EncrypTight User Guide
Table of Contents
Managing EncrypTight Users
Provisioning Appliances
Getting Started with Etems
Managing Appliances 117
Managing IP Networks
Managing Key Management Systems
Managing Network Sets
Creating Vlan ID Ranges for Layer 2 Networks
Policy Design Examples 211
Modifying the Etkms Properties File
Using Enhanced Security Features
Etep Configuration 299
302
Index 343
About This Document
Preface
Contacting Black Box Technical Support
Part I EncrypTight Installation and Maintenance
EncrypTight User Guide
Distributed Key Topologies
EncrypTight Overview
Topology Description
Network topologies
Layer 3 IP topologies
Layer 2 Ethernet topologies
Related topics
EncrypTight Elements
Policy Manager
EncrypTight Element Management System
Key Management System
Single Etkms for multiple sites
Policy Enforcement Point
Shared keys
Point-to-Point Negotiated Topology
Layer 2 Point-to-Point Deployment
Security within EncrypTight
Secure Key Storage within the Etkms
Secure Communications Between Devices
EncrypTight Component Connections
EncrypTight Deployment Planning
Etpm to Etkms Connections
Management Station Connections
Etpm and Etkms on Different Subnetworks
Etpm and Etkms on the Same Subnetwork
Etpm and Etkms in Layer 3 IP Policies
Out-of-band Etkms management in an Ethernet network
External Etkms to Etkms Connections
Connections for Backup ETKMSs
Etkms to Etkms Connections in Ethernet Networks
Connecting Multiple ETKMSs in an IP Network
Etkms to PEP Connections in IP Networks
Etkms to PEP Connections
In-line Etkms to PEP communications in IP networks
Etkms to PEP Connections in Ethernet Networks
IPv6 Address Support
Network Clock Synchronization
IPv6 address representations
Certificate Support
Address Format Address Representation
Network Addressing Options
Network Addressing for IP Networks
Addressing Method Description
Related topics
Before You Start
Installation and Configuration
Software Requirements
Hardware Requirements
EncrypTight management station requirements
Third party management station software
Installing EncrypTight Software for the First Time
EncrypTight Software Installation
To install the EncrypTight software
Firewall Ports
To uninstall EncrypTight
Uninstalling EncrypTight Software
Upgrading to a New Version of EncrypTight
Starting EncrypTight
Exiting EncrypTight
Management Station Configuration
To start Etems
Related topic
Securing the Management Interface
To enable the Microsoft FTP Server service
Enabling the Microsoft FTP Server
Etems communications options
Configuring ETKMSs
Installing ETKMSs
Configuring the Syslog Server
Etkms server connections
About Local ETKMSs
Basic Configuration for Local ETKMSs
Adding a Local Etkms
Starting the Local Etkms Automatically
Launching and Stopping a Local Etkms
To add a local Etkms
To launch a local Etkms
Prior to configuring the batch file do the following
Configuring External ETKMSs
To configure the batch file
Maintaining the start.bat file
To change the admin password
Changing the Admin Password
Logging Into the Etkms
To log into the Etkms
To change the root password
Changing the Root Password
To configure the network connection and hostname
Configure the Network Connection
Static IP Netmask Default Gateway IP address
IPv4
To set the hostname and IPv6 default gateway address
To configure the network interface
To set the default DNS server and configure the hosts file
IPv6
To set up time synchronization
Configure Time and Date Properties
To set the time zone
To restart the NTP daemon
Ntpq -p command output
To check the time source connection status
Field Description
Check the Status of the Hardware Security Module
Starting and Stopping the Etkms Service
To check the status of the Etkms service
Configuring Syslog Reporting on the ETKMSs
To configure syslog reporting on a Etkms
Checking the Status of the Etkms
Policy Enforcement Point Configuration
Passwords to change
Default User Accounts and Passwords
Managing Licenses
Etep Throughput Speeds
To install a license on the Etep
Installing Licenses
To enter EncrypTight licenses
Choose Tools Put License
Upgrading Licenses
Next Steps
Upgrading the EncrypTight License
Upgrading Etep Licenses
Next Steps
Installation and Configuration EncrypTight User Guide
Working with EncrypTight User Accounts
Managing EncrypTight Users
Task Administrator User
Configuring EncrypTight User Authentication
EncrypTight account types and privileges
Login Session Inactivity Timer
Password Authentication and Expiration
Common Access Card Authentication
DoD Login Banner
EncrypTight user name and password conventions
Login preferences default settings
Preference Setting
Parameter User Name Password
To change a password
Changing an EncrypTight User Password
To add an EncrypTight user account
To modify an EncrypTight user account
Example 2 Setting up new EncrypTight and Etep users
Example 1 Default EncrypTight user and default Etep user
How EncrypTight Users Work with Etep Users
Relationship between EncrypTight users and Etep users
Example 3 Adding a new Etep user to EncrypTight
Working with the EncrypTight Workspace
Maintenance Tasks
About the EncrypTight Workspace
To save a workspace to a new location
Saving a Workspace to a New Location
On the File menu, click Save Workspace To
To load an existing workspace
Loading an Existing Workspace
Deleting a Workspace
Moving a Workspace to a New PC
To move a workspace to a new PC
To delete a workspace
Schedule the Upgrade
Installing Software Updates
Prepare Etpm Status and Renew Keys
Upgrade the EncrypTight Software
Verify Etkms Status and Deploy Policies
To deploy policies
Upgrade PEP Software
On the Tools menu, click Upgrade Software
To upgrade software on the PEPs
FTP server site information for appliance software upgrades
Change the PEP Software Version and Check Status
Click Edit Multiple Configurations Software Version
To change the software version of the PEPs
To check the status of the PEPs
Upgrading External ETKMSs
Return Status Refresh and Key Renewal to Original Settings
To stop and remove the current Etkms software
To configure the new Etkms software
To install the new Etkms software
To mount the Cdrom drive
To start the Etkms software
Maintenance Tasks EncrypTight User Guide
Etems
Part II Working with Appliances using
EncrypTight User Guide
Getting Started with Etems
Defining Appliance Configurations
Etems Quick Tour
Interface configuration for a new ET1000A appliance
Pushing Configurations to Appliances
Upgrading Appliance Software
Comparing Configurations
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Policy and Certificate Support
Understanding the Etems Workbench
Editors
Appliance Manager perspective Views
Perspectives
Toolbars
To open a perspective
Etems toolbar
Appliance Manager toolbar
Status Indicators
Certificate Manager toolbar
Status Indicator Description
Appliance status indicators
Understanding Roles
EncrypTight User Types
Modifying Communication Preferences
Function Administrator Ops
Appliance roles for ETEPs
To change communication preferences
General communication preferences
Strict authentication communication preferences
Preference Description
Enable Certificate
Ignore CRL access
CRL File Location
Policy Extensions
Provisioning Basics
Provisioning Appliances
New Appliance editor for the ET1000A To add a new appliance
Adding a New Appliance
Saving appliance configurations
Saving an Appliance Configuration
To push Etems configurations to appliances
On the Tools menu, click Put Configurations
Viewing Appliance Status
Put configuration status
Result Description
Appliances view
To configure automatic status checking
Etems
To apply a filter to the appliances in the Appliances view
Filtering Appliances Based on Address
To reboot appliances
Rebooting Appliances
Appliance User Management
Etep User Roles
Default user names and passwords on the Etep
Configuring the Password Enforcement Policy
Role Default user name Default password
Appliance roles for ETEPs v 1.4 and later
Strong Password Policy Conventions
Default Password Policy Conventions
User Name Conventions
Upgrading Software
Removing ETEPs From Service
Adding Etep Users
Managing Appliance Users
To add a user to the Etep
On the Tools menu, click Appliance User Add User
Default password Strong password Parameter Policy
Password policy values
Deleting Etep Users
Modifying Etep User Credentials
To modify Etep user credentials
On the Tools menu, click Appliance User Modify User
To delete a user from the Etep
Viewing Etep Users
On the Tools menu, click Appliance User Delete User
Customizing the Default Configuration
Working with Default Configurations
To customize the default configuration
On the Edit menu, click Default Configuration
To return the default values to factory settings
Restoring the Etems Default Configurations
On the Edit menu, click Default Configurations
Provisioning Large Numbers of Appliances
Importing Configurations from a CSV File
Creating a Configuration Template
Attribute Description
To import appliance configurations to Etems
Remote and local keywords and attributes
Importing Remote and Local Interface Addresses
Changing Configuration Import Preferences
Checking the Time on New Appliances
Shutting Down Appliances
Shutdown operational codes
To shut down the Etep
Managing Appliances
Editing Configurations
Changing the Address on the Appliance
Changing the Management IP Address
To change the management IP address on the appliance
Change Management IP window Related topics
Changing the Address in Etems
Operation failed message in response to management IP change
Changing the Date and Time
Changing Settings on Multiple Appliances
Changing Settings on a Single Appliance
To edit the configuration of a single appliance
To change the date and time
Deleting Appliances
To update an appliance setting on multiple appliances
Connecting to the Command Line Interface
Connecting Directly to an Appliance
Upgrading Appliance Software
To delete appliances
124 EncrypTight User Guide
To upgrade software
126 EncrypTight User Guide
Canceling an Upgrade
Restoring the Backup File System
What to do if an Upgrade is Interrupted
Checking Upgrade Status
To restore the appliance file system from a backup copy
Part III Using Etpm to Create Distributed Key Policies
130 EncrypTight User Guide
Opening Etpm
Getting Started with Etpm
About the Etpm User Interface
To open Etpm
Etpm perspective
Component Chapter
EncrypTight Components View
Editors
Status indicators
Etpm Status Indicators
Policy View
To edit an element from the policy view
Sorting and Using Drag and Drop
Etpm Toolbar
To enable or disable automatic status checking
Etpm Status Refresh Interval
Etpm toolbar
IP Policies
About Etpm Policies
Ethernet Policies
Policy generation and distribution
Policy Generation and Distribution
Key generation with one Etkms
Key generation with multiple ETKMSs
Creating a Policy An Overview
Network B
Network a
Network Set a
Network Set B
To create a policy
144 EncrypTight User Guide
EncrypTight User Guide 145
146 EncrypTight User Guide
Provisioning PEPs
Managing Policy Enforcement Points
Configuration Description
EncrypTight PEP configuration
Adding a New PEP in Etems
On the Advanced tab, select Enable Sntp Client
On the Features tab, select Enable passing TLS traffic
To add a new PEP using Etpm
Adding a New PEP Using Etpm
Adding Large Numbers of PEPs
To push Etems configurations to PEPs
Pushing the Configuration
To edit a PEP’s configuration
Editing PEPs
Select Edit Multiple Configurations Sntp Client
To change the NTP settings for multiple PEPs
Editing Multiple PEPs
Editing PEPs From Etpm
Changing the IP Address of a PEP
Deleting PEPs
Changing the PEP from Layer 3 to Layer 2 Encryption
To change the IP address of a PEP
To delete PEPs
Etkms connections
Managing Key Management Systems
To add an Etkms
Adding ETKMSs
Deleting ETKMSs
Editing ETKMSs
Etkms entries
To edit an existing Etkms
To delete an existing Etkms
Adding Networks
Managing IP Networks
Network entries
To add a network
Network IP
Address Network Mask
Grouping Networks into Supernets
Advanced Uses for Networks in Policies
Using Non-contiguous Network Masks
IP Address Network Mask
Networks definitions
Deleting Networks
Editing Networks
To edit an existing network
To delete a network
Managing IP Networks 166 EncrypTight User Guide
Network Sets
Managing Network Sets
IP address Mask 40.32.21.0 255.255.255.0
Types of Network Sets
IP address Mask 40.55.11.0 255.255.255.0
IP address Mask
Network set for a collection of networks
To add a Network Set
Adding a Network Set
Network Set fields
System
Key Management
Network Addressing
Mode
Network Set editor
Importing Networks and Network Sets
Networks and network sets import document format in Excel
Deleting a Network Set
Editing a Network Set
To import networks and network sets into Etpm
To edit a Network Set
To delete an existing network set
Managing Network Sets 176 EncrypTight User Guide
Adding a Vlan ID Range
Creating Vlan ID Ranges for Layer 2 Networks
To add a new Vlan ID Range
Lower Vlan ID
Vlan ID range entries
Upper Vlan ID
Deleting a Vlan ID Range
Editing a Vlan ID Range
To edit a Vlan ID range
To delete an existing Vlan ID range
180 EncrypTight User Guide
Policy Concepts
Creating Distributed Key Policies
Schedule for Renewing Keys and Refreshing Policy Lifetime
Policy Priority
Encapsulation
Policy Types and Encryption Methods
Layer 2 Ethernet payload encryption
Aria Encryption
Encryption and Authentication Algorithms
To use Aria in an encryption policy, do the following
Using Encrypt All Policies with Exceptions
Addressing Mode
Key Generation and ETKMSs
Encrypt all policy with exceptions
Policy Size and Etep Operational Limits
Policy Policy Type Priority Action Protocol Covered
Minimizing Policy Size
To add a new Layer 2 mesh policy
Adding Layer 2 Ethernet Policies
Layer 2 Mesh policy entries
Layer 2 Mesh policy editor
Adding a Hub and Spoke Policy
Adding Layer 3 IP Policies
Hub and spoke policy entries
To add a new hub and spoke policy
Addressing
IPSec
Minimize Policy
Size
Hub and spoke policy editor
To add a new mesh policy
Adding a Mesh Policy
Mesh policy entries
Specifies a method for reducing the policy size
Mesh policy editor
Multicast network example
Adding a Multicast Policy
Multicast policy entries
To add a multicast policy
Network
Multicast
Multicast policy editor
To add a point-to-point policy
Adding a Point-to-point Policy
Point-to-point policy entries
Network Set
Point a
Point a Ports
Point B
Point-to-point policy editor
Adding Layer 4 Policies
Verifying Policy Rules Before Deployment
Policy Deployment
To create a new Layer 4 policy
To enable or disable the deployment warning
Setting Deployment Confirmation Preferences
Deploying Policies
To verify policies
Deleting Policies
Editing a Policy
To edit an existing policy
Editing policies
To delete all policies
To delete an existing policy
Select Tools Clear Policies
Basic Layer 2 Point-to-Point Policy Example
Policy Design Examples
Setting PEP
Layer 2 Ethernet Policy Using Vlan IDs
Point-to-point Layer 2 encryption policy
Policy 3 Discard All Other
Policy 2 Partner and Partner Portal Server
Encrypt Traffic Between Regional Centers
Complex Layer 3 Policy Example
Network sets for mesh policy
Encrypt Traffic Between Regional Centers and Branches
Encrypt all mesh policy
Region a hub and spoke policy
Network sets for the hub and spoke policies
Region C hub and spoke policy
Region B hub and spoke policy
Region D hub and spoke policy
Field
Pass protocol 88 in the clear mesh policy
Passing Routing Protocols
EncrypTight User Guide 219
Policy Design Examples 220 EncrypTight User Guide
Part IV Troubleshooting
222 EncrypTight User Guide
Possible Problems and Solutions
Etems Troubleshooting
Config to Appliance
Symptom Explanation and possible solutions
Appliance Unreachable
Preferences
Disable-trusted-hosts CLI command
Appliance Configuration
Appliance Tools Reboot
Pushing Configurations
Compare Config to Appliance . Do one of the following
About upgrades show system-log and show upgrade Status
Software Upgrades
Pinging the Management Port
To ping the management port
Retrieving Appliance Log Files
Tools preferences To change the default ping tool
On the Tools menu, click Retrieve Appliance Logs
To retrieve log files from an appliance
FTP server site information for log retrieval
Viewing Statistics
Viewing Diagnostic Data
Statistic Description
Etep Statistics
Exporting SAD and SPD Files
Viewing Port and Discard Status
To access the appliance CLI
CLI Diagnostic Commands
Viewing the Application Log from within EncrypTight
Working with the Application Log
To view the log information
Sending Application Log Events to a Syslog Server
Setting Log Filters
Exporting the Application Log
Log File Actions
Other Application Log Actions
Icon Description
Learning About Problems
Etpm and Etkms Troubleshooting
Monitoring Status
Etpm status problems and solutions
Symptoms and Solutions
Etep PEPs, see the EncrypTight User Guide
Policy Errors
Renew Key Errors
Status Errors
Etpm Log Files
Viewing Log Files
Etkms Log Files
Linux Commands
Etkms Troubleshooting Tools
Command Description
Etkms Server Operation
Resetting the Admin Password
PEP Troubleshooting Tools
Optimizing Time Synchronization
Shutting Down or Restarting an External Etkms
Statistics
To disable the Sntp client on multiple PEPs
Etep PEP Policy and Key Information
To view statistics
Replacing Licensed ETEPs
Troubleshooting Policies
Checking Traffic and Encryption Statistics
To export SAD or SPD files from Etep PEPs
Placing PEPs in Bypass Mode
Solving Policy Problems
Viewing Policies on a PEP
Expired Policies
Allowing Local Site Exceptions to Distributed Key Policies
Cannot Add a Network Set to a Policy
Solving Network Connectivity Problems
Modifying EncrypTight Timing Parameters
Certificate Implementation Errors
Cannot Communicate with PEP
Invalid Certificate Error
Etkms Boot Error
Invalid Parameter in Function Call
Enter strict-client-authentication disable
To disable strict authentication on ETEPs
Etpm and Etkms Troubleshooting 252 EncrypTight User Guide
Part V Reference
254 EncrypTight User Guide
About the Etkms Properties File
Modifying the Etkms Properties File
Digital Certificate Configuration
Hardware Security Module Configuration
Logging Setup
Peer Etkms and Etpm Communications Timing
Base Directory for Storing Operational State Data
PEP Communications Timing
Policy Refresh Timing
PEP Communications Timing
Page
About Enhanced Security Features
Using Enhanced Security Features
About Strict Authentication
How to Reference
Prerequisites for Using Certificates with EncrypTight
Prerequisites
Order of Operations
Certificate Information
Setting Description
Distinguished name information
Usage, you type this string as follows
Using Certificates in an EncrypTight System
Changing the EncrypTight Keystore Password
Changing the Keystore Password
Changing the Etkms Keystore Password
To change the EncrypTight keystore password
Changing the Keystore Password on a Etkms
Changing the Password Used in the Etkms Properties File
Changing the Keystore Password on a Etkms with an HSM
To change the password listed in the Etkms properties file
Restart the Etkms Service To start the Etkms service
To configure the certificate policies extension for ETEPs
Configuring the Certificate Policies Extension
Click Enable Policy Extensions
Click Enable Certificate Policy Extensions
To configure certificate policy extensions for ETKMSs
Etkms Certificate Policies Entries
Parameter Description
EncrypTight User Guide 271
Generating a Key Pair
Working with Certificates for EncrypTight and the ETKMSs
Requesting a Certificate
Keytool genkeypair Command
To generate a key pair
To create the certificate request
Importing a CA Certificate
To install a CA certificate
Importing a CA Certificate Reply
Keytool Parameters for Importing a CA Certificate
Working with Certificates and an HSM
Configuring the HSM for Keytool
Exporting a Certificate
Generating a Key Pair for use with the HSM
Importing CA Certificates into the HSM
Generating a Certificate Signing Request for the HSM
Working with Certificates for the ETEPs
Importing Signed Certificates into the HSM
To start the Certificate Manager do one of the following
Understanding the Certificate Manager Perspective
Working with External Certificates
Certificate Manager Workflow
Obtaining External Certificates
To install an external certificate
Installing an External Certificate
To obtain a CA certificate from a CA
Requesting a Certificate
Working with Certificate Requests
282 EncrypTight User Guide
Viewing a Pending Certificate Request
Installing a Signed Certificate
Certificate usage
To view a pending certificate signing request
Setting Certificate Request Preferences
Canceling a Pending Certificate Request
To cancel a pending certificate request
To set certificate request preferences
Certificate request preference fields
Managing Installed Certificates
Viewing a Certificate
To export an installed certificate
Exporting a Certificate
Validating Certificates
Validating Certificates Using CRLs
Deleting a Certificate
To delete an external certificate
Configuring CRL Usage on ETEPs
Configuring CRL Usage in EncrypTight and the ETKMSs
To use CRLs with the EncrypTight software
To use CRLs with the Etkms
To install a CRL on the Etep
Validating Certificates Using Ocsp
Handling Revocation Check Failures
To view CRLs
Click Enable Online Certificate Status Protocol Ocsp
To set up Ocsp in EncrypTight
EncrypTight Ocsp Options
Options Description
To set up Ocsp on the ETEPs
To set up Ocsp in the Etkms
Click Enable Ocsp
Ocsp Settings
To enable strict authentication in the EncrypTight software
Enabling and Disabling Strict Authentication
To enable strict authentication on the Etkms
To enable strict authentication on PEPs
Clear the Enable Strict Client Authentication box
To disable strict authentication
To disable strict authentication from the command line
Removing Certificates
To remove certificates
Using a Common Access Card
Select Tools Clear Certificates
Enabling Common Access Card Authentication
Configuring User Accounts for Use With Common Access Cards
To add common names to the Etkms
Click XML-RPC Certificate Authentication
To enable CAC Authentication on the Etep
To enable CAC Authentication on the Etkms
To enable CAC Authentication in EncrypTight
Handling Common Name Lookup Failures
To specify how to handle common name failures
Using Enhanced Security Features 298 EncrypTight User Guide
Etep Configuration
Product Family and Software Version
Identifying an Appliance
Appliance Name
To configure appliance interfaces
Interface Configuration
Throughput Speed
Management Port Addressing
ET0100A interfaces configuration Related topics
IPv4 management port addressing
IPv4 Addressing
IPv6 management port addressing
IPv6 Addressing
Link speeds on the management port
Auto-negotiation All Ports
Transparent Mode
Remote and Local Port Settings
Link speeds on the local and remote ports
Policy Type Mode of operation
When to use transparent mode
Local and Remote Port IP Addresses
Default Gateway
Transmitter Enable
IP Address and Subnet Mask
Dhcp Relay IP Address
Transmitter Enable settings on the Etep
Ignore DF Bit settings
Reassembly Mode
Reassembly mode settings
Ignore DF Bit
Trusted host list
Trusted Hosts
To add a trusted host
Inbound trusted host protocols used by EncrypTight
Protocol
Outbound host Appliance Editor Tab
System Information
Snmp Configuration
Snmp system information
Community Strings
To define a community name
Under Community Strings, click Add
Traps reported on the Etep
Traps
Trap Description
SNMPv2 Trap Hosts
To configure a trap host
SNMPv3
SNMPv3 Configuration Related topics
Retrieving and Exporting Engine IDs
Generating the Engine ID
To retrieve engine IDs
Viewing SNMPv3 Engine IDs Related topics
Configuring the SNMPv3 Trap Host Users
SNMPv3 trap host users
SNMPv3 Trap Host configuration To configure a trap host user
Etep Logging tab
Logging Configuration
Log facilities
Log Event Settings
Facility Description
Log priorities
Defining Syslog Servers
To define a syslog server
Under Syslog Servers, click Add
Log file sizes
Log File Management
Log name File size
Internals logs
Log files extracted from the Etep Related topics
Advanced Configuration
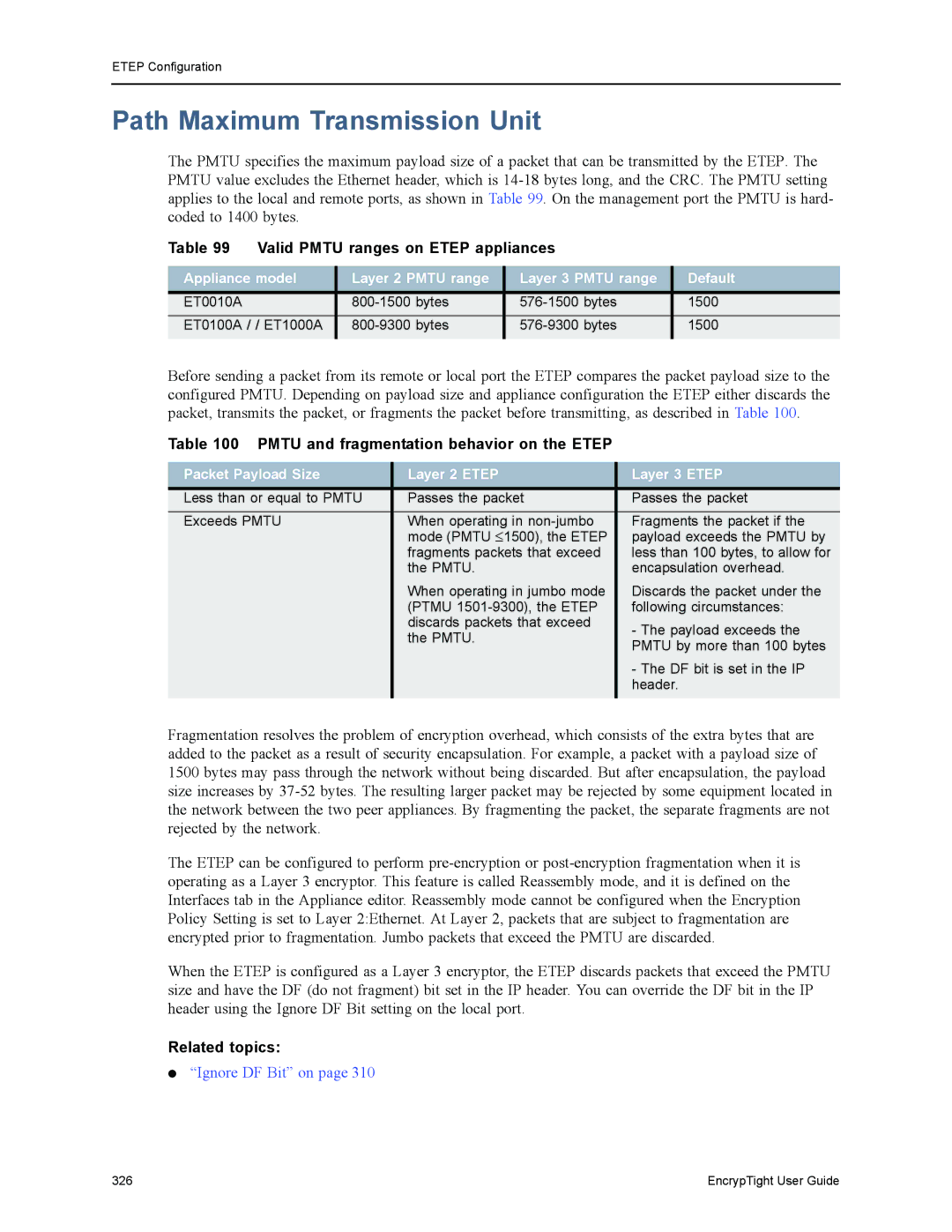
Valid Pmtu ranges on Etep appliances
Path Maximum Transmission Unit
Pmtu and fragmentation behavior on the Etep
Packet Payload Size Layer 2 Etep Layer 3 Etep
Password Strength Policy
CLI Inactivity Timer
Non IP traffic handling configuration
Non IP Traffic Handling
XML-RPC Certificate Authentication
Sntp Client Settings
SSH Access to the Etep
To configure the NTP client
IKE Vlan Tags
Ocsp Settings
Features Configuration
Certificate Policy Extensions
IKE Vlan Tags
Enabling Fips Mode
Fips Mode
Fips approved encryption and authentication algorithms
Encryption algorithms Authentication algorithms
Disabling Fips
Policy Type Action upon entering Fips mode
Verifying Fips Status on the Etep
Operational Notes
EncrypTight settings
EncrypTight Settings
Setting Definition
Encryption policy settings
Encryption Policy Settings
Working with Policies
Creating Layer 2 Point-to-Point Policies
Using EncrypTight Distributed Key Policies
To launch Etpm from Etems
Etep Policy tab
Using Group IDs
Using Preshared Keys for IKE Authentication
Selecting a Role
How the Etep Encrypts and Authenticates Traffic
Selecting the Traffic Handling Mode
IKE Phase 2 Parameters
Parameter Value
Interfaces defaults
Factory Defaults
Interfaces Default Setting
Interfaces
Snmp defaults
Trusted hosts defaults
Trusted Hosts
Policy
Logging
Advanced
Hard-coded Settings
Features
Features defaults
Features Default Setting
Numerics
Index
Index
EncrypTight User Guide 345
Etpm
See also HSM Https TLS
348 EncrypTight User Guide
EncrypTight User Guide 349
350 EncrypTight User Guide
See also TLS trap configuration
352 EncrypTight User Guide
Black Box Tech Support FREE! Live /7