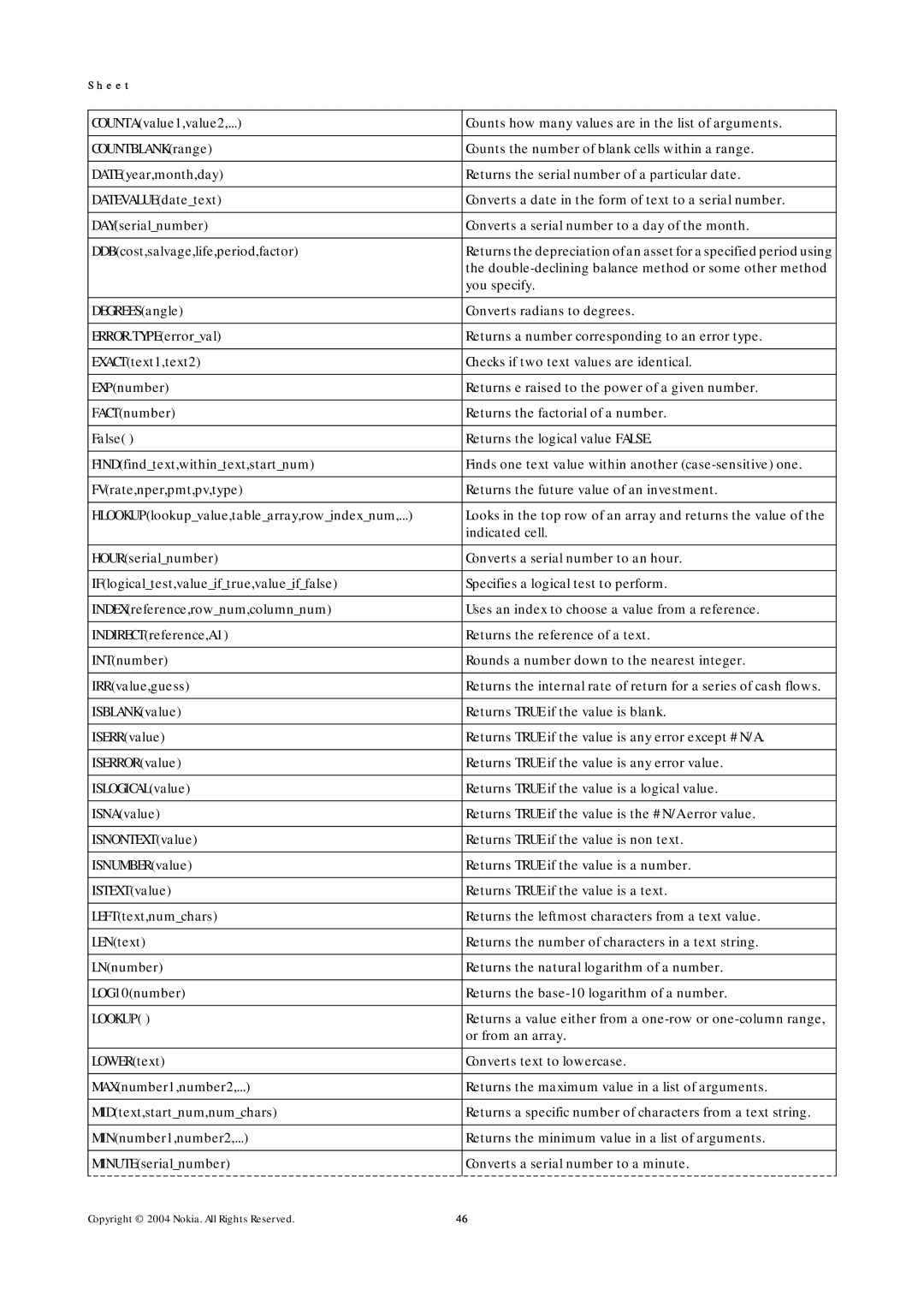
9500 specifications
The Nokia 9500 Communicator, launched in 2004, stands as a landmark device in the evolution of mobile technology, blending the features of a smartphone with the functionality of a handheld computer. It was part of Nokia's Communicator series, which was known for its advanced features, and the 9500 was particularly significant due to its innovative design and robust capabilities.One of the standout features of the Nokia 9500 is its distinctive clamshell design. When closed, it resembles a traditional mobile phone, compact and easy to carry. However, upon opening, the device reveals a full QWERTY keyboard and a large display, offering an exceptional typing experience for those who frequently send emails or create documents on the go. The keyboard is spacious and tactile, making it ideal for productivity tasks.
The 9500 is equipped with the Symbian OS, specifically the Series 80 user interface, which was optimized for the Communicator's unique form factor. Users could multitask efficiently, switching between applications seamlessly, which was a remarkable feature for its time. It supported various productivity applications including calendar, contacts, and word processing, enhancing its appeal to business users.
In terms of connectivity, the Nokia 9500 offers a range of options. It includes support for GPRS, providing users with internet access even while on the move. Wi-Fi capabilities further expanded its utility, allowing for faster data transfer rates and easier access to the internet in hot spots. Bluetooth technology was also included, enabling wireless data sharing with other devices.
The device features a 640x200 pixel display, which was impressive for its time, ensuring that both text and images were clear and easily readable. The Nokia 9500 also came with a camera, which was a novelty for mobile devices in the early 2000s, allowing users to capture images on the go.
Another important aspect of the 9500 is its battery life. It was designed to support extended usage, making it a reliable choice for professionals who needed to stay connected throughout the day. The device also supported expandable memory through a miniSD card slot, providing further flexibility for users to store more data.
In summary, the Nokia 9500 Communicator was a pioneering device that combined the functionalities of a mobile phone and a laptop. With its robust design, keyboard, productivity applications, and connectivity options, it set a foundation for future smartphones, showcasing what mobile computing could achieve long before the era of modern smartphones.