Programming Manual
Page
Foreword
FX Series Programmable Controllers
FX Series Programmable Controllers
FAX Back Combined Programming Manual J
FX Series Programmable Controllers
Software Warnings
Hardware Warnings
FX Series Programmable Controllers
Contents
STL Programming
Applied Instructions
Rotation And Shift Functions 30 to
External FX Serial Devices Functions 80 to
Execution Times And Instructional
10-1
Viii
FX Series Programmable Controllers
Chapter Contents
Overview
Introduction
What do You Need to Program a PLC?
What is a Programmable Controller?
Current Generation CPU all versions
Special considerations for programming equipment
Manual name Number FX Base Unit Hardware
Assocciated Manuals
Manual name Number FX DU, GOT and DM units
Memo
Basic Program Instructions
FX Series Programmable ControllersBasic Program Instructions
Detailed device information
What is a Program?
Outline of Basic Devices Used in Programming
Example
How to Read Ladder Logic
Program example
Load, Load Inverse
OUT instruction
Out
Timer and Counter Variations
Double Coil Designation
Use of dual coils
Last coil effect
Peripheral limitations
And, And Inverse
ORI
Or, Or Inverse
Single Operation flags M2800 to M3071
Load Pulse, Load Trailing Pulse
LDF ANF OUT
Pulse, And Trailing Pulse
ORF ORB
Or Pulse, Or Trailing Pulse
Sequential processing limitations
Or Block
Batch processing limitations
ANB
Block
MPS, MRD and MPP usage
13 MPS, MRD and MPP
Multiple program examples
MCR
Master Control and Reset
Nested MC program example
Resetting timers and counters
Set and Reset
16.1Basic Timers, Retentive Timers And Counters
Timer, Counter Out & Reset
Retentive timers
High Speed Counters
Bit counters
Availability of devices
Normal 32 bit Counters
Leading and Trailing Pulse
PLF
Usages for INV
Inverse
No Operation
No Operation
Program scan
20 End
Memo
STL Programming
FX Series Programmable ControllersSTL Programming
General note
What is STL, SFC And IEC1131 Part 3?
Look Inside an STL
How STL Operates
Each step is a program
Activating new states
How To Start And End An STL Program
Combined SFC Ladder representation
Embedded STL programs
Returning to Standard Ladder
Initial Steps
Terminating an STL Program
Moving Between STL Steps
Using SET to drive an STL coil
Out is used for distant jumps
Using OUT to drive an STL coil
OUT is used for loops and jumps
Basic Notes On The Behavior Of STL programs
Rules and Techniques For STL programs
T001 K20 K50
Method 2 Special Single Pulse Flags
Single Signal Step Control
Method 1 Using locking devices
Restrictions on using applied instructions
Restrictions Of Some Instructions When Used With STL
Using ‘jump’ operations with STL
STL OUT SET
Using STL To Select The Most Appropriate Program
Limits on the number of branches
Using STL To Activate Multiple Flows Simultaneously
Limits on the number of branches
Instruction Format
General Rules For Successful STL Branching
General Precautions When Using The FX-PCS/AT-EE Software
Simple STL Flow
Programming Examples
SET STL
Identification of normally closed contacts
Selective Branch/ First State Merge Example Program
Points to note
Full STL flow diagram/program
Advanced STL Use
Devices in Detail
FX Series Programmable ControllersDevices in Detail
Device Mnemonic
Configuration details
Inputs
Available devices
Alias O/P
Outputs
Device Mnemonic Y
General Stable State Auxiliary Relays
Auxiliary Relays
Device Mnemonic M
External loads
Battery Backed/ Latched Auxiliary Relays
Special Single Operation Pulse Relays
Special Diagnostic Auxiliary Relays
General Stable State State Relays
State Relays
Device Mnemonic S
PLC FX 1S FX 1N FX 2N
Battery Backed/ Latched State Relays
IST instruction
Assigned states
Monitoring STL programs
STL/SFC programming
Annunciator Flags
Device Mnemonic P
Pointers
Jumping to the end of the program
Device availability
Pointer position
Interrupt Pointers
Additional applied instructions
Nested levels
Input Interrupts
Timer Interrupts
Rules of use
Disabling Individual Interrupts
Driving special auxiliary relays
Disabling high speed counter interrupts
Additional notes
Example device usage N/A
Constant K
Constant H
Device Mnemonic K
Device Mnemonic T
Timers
Timer accuracy
Driving special auxiliary coils
General timer operation
Selectable Timers
Retentive Timers
Using timers in interrupt or ‘CALL’ subroutines
Condition
Internal timer accuracy
Timers Used in Interrupt and ‘CALL’ Subroutines
Timer Accuracy
Device Mnemonic C
Setting ranges for counters
Counters
High speed counters
General/ Latched 16bit UP Counters
Battery backed/latched counters
General/ Latched 32bit Bi-directional Counters
Battery backed/ latched counters
Selecting the counting direction
Further uses None
Basic high speed counter operation
Basic High Speed Counter Operation
Driving high speed counter coils
Availability of High Speed Counters
Input assignment
Counter Speeds
Calculating the maximum combined counting speed on FX1S
Using the SPD instruction
Device specification
Setting range
Direction setting
RST
Device size
11.5 2 Phase Bi-directional Counters C246 to C250
11.6 A/B Phase Counters C252 to C255
Example device usage None
Data Registers
Device Mnemonic D
General Use Registers
Data register updates
Data retention
Special Diagnostic Registers
Using the FX2-40AW/AP
Use of diagnostic registers
Battery Backed/ Latched Registers
Program memory registers
Special caution when using FX1S
Writing to file registers
File Registers
Uses
Externally Adjusted Registers
Available forms
Index Registers
Use of Modifiers with Applied Instruction Parameters
Device Mnemonic V,Z
Misuse of the Modifiers
Using Multiple Index Registers
Modifying a Constant
Bit Devices, Individual and Grouped
Bits, Words, BCD and Hexadecimal
Assigning grouped bit devices
Moving grouped bit devices
Assigning I/O
Interpreting Word Data
Word Devices
FX Series Programmable Controllers
Word Data Summary
Binary Coded Decimal value= Error
Inverted7 Additional1
14.4 Two’s Compliment
Some useful constants
Floating Point And Scientific Notation
Scientific Notation
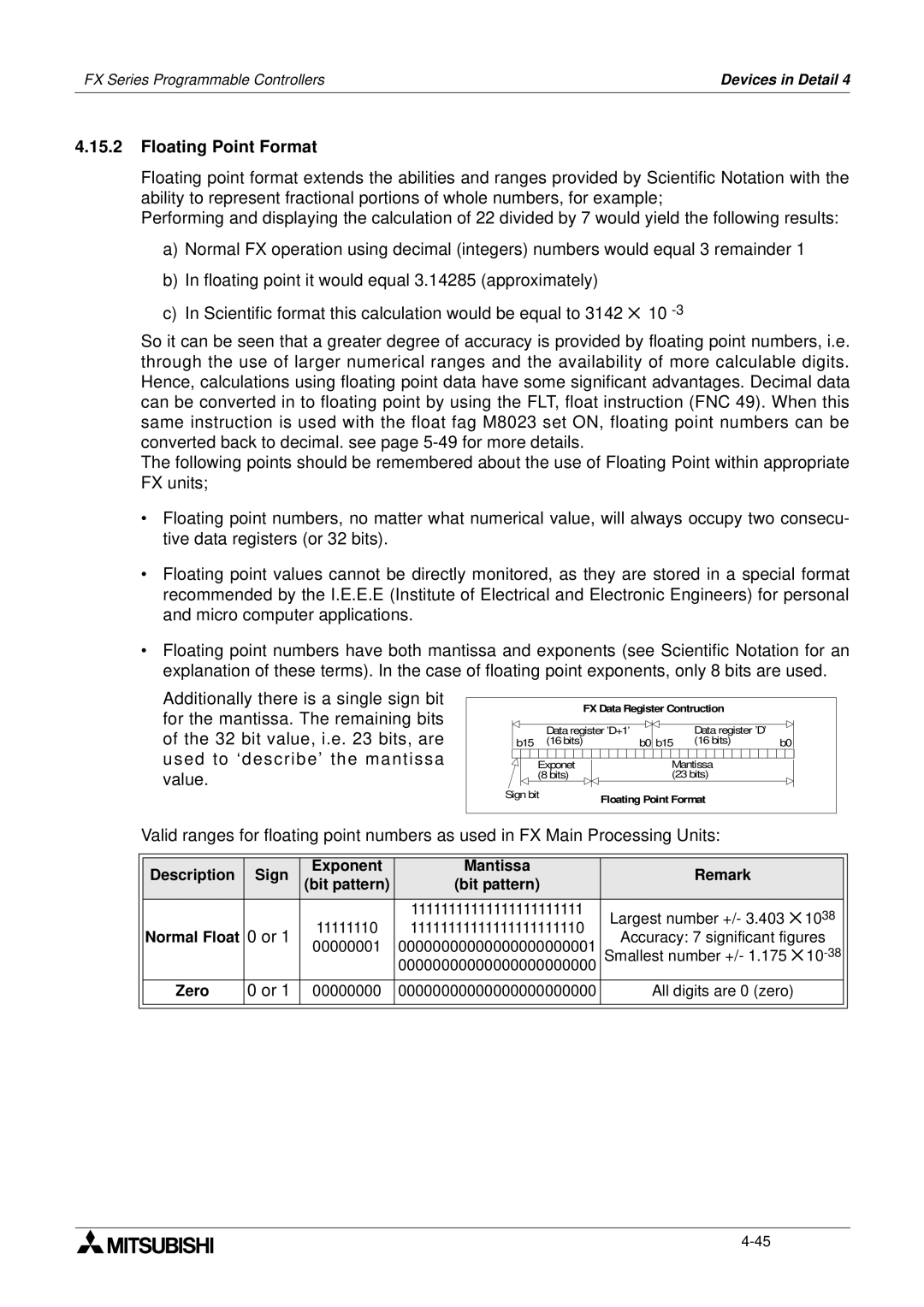
Floating Point Format
FLT