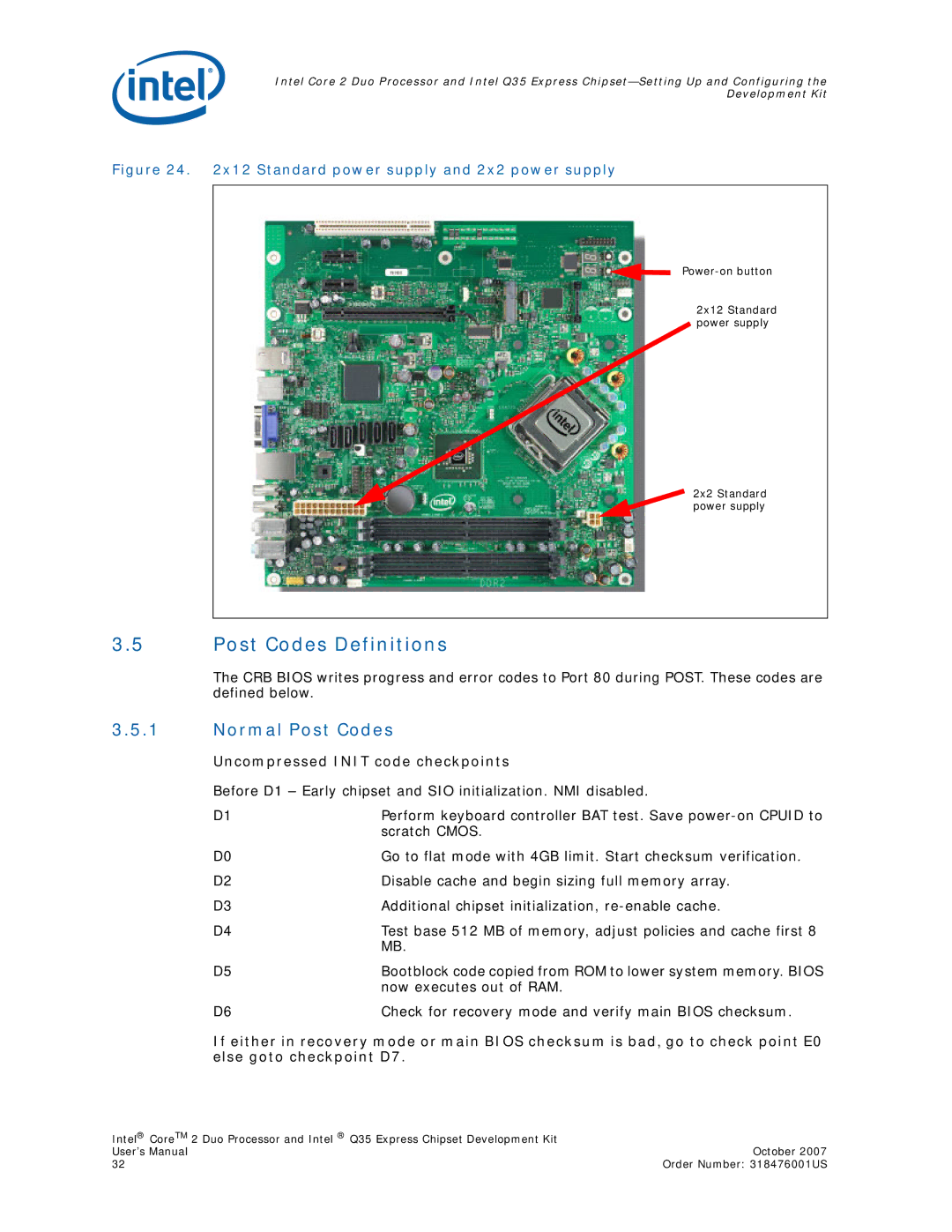
Q35 Express, Core 2 Duo specifications
The Intel Core 2 Duo is a line of dual-core processors that was introduced by Intel in 2006. It represented a significant advancement in semiconductor design, offering improved performance and efficiency over its predecessors. The Core 2 Duo processors were built on Intel's 65nm manufacturing process and later transitioned to a 45nm process, allowing for higher clock speeds and lower power consumption.One of the main features of the Core 2 Duo is its dual-core architecture. This allows the processor to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, enhancing multitasking capabilities. It is equipped with features such as Intel's Smart Cache, which optimizes the efficiency of memory usage by allowing both cores to access the cache. The processors also support Intel's Enhanced SpeedStep technology, which dynamically adjusts voltage and frequency according to workload, contributing to energy savings.
In terms of performance, the Core 2 Duo is capable of delivering high processing power for a wide range of applications, from everyday computing tasks to more demanding workloads like multimedia editing. The architecture supports 64-bit processing, enabling the use of more than 4GB of RAM, a significant improvement for performance-intensive applications.
The Q35 Express chipset complemented the Core 2 Duo processors, offering enhanced graphics capabilities through Intel's GMA X3100 integrated graphics. This chipset supports various technologies, including Intel vPro, which provides manageability features for enterprise users and enhances security. The Q35 Express also facilitates support for Intel’s Active Management Technology, allowing IT departments to remotely manage computers, even when powered off.
Furthermore, the Q35 Express chipset supports numerous connectivity and expansion options. It includes support for Intel High Definition Audio, providing a high-quality audio experience, and offers multiple PCI Express lanes for graphics and other expansion cards. The chipset supports up to 8 USB ports and SATA interface for connecting storage devices, making it well-suited for both consumer and business applications.
Overall, the Intel Core 2 Duo processors, along with the Q35 Express chipset, provide a robust and reliable platform suitable for a variety of uses. Their combination of dual-core performance, energy efficiency, and enhanced graphics support ensures that they continue to be relevant for many users well beyond their initial launch.