Black Box LR11xx Series Router Configurations Guide
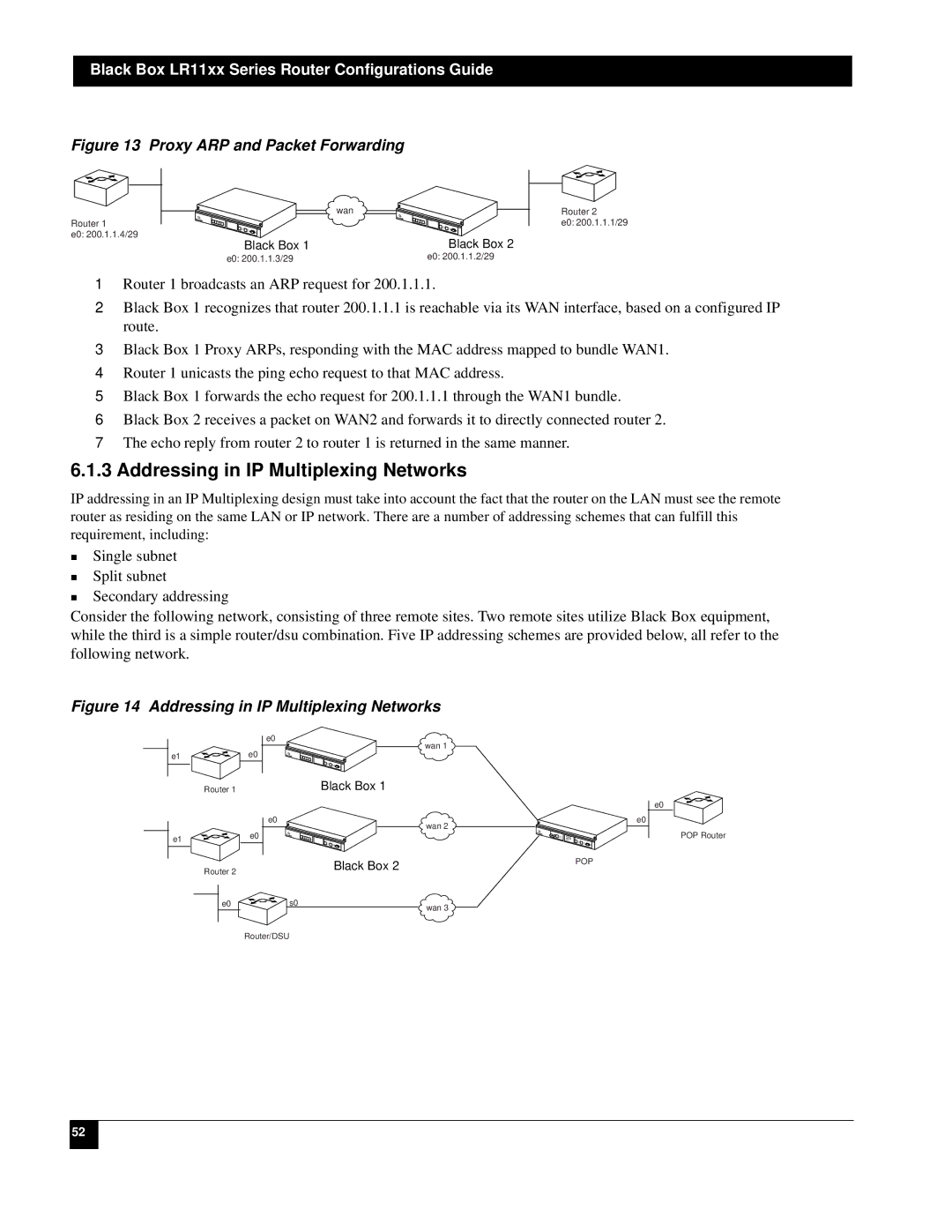
Figure 13 Proxy ARP and Packet Forwarding
Router 1
e0: 200.1.1.4/29
| wan |
Black Box 1 | Black Box 2 |
e0: 200.1.1.3/29 | e0: 200.1.1.2/29 |
Router 2
e0: 200.1.1.1/29
1Router 1 broadcasts an ARP request for 200.1.1.1.
2Black Box 1 recognizes that router 200.1.1.1 is reachable via its WAN interface, based on a configured IP route.
3Black Box 1 Proxy ARPs, responding with the MAC address mapped to bundle WAN1.
4Router 1 unicasts the ping echo request to that MAC address.
5Black Box 1 forwards the echo request for 200.1.1.1 through the WAN1 bundle.
6Black Box 2 receives a packet on WAN2 and forwards it to directly connected router 2.
7The echo reply from router 2 to router 1 is returned in the same manner.
6.1.3 Addressing in IP Multiplexing Networks
IP addressing in an IP Multiplexing design must take into account the fact that the router on the LAN must see the remote router as residing on the same LAN or IP network. There are a number of addressing schemes that can fulfill this requirement, including:
Single subnet
Split subnet
Secondary addressing
Consider the following network, consisting of three remote sites. Two remote sites utilize Black Box equipment, while the third is a simple router/dsu combination. Five IP addressing schemes are provided below, all refer to the following network.
Figure 14 Addressing in IP Multiplexing Networks
| e0 |
|
| wan 1 |
| e0 |
|
| |
e1 |
|
|
| |
| Router 1 |
| Black Box 1 |
|
| e0 |
|
| e0 |
|
|
|
| wan 2 |
e1 | e0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| Black Box 2 | POP |
| Router 2 |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
| e0 | s0 |
| wan 3 |
|
|
|
|
e0
POP Router
Router/DSU
52