6. Air Purging
Air and moisture remaining in the refrigerant system have undesirable effects as indicated below. Therefore, they must be purged completely.
●pressure in the system rises
●operating current rises
●cooling (or heating) efficiency drops
●moisture in the air may freeze and block capillary tubing
●water may lead to corrosion of parts in the refrigerant system
■Air Purging with a Vacuum Pump (for Test Run)
(1)Check that each tube (both narrow and wide tubes) between the indoor and outdoor units have been properly connected and all wiring for the test run has been completed. Note that both narrow and wide tube service valves on the outdoor unit are kept closed at this stage.
(2)Using an adjustable wrench or box wrench, remove the valve caps from the service valve on both nar- row and wide tubes.
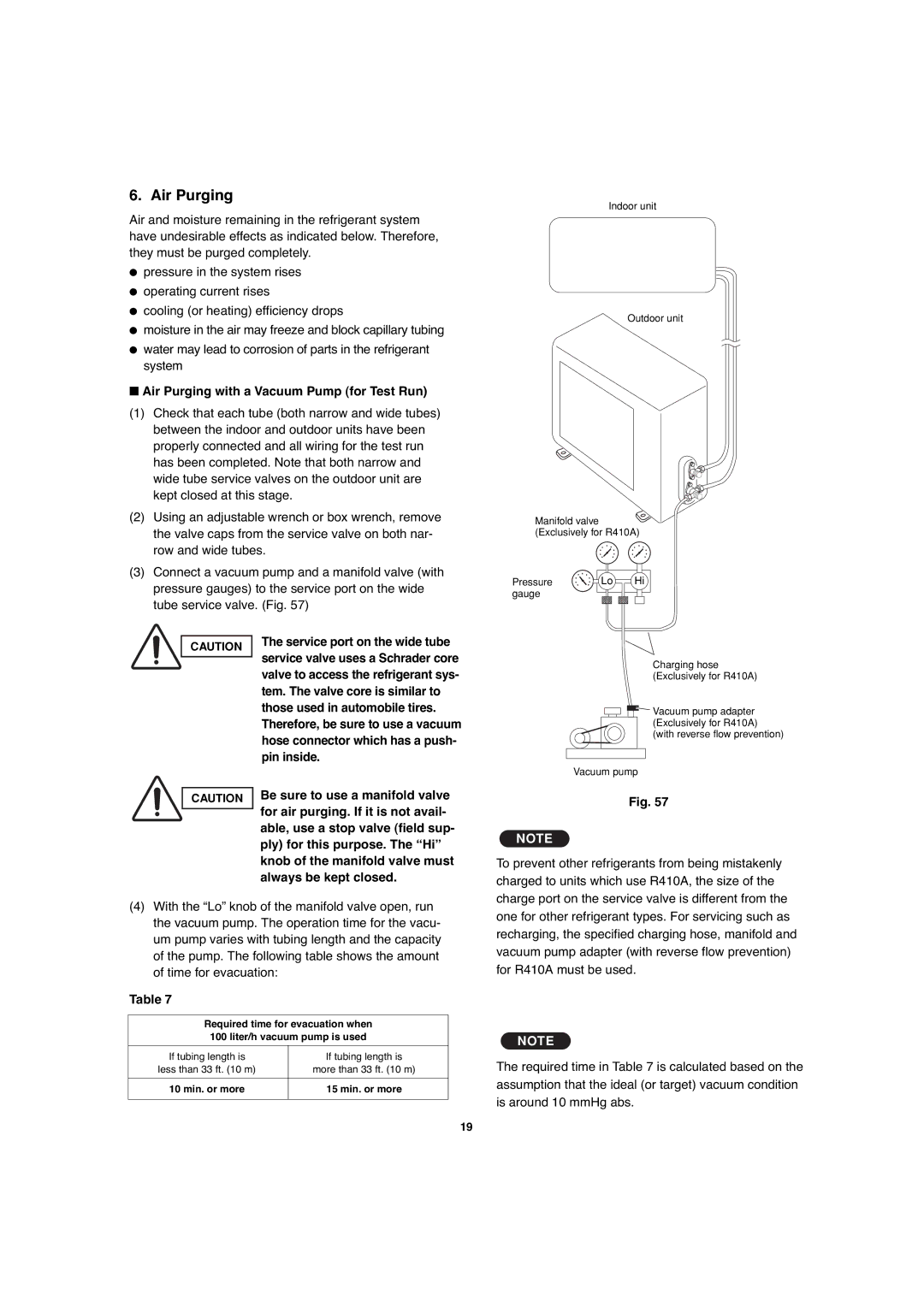
(3)Connect a vacuum pump and a manifold valve (with pressure gauges) to the service port on the wide tube service valve. (Fig. 57)
CAUTION | The service port on the wide tube | |
service valve uses a Schrader core | ||
| ||
| ||
| valve to access the refrigerant sys- | |
| tem. The valve core is similar to | |
| those used in automobile tires. | |
| Therefore, be sure to use a vacuum | |
| hose connector which has a push- | |
| pin inside. |
CAUTION Be sure to use a manifold valve for air purging. If it is not avail-
able, use a stop valve (field sup- ply) for this purpose. The “Hi” knob of the manifold valve must always be kept closed.
(4)With the “Lo” knob of the manifold valve open, run the vacuum pump. The operation time for the vacu- um pump varies with tubing length and the capacity of the pump. The following table shows the amount of time for evacuation:
Table 7
Required time for evacuation when 100 liter/h vacuum pump is used
If tubing length is | If tubing length is |
less than 33 ft. (10 m) | more than 33 ft. (10 m) |
|
|
10 min. or more | 15 min. or more |
|
|
Indoor unit
Outdoor unit
Manifold valve (Exclusively for R410A)
Pressure | Lo | Hi |
gauge |
|
|
Charging hose (Exclusively for R410A)
![]()
![]()
![]() Vacuum pump adapter (Exclusively for R410A) (with reverse flow prevention)
Vacuum pump adapter (Exclusively for R410A) (with reverse flow prevention)
Vacuum pump
Fig. 57
NOTE
To prevent other refrigerants from being mistakenly charged to units which use R410A, the size of the charge port on the service valve is different from the one for other refrigerant types. For servicing such as recharging, the specified charging hose, manifold and vacuum pump adapter (with reverse flow prevention) for R410A must be used.
NOTE
The required time in Table 7 is calculated based on the assumption that the ideal (or target) vacuum condition is around 10 mmHg abs.
19