PN-SS01 PN-SS02 PN-SV01
Contents
Schedule Management
Creating/Editing Schedules
Panel Management and Option
Distributing schedules
Key/Mouse Monitoring
Schedule Reception/Program Display
Monitoring status
Introduction
Precautions on use
Model No Serial No
Notation
How to read this manual
Trademarks
Icons
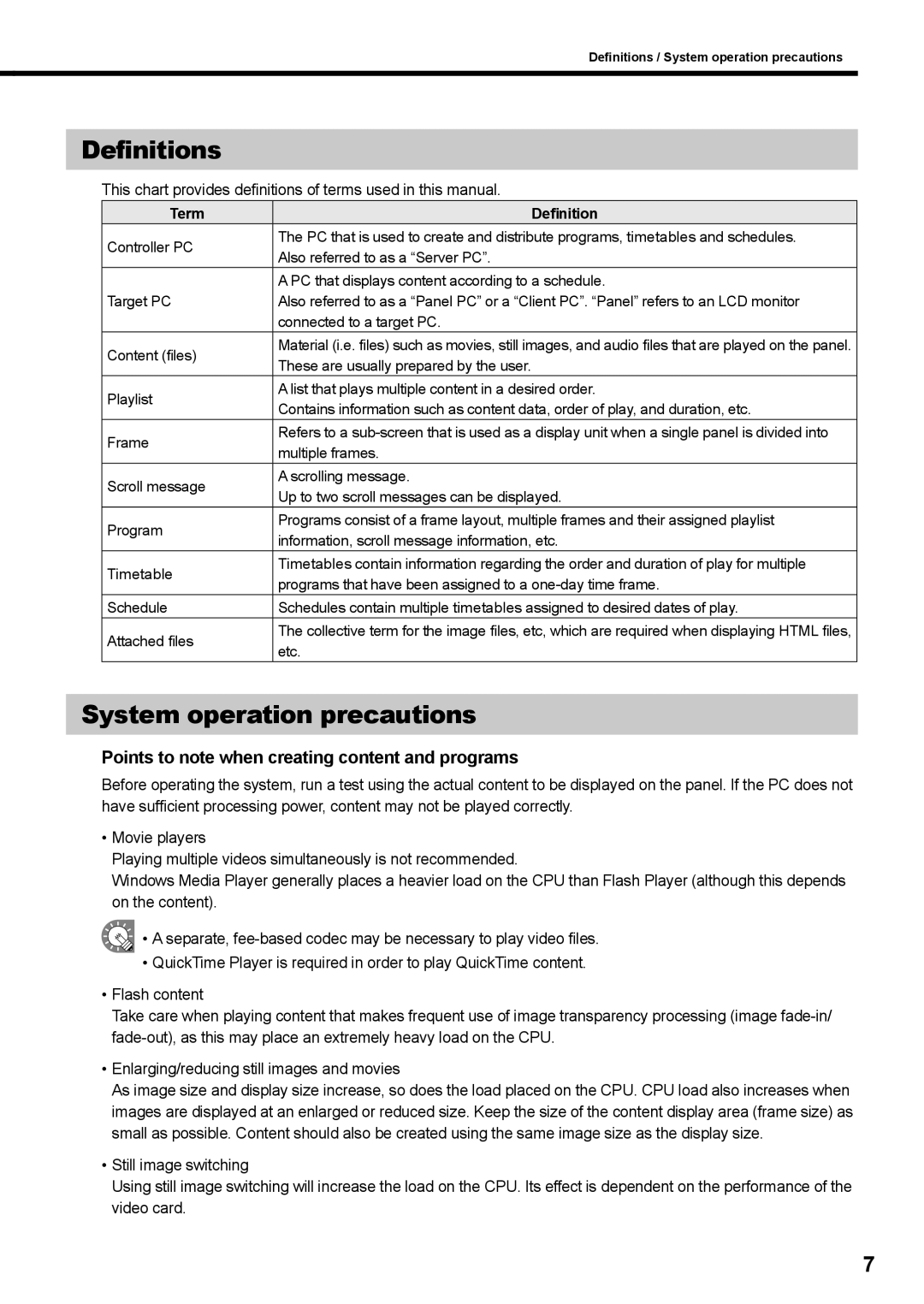
Definitions
System operation precautions
Points to note when creating content and programs
This chart provides defnitions of terms used in this manual
PC internal clock
Backups
Daisy chain configuration
Continuous operation of target PC
Program distribution workflow
Features of Sharp Digital Signage Software
Server Scheduler
Network Version Program Editor
Status Monitoring Tool
FTP Server
Required operating environment
Installing/Launching
Description
Welcome to the Install Shield wizard... window, click Next
Installing Sharp Digital Signage Software
Installing Sharp Digital Signage Software
If using the Sharp Digital Signage Software CD-ROM
Click Next
Installation will start
Click Install
Click Finish
User Accounts dialog box will appear
Setting the environment of the target PC
Auto login settings
Command Prompt window will appear
Screen saver settings
Welcome Center settings Windows Vista only
Select None from the Screen saver list Click OK
Power control
Screen Saver Settings dialog box will appear
Power Options Properties dialog box will appear
Power Options dialog box will appear
Windows Sidebar Gadget settings Windows Vista Only
Return to the Power Options dialog box
IME Toolbar settings
Active desktop settings Windows XP Only
Windows Update settings
Taskbar settings Windows XP/Vista only
System Properties dialog box will appear
Change settings dialog box will appear
Resident application settings
New Inbound Rule Wizard dialog box will appear
Personal firewall settings
Button at
Top right of each window
Select the Remove option button, and click Next
Uninstalling Sharp Digital Signage Software
Click Yes
Uninstallation is now complete
Launcher window
Launching and closing the Launcher window
Launching the Launcher window
Closing the Launcher window
Panel control Fp.78
Timetable creation/editing Fp.60
Schedule creation/editing Fp.70
Schedule distribution Fp.84
Main Program Editor window
Program Creation/Editing
Main Program Editor window
Launching Program Editor
Tabs
Settings window
Menus
Toolbar
File extension Content type Required software
Valid content files
File types that can be used as content are as follows
Content name File type
Set a Screen Top-Left Position
Positioning content Layout
Set the Screen Size
Frame2 Width =
Set Frame Layout
Message1 Width =
Set the Interval for the grid
Using the grid
Using a layout you have created
Display priority order
URL tab
Setting the background/frames
Viewer Path tab
Playlists
Content preview
Icon Menu option Description
Properties of content
Background color when content is not displayed
Parameters for EXE file Displays parameters for EXE fles
Setting the scroll message
Layout
Picture Transition
For more details about Scroll Message Editor, refer to p.40
Title bar
Title bar Menus Toolbar Settings window
Creating scroll message files
Create a message to be displayed in a scroll message
Toolbar buttons icons perform the following actions
Settings window
Menus
Toolbar
Set Background
Set the Message Format
Tag Explanation
Save As dialog box will appear
Set Scrolling
Set the scroll direction and speed of scroll messages
Click Save Scroll Message from the File menu. Or click
Setting audio and music
Save program
Setting the PIP window
If using a PN-655 monitor
Saving a program
Program thumbnails
Save program as
Program Folder
You can also preview a program by clicking
Opening a program
Checking a program
Open Program dialog box will appear
Deleting a program
Preview Program Display Settings
Click Close
Duration may be different from the actual duration
Displaying program properties
Change program names and program colors
Properties of Program dialog box will appear
Export Program dialog box will appear
Importing/exporting a program
Exporting a program
Select the folder to export dialog box will appear
From the File menu, click Import Program
Importing a program
Select the program to import dialog box will appear
This will launch Conditional Content Editor
Conditional Content
Conditional Content Editor
Tabs
Function of each button icon is as follows
Set details for the tab that you selected
Compatible Content File Formats
Creating Conditional Content
Configuring Conditional Contents
Coordinate of top left corner of frame
Conditional Content
Preview Content
Click the icon
Properties of content
Displays parameters for EXE fles
Parameters
Term
Play Condition Setting
Conditional Content and Total Duration
Condition Name
Main Timetable Editor window
Creating/Editing a Timetable
Main Timetable Editor window
Launching Timetable Editor
Timetable
Program/Panel Control list
Displays a timetable
Or alternatively, double-click the program
Creating a timetable
Registering a program in the timetable
Select the program folder containing the program
Registering panel control in a timetable
Command Description
Click the Panel Control tab
Set the Time
Set the Start and End times. Specify times between 0000
Adjusting a timetable
Changing the timetable span
New times will be reflected in the timetable
Save timetable
Adjusting the scale
Saving a timetable
Opening a timetable
From the File menu, click Preview Timetable
Checking a timetable
Deleting a timetable
Changing timetable name and timetable color
Timetable export is now complete
Importing/exporting a timetable
Exporting a timetable
Export Timetable dialog box will appear
From the File menu, click Import Timetable
Importing a timetable
Select the timetable to import dialog box will appear
Main Schedule Editor window
Creating/Editing Schedules
Main Schedule Editor window
Launching Schedule Editor
Calendar
Timetable list
Timetable folder
Edit menu, click Add Timetable to Schedule
Add Timetable to Schedule dialog box will appear
Set a Span
Month
Save schedule as
Saving a schedule
Opening a schedule
Save schedule
Selected schedule will be deleted
Deleting a schedule
Changing schedule name
Delete unnecessary schedules
Schedule export is now complete
Importing/exporting a schedule
Exporting a schedule
Export Schedule dialog box will appear
From the File menu, click Import Schedule
Importing a schedule
Select the schedule to import dialog box will appear
Main Panel Management window
Panel Management and Option
Managing panels
Launching Panel Control Management
Set the options
Adding/editing a panel
Buttons
Click Edit to edit an existing panel
Names must be within 50 characters
Click Add or Cancel
Adding/editing a group
Select the parent group Enter a Group name
Deleting a panel or group
Controlling a panel manually
Registering a license code
Option
Launching Option
Checking version information
Click the FTP Setting tab Set the Default to Add the Panel
Adding default panel settings for panels
Main Schedule Distribution Tool window
Distributing schedules
Main Schedule Distribution Tool window
Launching Schedule Distribution Tool
Select a schedule
Distributing schedules
Distributing via a network
Click Distribute schedule or program to the panel
Set Distribution Options
Select a Distribution Date Time
Button Name Description Relevant
These instructions only apply to the Standalone Version
Distributing to your own PC
Click Distribute schedule or program to the panel
Confrmation dialog box will appear again
Selection of the Drive to Transfer dialog box will appear
Select a program, and click Next
Displaying break-in programs
Distributing via a network and making a break-in display
Selection of the Break-in Program dialog box will appear
Set the Display Time of Break-in Program area
Check the distribution settings, and click Finish
Confrmation dialog box will appear. Proceed to step
This function is only available with the Standalone Version
Distributing to your own PC and making a break-in display
Set a Display Time
Schedule Distribution Tool
Deleting reserved distributions
List of Reserved Distribution/List of Distribution Log
List of Reserved Distribution
List of Distribution Log
Enter a File Name, and click Save
Deleting the entire distribution log
Outputting CSV File of Distribution Log
Distribution log can be output as a CSV fle
Server Scheduler
Schedule Management
Windows Task Manager dialog will appear
Services window will appear
FTP Server
Launching the FTP Server
Client Scheduler menu
Setting
Client Scheduler
Launching Client Scheduler
Hide task bar while showing check box
100
FTP Server tab Sets the FTP Server
Power Control tab
101
Display Area tab
102
103
Exiting Client Scheduler
Set the target PC to Contents direct distribute mode
104
Version information
105
Program Viewer
Remove it from the safe removal icon in the Task Tray
Key/Mouse Monitoring Tool menu
Key/Mouse Monitoring
Key/Mouse Monitoring Tool Window
Launching the Key/Mouse Monitoring Tool window
Operation Set the action of the registered mouse operation
107
Click Detail
Assign for mouse input will appear
About
108
Exit
Main Status Monitoring Tool window
Monitoring status
Main Status Monitoring Tool window
Launching Status Monitoring Tool
Acquisition
110
Panel icon/thumbnail
111
Group tree
Panel list
Acquiring status of selected panels
Acquiring and displaying panel status
112
Target PC can be turned on and off, and restarted
Setting panels for which status will not be obtained
Controlling target PC power
113
Panel property dialog box will appear
Check the settings, and click Close
Displaying detailed information for a panel
114
115
Changing thumbnail size
Small Medium
Set advanced settings for panel status acquisition
Setting the operation environment
116
PN-SS01/SS02/SV01 10D2