PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
2. | Interface |
|
| |
Interface Types |
|
| ||
RS232 interface |
|
| ||
|
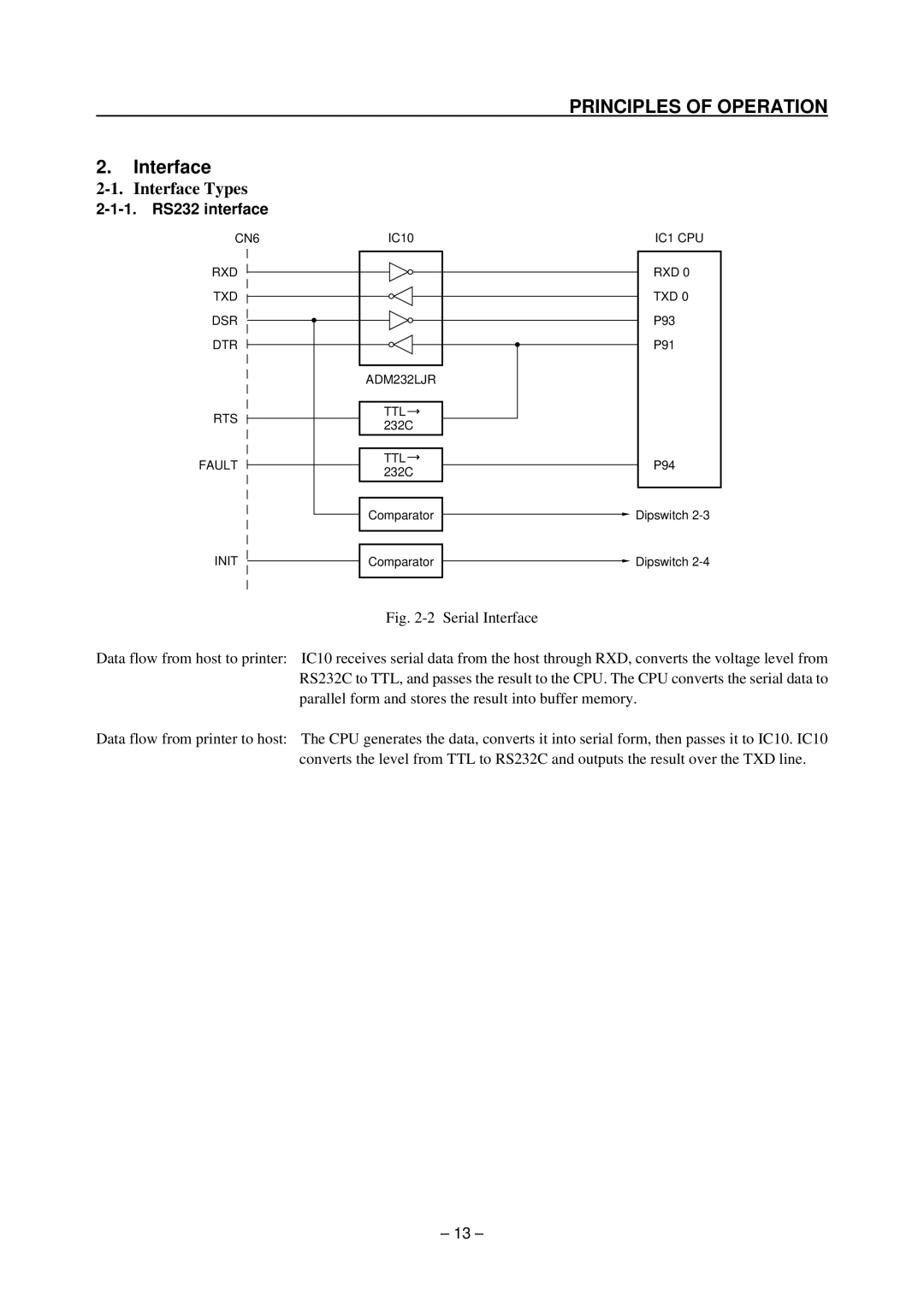
| CN6 | IC10 | IC1 CPU |
|
| RXD |
| RXD 0 |
|
| TXD |
| TXD 0 |
|
| DSR |
| P93 |
|
| DTR |
| P91 |
|
|
| ADM232LJR |
|
|
| RTS | TTL |
|
|
| 232C |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
| FAULT | TTL | P94 |
|
| 232C | ||
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| Comparator | Dipswitch |
INIT
Comparator
![]() Dipswitch
Dipswitch
Fig. 2-2 Serial Interface
Data flow from host to printer: IC10 receives serial data from the host through RXD, converts the voltage level from RS232C to TTL, and passes the result to the CPU. The CPU converts the serial data to parallel form and stores the result into buffer memory.
Data flow from printer to host: The CPU generates the data, converts it into serial form, then passes it to IC10. IC10 converts the level from TTL to RS232C and outputs the result over the TXD line.
– 13 –