82 | 5 Configuring IDE Software RAID |
Selecting a RAID Level
To ensure the best performance, you should select the optimal RAID level when you create a system drive. The optimal RAID level for your disk array depends on the following factors:
•Number of drives in the disk array
•Capacity of the drives in the array
•Need for data redundancy
•Disk performance requirements
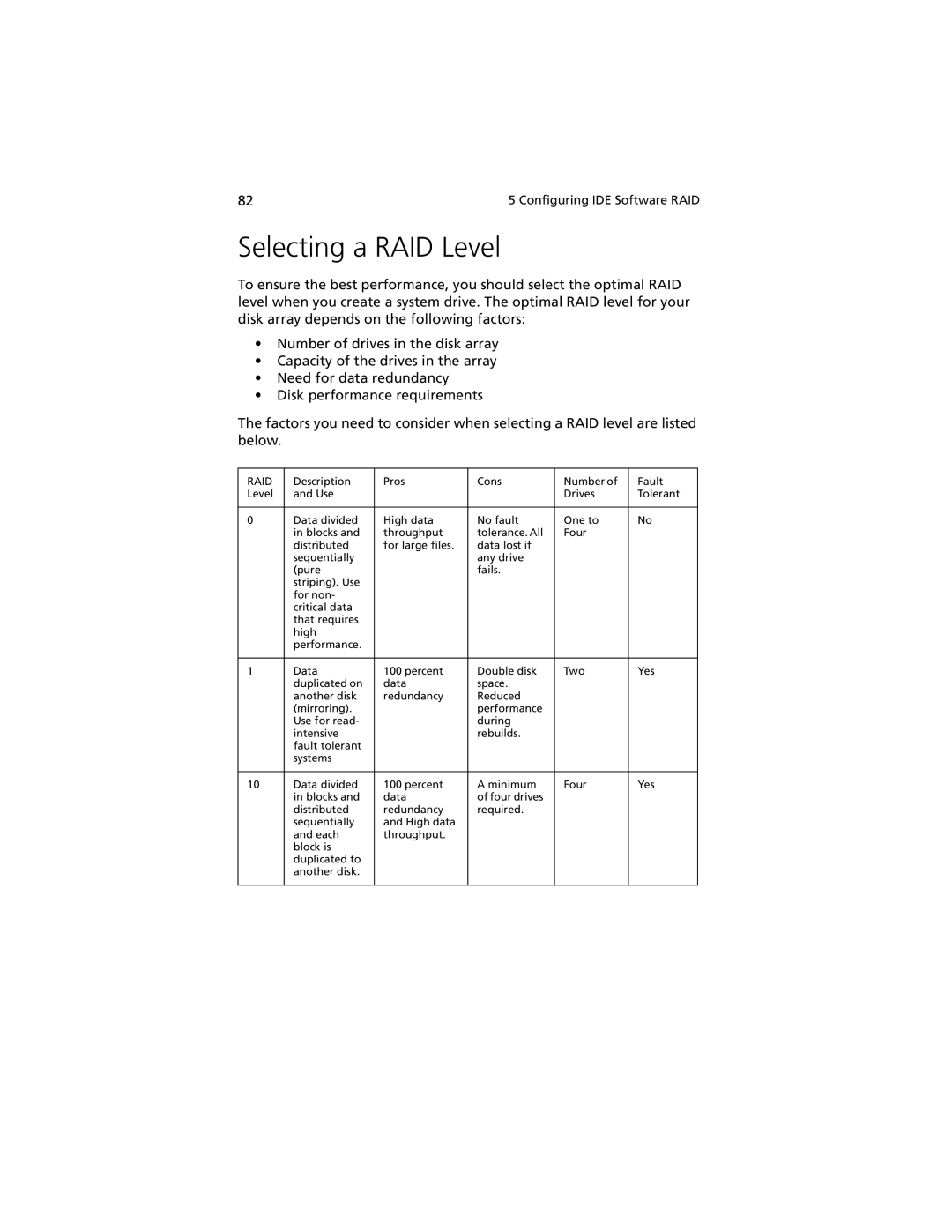
The factors you need to consider when selecting a RAID level are listed below.
RAID | Description | Pros | Cons | Number of | Fault |
Level | and Use |
|
| Drives | Tolerant |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 | Data divided | High data | No fault | One to | No |
| in blocks and | throughput | tolerance. All | Four |
|
| distributed | for large files. | data lost if |
|
|
| sequentially |
| any drive |
|
|
| (pure |
| fails. |
|
|
| striping). Use |
|
|
|
|
| for non- |
|
|
|
|
| critical data |
|
|
|
|
| that requires |
|
|
|
|
| high |
|
|
|
|
| performance. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 | Data | 100 percent | Double disk | Two | Yes |
| duplicated on | data | space. |
|
|
| another disk | redundancy | Reduced |
|
|
| (mirroring). |
| performance |
|
|
| Use for read- |
| during |
|
|
| intensive |
| rebuilds. |
|
|
| fault tolerant |
|
|
|
|
| systems |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 | Data divided | 100 percent | A minimum | Four | Yes |
| in blocks and | data | of four drives |
|
|
| distributed | redundancy | required. |
|
|
| sequentially | and High data |
|
|
|
| and each | throughput. |
|
|
|
| block is |
|
|
|
|
| duplicated to |
|
|
|
|
| another disk. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|