Troubleshooting the WLAN
Troubleshooting
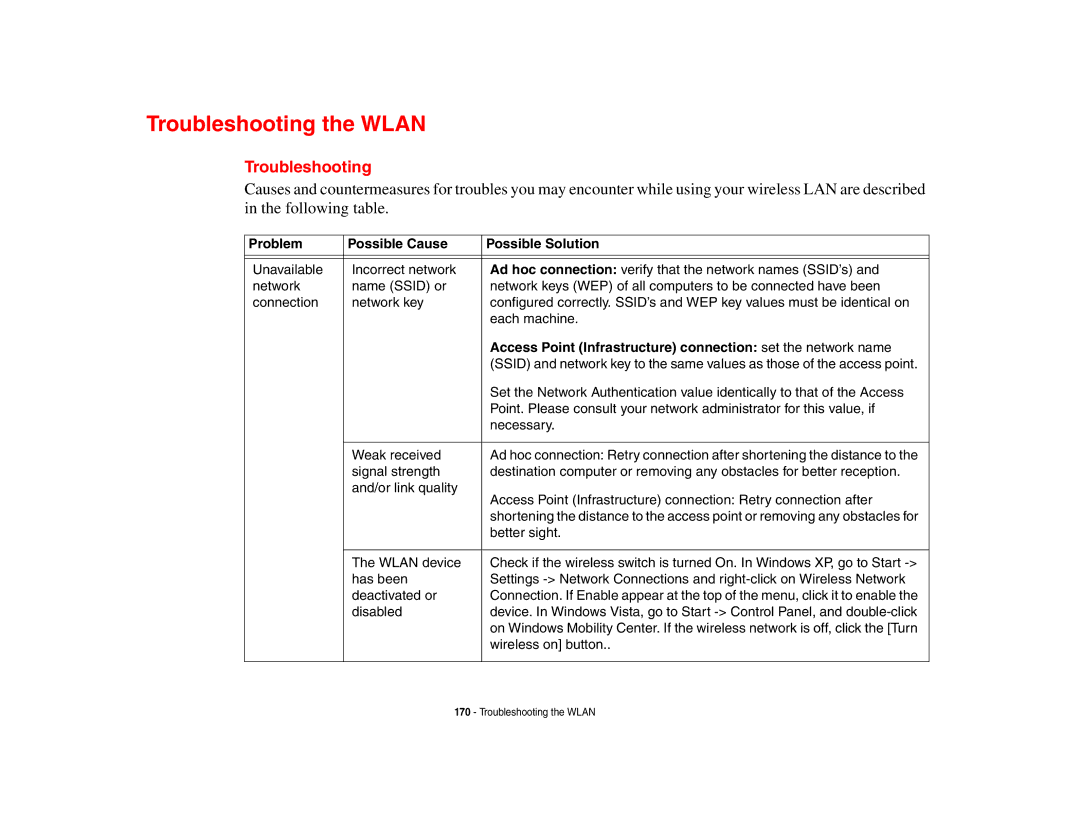
Causes and countermeasures for troubles you may encounter while using your wireless LAN are described in the following table.
Problem | Possible Cause | Possible Solution |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unavailable | Incorrect network | Ad hoc connection: verify that the network names (SSID’s) and |
network | name (SSID) or | network keys (WEP) of all computers to be connected have been |
connection | network key | configured correctly. SSID’s and WEP key values must be identical on |
|
| each machine. |
|
| Access Point (Infrastructure) connection: set the network name |
|
| (SSID) and network key to the same values as those of the access point. |
|
| Set the Network Authentication value identically to that of the Access |
|
| Point. Please consult your network administrator for this value, if |
|
| necessary. |
|
|
|
| Weak received | Ad hoc connection: Retry connection after shortening the distance to the |
| signal strength | destination computer or removing any obstacles for better reception. |
| and/or link quality | Access Point (Infrastructure) connection: Retry connection after |
|
| |
|
| shortening the distance to the access point or removing any obstacles for |
|
| better sight. |
|
|
|
| The WLAN device | Check if the wireless switch is turned On. In Windows XP, go to Start |
| has been | Settings |
| deactivated or | Connection. If Enable appear at the top of the menu, click it to enable the |
| disabled | device. In Windows Vista, go to Start |
|
| on Windows Mobility Center. If the wireless network is off, click the [Turn |
|
| wireless on] button.. |
|
|
|
170 - Troubleshooting the WLAN