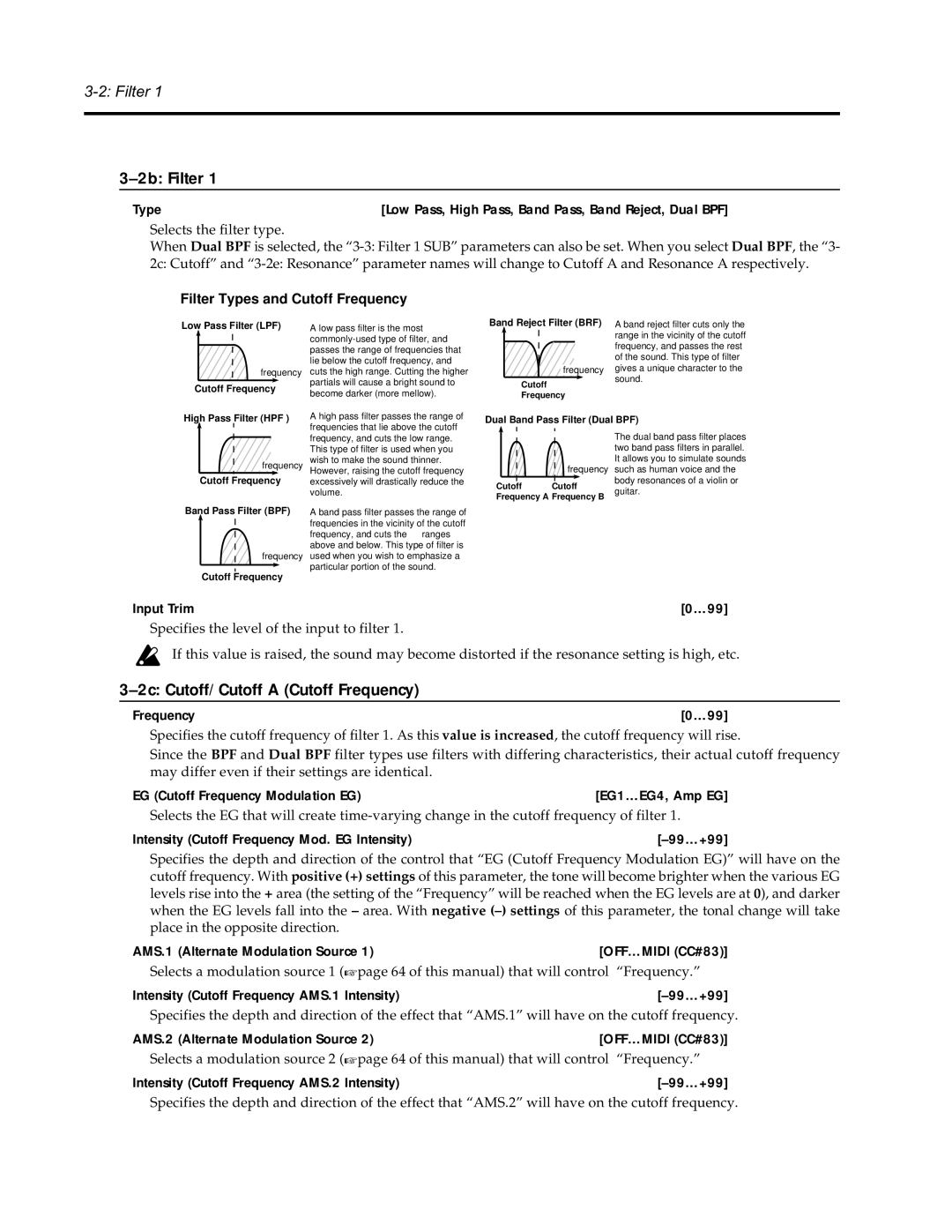
Synthesizer specifications
Korg synthesizers have established themselves as a powerhouse in the music production landscape, combining cutting-edge technology with user-friendly features to cater to musicians, producers, and sound designers alike. These iconic instruments have continuously evolved since the company’s inception in 1963, embodying innovation and quality.One of the defining features of Korg synthesizers is their diverse range of models which cater to different musical styles and needs. From the grand M1 synthesizer that popularized MIDI in the late 1980s to the more recent Minilogue and Prologue, each model presents unique capabilities. The Minilogue offers a straightforward interface and powerful four-voice polyphony, ideal for both novices and seasoned musicians. In contrast, the Prologue, with its advanced circuitry and multi-engine technology, provides extensive sound design possibilities.
Korg synthesizers are known for their rich sound engines. Many models utilize the proprietary EDS (Enhanced Definition Synthesis) technology, which delivers detailed and dynamic sounds. Users can expect a broad sonic palette, facilitating everything from lush pads to biting leads. The multi-engine architecture found in the Prologue adds another layer of versatility, allowing for the integration of wavetable and FM synthesis alongside traditional analog sounds.
Another key characteristic of Korg synthesizers is their connectivity options. Most models are equipped with MIDI, USB, and audio outputs, making them easy to integrate into any studio setup or live performance rig. The ability to control virtual instruments and external devices through MIDI enhances the functionality of Korg synthesizers, enabling seamless integration into modern production environments.
Korg emphasizes portability with many of its synthesizers. The compact design of products like the Volca series allows musicians to create music on the go, making them ideal for traveling artists. Each Volca unit houses powerful synthesis technology within a small footprint, ensuring that users don’t sacrifice quality for convenience.
Korg also recognizes the importance of community and education in music production. The company frequently updates its synthesizers with new patches, features, and sound libraries, empowering users to keep their sounds fresh and relevant. Additionally, Korg offers various online resources, tutorials, and forums to support their users in exploring the full potential of their synthesizers.
Overall, Korg synthesizers encapsulate a balance of tradition and innovation. With their rich sound engines, user-friendly interfaces, and extensive connectivity options, they remain a favorite among musicians and producers seeking to push the boundaries of their sound. As technology progresses, Korg continues to set new standards in the world of synthesizers, inspiring creativity and musical exploration.