Identifying Port Adapter Slot and
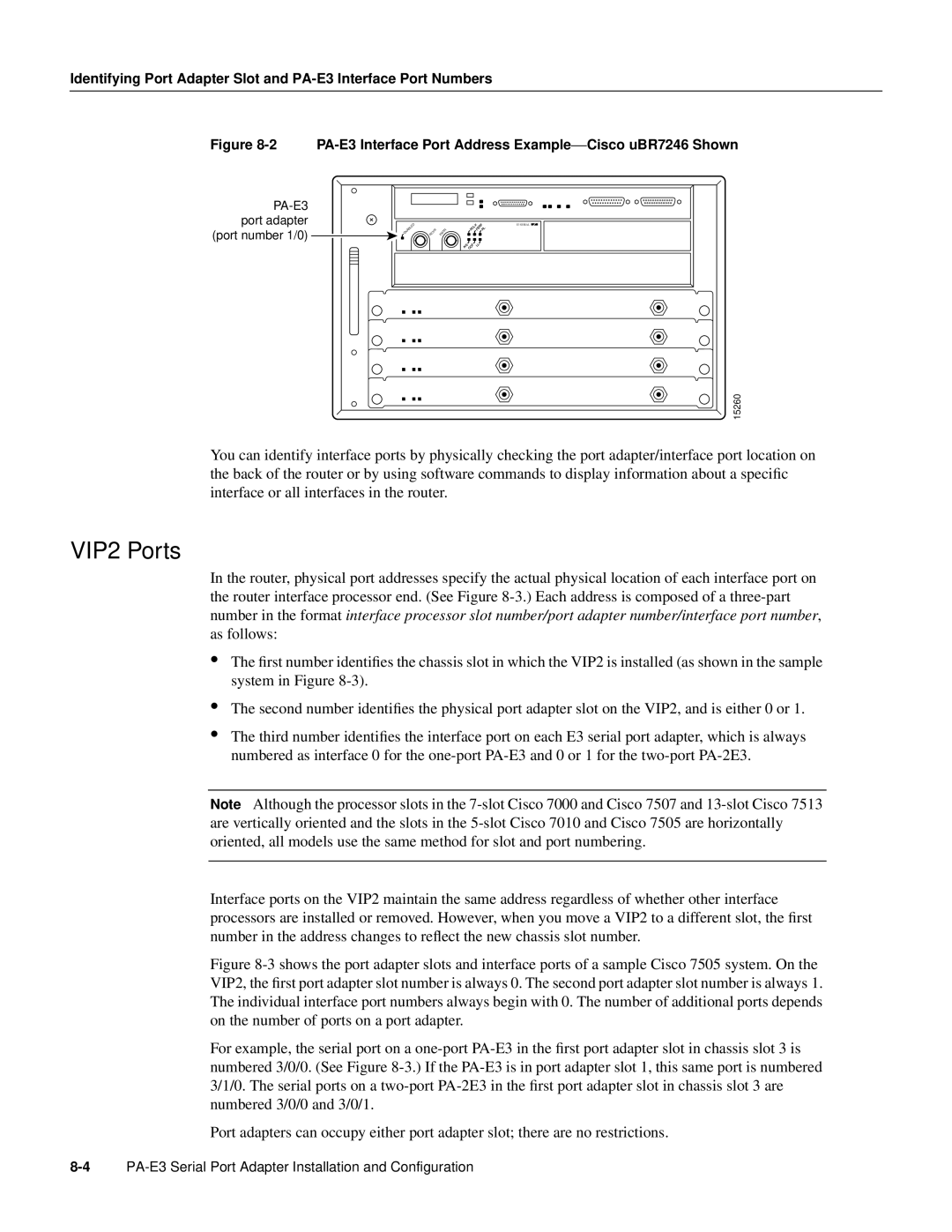
Figure 8-2 PA-E3 Interface Port Address Example— Cisco uBR7246 Shown
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
port adapter | ENABLED |
|
| K | F | E3 SERIAL | |
(port number 1/0) | RCVR XMTR | R | CL | FER RL |
| ||
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| IS | F | LL |
|
|
|
|
| A OO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 15260 |
You can identify interface ports by physically checking the port adapter/interface port location on the back of the router or by using software commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
VIP2 Ports
In the router, physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router interface processor end. (See Figure
•The first number identifies the chassis slot in which the VIP2 is installed (as shown in the sample system in Figure
•The second number identifies the physical port adapter slot on the VIP2, and is either 0 or 1.
•The third number identifies the interface port on each E3 serial port adapter, which is always numbered as interface 0 for the
Note Although the processor slots in the
Interface ports on the VIP2 maintain the same address regardless of whether other interface processors are installed or removed. However, when you move a VIP2 to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new chassis slot number.