108 Appendix A: Basic call flows |
| Nortel Networks Confidential |
|
|
|
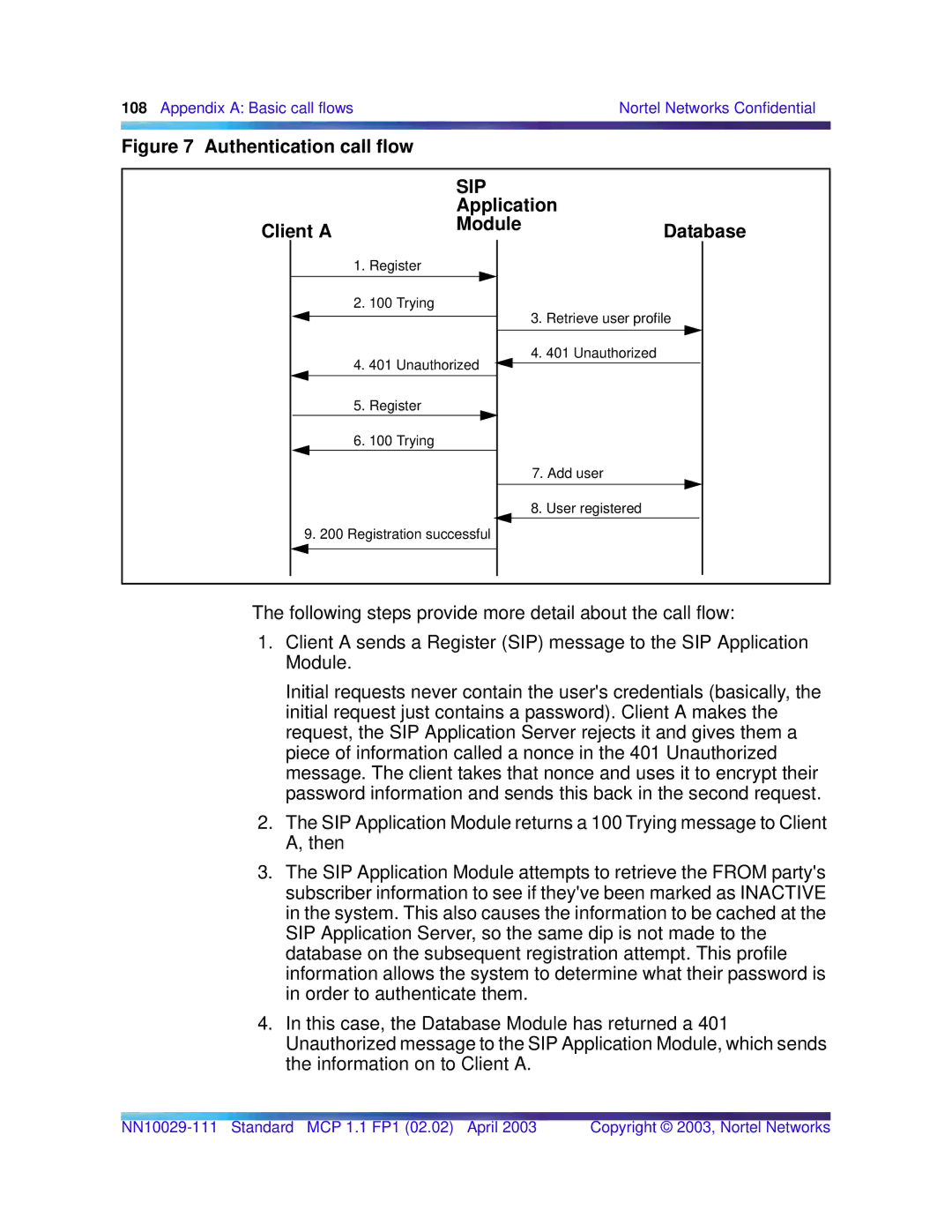
Figure 7 Authentication call flow |
|
|
|
|
|
| SIP |
|
| Application |
|
Client A | Module | Database |
|
1.Register
2.100 Trying
4.401 Unauthorized ![]()
5.Register
6.100 Trying
9.200 Registration successful
3.Retrieve user profile
4.401 Unauthorized
7.Add user
8.User registered
The following steps provide more detail about the call flow:
1.Client A sends a Register (SIP) message to the SIP Application Module.
Initial requests never contain the user's credentials (basically, the initial request just contains a password). Client A makes the request, the SIP Application Server rejects it and gives them a piece of information called a nonce in the 401 Unauthorized message. The client takes that nonce and uses it to encrypt their password information and sends this back in the second request.
2.The SIP Application Module returns a 100 Trying message to Client A, then
3.The SIP Application Module attempts to retrieve the FROM party's subscriber information to see if they've been marked as INACTIVE in the system. This also causes the information to be cached at the SIP Application Server, so the same dip is not made to the database on the subsequent registration attempt. This profile information allows the system to determine what their password is in order to authenticate them.
4.In this case, the Database Module has returned a 401 Unauthorized message to the SIP Application Module, which sends the information on to Client A.
Copyright © 2003, Nortel Networks |