Configuring OSPF | OSPF Overview |
|
|
|
|
Equal Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) Routing
Using information from its continuously updated databases, OSPF calculates the shortest path to a given destination. Shortest path is determined from metric values at each hop along a path. At times, two or more paths to the same destination will have the same metric cost.
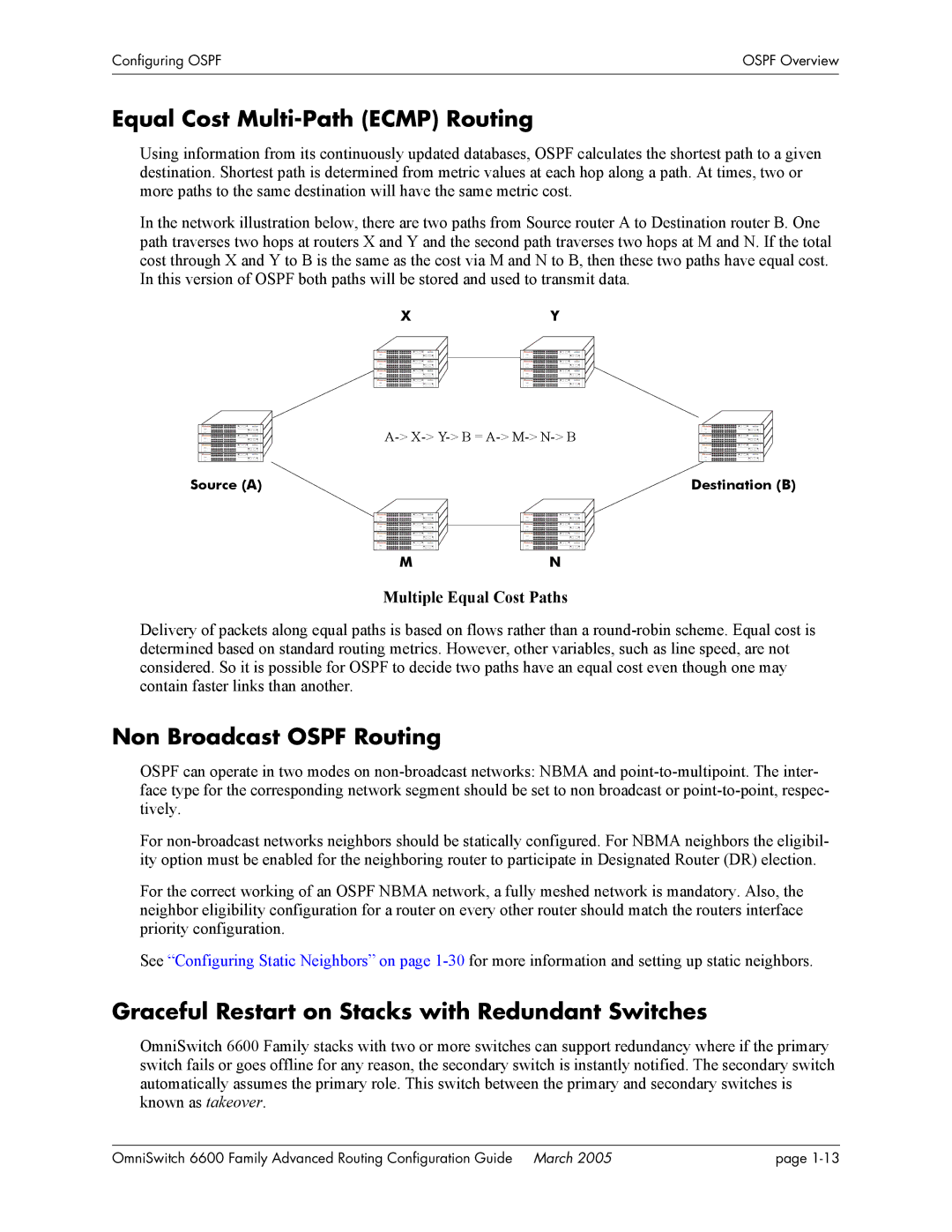
In the network illustration below, there are two paths from Source router A to Destination router B. One path traverses two hops at routers X and Y and the second path traverses two hops at M and N. If the total cost through X and Y to B is the same as the cost via M and N to B, then these two paths have equal cost. In this version of OSPF both paths will be stored and used to transmit data.
XY
Source (A) | Destination (B) |
M |
N |
Multiple Equal Cost Paths
Delivery of packets along equal paths is based on flows rather than a
Non Broadcast OSPF Routing
OSPF can operate in two modes on
For
For the correct working of an OSPF NBMA network, a fully meshed network is mandatory. Also, the neighbor eligibility configuration for a router on every other router should match the routers interface priority configuration.
See “Configuring Static Neighbors” on page
Graceful Restart on Stacks with Redundant Switches
OmniSwitch 6600 Family stacks with two or more switches can support redundancy where if the primary switch fails or goes offline for any reason, the secondary switch is instantly notified. The secondary switch automatically assumes the primary role. This switch between the primary and secondary switches is known as takeover.
OmniSwitch 6600 Family Advanced Routing Configuration Guide March 2005 | page |