HARDWARE INSTALLATION | 6 |
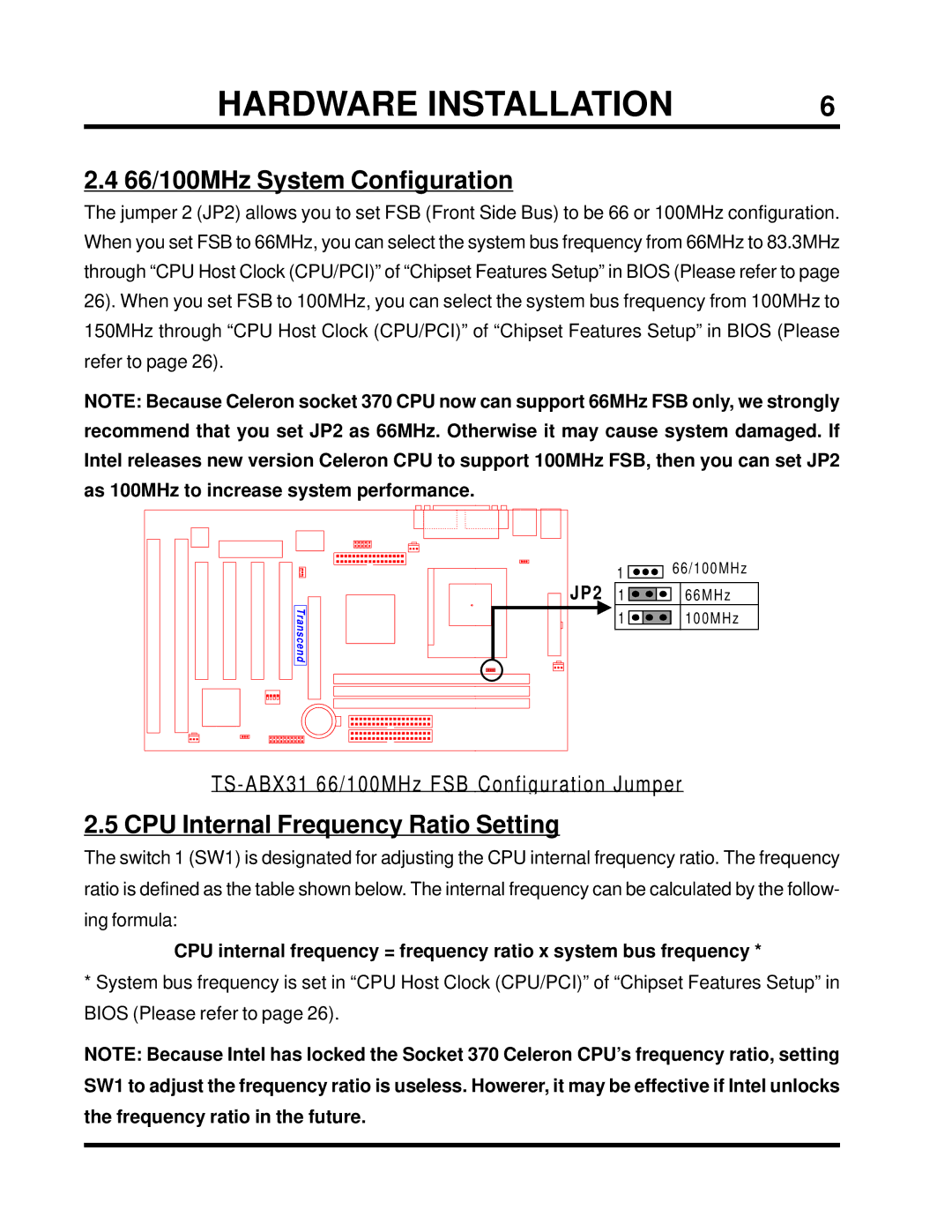
2.4 66/100MHz System Configuration
The jumper 2 (JP2) allows you to set FSB (Front Side Bus) to be 66 or 100MHz configuration. When you set FSB to 66MHz, you can select the system bus frequency from 66MHz to 83.3MHz through “CPU Host Clock (CPU/PCI)” of “Chipset Features Setup” in BIOS (Please refer to page 26). When you set FSB to 100MHz, you can select the system bus frequency from 100MHz to 150MHz through “CPU Host Clock (CPU/PCI)” of “Chipset Features Setup” in BIOS (Please refer to page 26).
NOTE: Because Celeron socket 370 CPU now can support 66MHz FSB only, we strongly recommend that you set JP2 as 66MHz. Otherwise it may cause system damaged. If Intel releases new version Celeron CPU to support 100MHz FSB, then you can set JP2 as 100MHz to increase system performance.
| 1 | 66/100MHz |
JP2 |
| |
1 | 66MHz | |
Tra | 1 | 100MHz |
nscend |
|
|
2.5 CPU Internal Frequency Ratio Setting
The switch 1 (SW1) is designated for adjusting the CPU internal frequency ratio. The frequency ratio is defined as the table shown below. The internal frequency can be calculated by the follow- ing formula:
CPU internal frequency = frequency ratio x system bus frequency *
* System bus frequency is set in “CPU Host Clock (CPU/PCI)” of “Chipset Features Setup” in BIOS (Please refer to page 26).
NOTE: Because Intel has locked the Socket 370 Celeron CPU’s frequency ratio, setting SW1 to adjust the frequency ratio is useless. Howerer, it may be effective if Intel unlocks the frequency ratio in the future.