In Figure 14, the repeater unit listens on FA for transmissions from both the base station and the remote. The example shows a
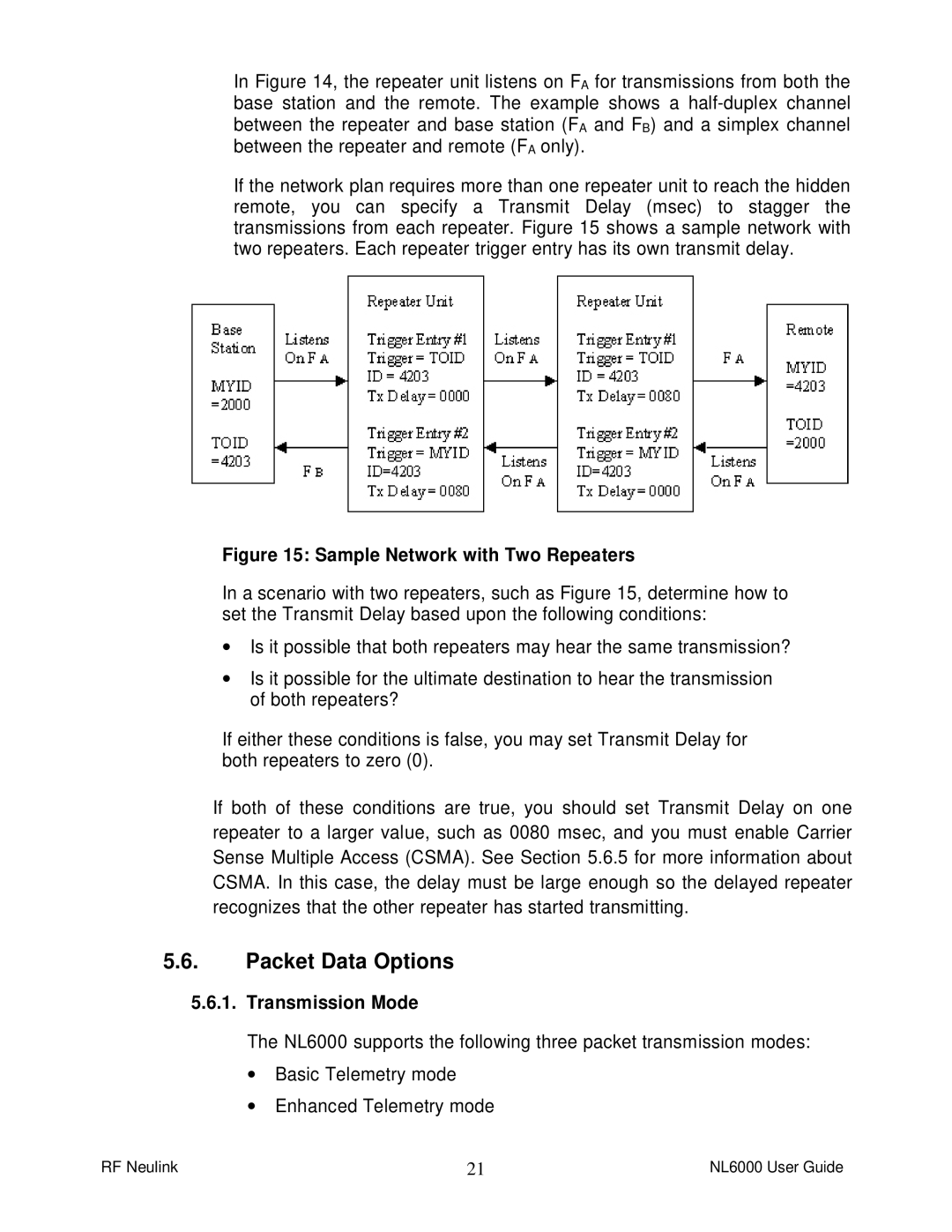
If the network plan requires more than one repeater unit to reach the hidden remote, you can specify a Transmit Delay (msec) to stagger the transmissions from each repeater. Figure 15 shows a sample network with two repeaters. Each repeater trigger entry has its own transmit delay.
Figure 15: Sample Network with Two Repeaters
In a scenario with two repeaters, such as Figure 15, determine how to set the Transmit Delay based upon the following conditions:
∙Is it possible that both repeaters may hear the same transmission?
∙Is it possible for the ultimate destination to hear the transmission of both repeaters?
If either these conditions is false, you may set Transmit Delay for both repeaters to zero (0).
If both of these conditions are true, you should set Transmit Delay on one repeater to a larger value, such as 0080 msec, and you must enable Carrier
Sense Multiple Access (CSMA). See Section 5.6.5 for more information about
CSMA. In this case, the delay must be large enough so the delayed repeater
recognizes that the other repeater has started transmitting.
5.6.Packet Data Options
5.6.1.Transmission Mode
The NL6000 supports the following three packet transmission modes:
∙Basic Telemetry mode
∙Enhanced Telemetry mode
RF Neulink | 21 | NL6000 User Guide |