traffic must pass through an intermediate, untrusted network. Transport Mode is used for
© 2012 CRADLEPOINT, INC. | PLEASE VISIT HTTP://KNOWLEDGEBASE.CRADLEPOINT.COM/ FOR MORE HELP AND RESOURCES | PAGE 120 |