HP Part Number 00015-90001 Edition 2.4, Sep
HP-15C Owner’s Handbook
Legal Notice
Introduction
Contents
Display and Continuous Memory
Contents
Program Branching and Controls
Program Editing
Subroutines
Indirect Display Control
Calculating With Complex Numbers
Calculating With Matrices
Numerical Integration
Appendix C Memory Allocation
Contents Appendix a Error Conditions
Appendix D a Detailed Look at
Appendix E a Detailed Look at f
Function Summary and Index
Contents Appendix F Batteries
Programming Summary and Index
Subject Index
Quick Look at
HP-15C Problem Solver
To Compute Keystrokes Display
Manual Solutions
Keystrokes Display
Programmed Solutions
001-42,21,11
KeystrokesDisplay
002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 8313
300.51
HP-15C a Problem Solver
Part l HP-15C Fundamentals
Getting Started
Power On and Off
Keyboard Operation
Section
Changing Signs
Prefix Keys
Keying in Exponents
I O m ´ P I l F T s ? t H b
Clear Keys
Display Clearing ` and −
Digit entry not terminated
Clears only the last digit
One-Number Functions
Calculations
Two-Number Functions
6532
26.0000 22.0000 5000
17 +
13.0000
78.0000
Number Alteration Functions
Numeric Functions
General Functions
One-Number Functions
Trigonometric Operations
Time and Angle Conversions
Pressing Calculates
7069
Degrees/Radians Conversions
Radians
40.5000
Hyperbolic Functions
Logarithmic Functions
Two-Number Functions
Power Function
Percentages
To Calculate Keystrokes Display
Enters the base number the price
Polar and Rectangular Coordinate Conversions
Calculates 3% of $15.76 the tax
Polar Conversion. Pressing
Keystrokes Display
Automatic Memory Stack Stack Manipulation
Automatic Memory Stack Last X, and Data Storage
Automatic Memory Stack Registers
Always displayed
Stack Manipulation Functions
Memory Stack, Last X, and Data Storage
Lost
Lost
287.0000
Last X Register and K
22.2481
12.9000
Calculator Functions and the Stack
13.9 +
20.6475
+15 X15
Order of Entry and the v Key
7 +
Nested Calculations
65.0000
69.0000
Arithmetic Calculations With Constants
5 ‛15 Keys
Keystrokes Display Growth factor
1000
000
Storing and Recalling Numbers
Storage Register Operations
322.5000
520.8750
Storage and Recall Arithmetic
Clearing Data Storage Registers
For recall arithmetic
For storage arithmetic
Overflow and Underflow
Problems
24 l-0
15.0000
Memory Stack, Last X, and Data Storage
Statistics Functions
Probability Calculations
60.0000
270,725.0000
Random Number Generator
5764
3422
Registers
Accumulating Statistics
Register Contents
Metric tons per Hectare, y
20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 Kg per hectare
20 z 61v 40 z 7.21 60 z 7.78 80 z l
Σy2
20 w 20 z
Correcting Accumulated Statistics
Mean
Standard Deviation
40.00
31.62
Linear Regression
Standard deviation about the mean nitrogen
Application
Linear Estimation and Correlation Coefficient
Statistics Functions
70 ´j
Other Applications
Display Continuous Memory
Display Control
Fixed Decimal Display
Engineering Notation Display
Scientific Notation Display
234568
234567
Special Displays
Round-Off Error
Mantissa Display
Annunciators
Digit Separators
Error Display
12,345.67
12.345.6700
Low-Power Indication
Continuous Memory
Status
Resetting Continuous Memory
Page
Part ll HP-15C Programming
Mechanics
Programming Basics
Creating a Program
Loading a Program
´b a
Programming Basics
Intermediate Program Stops
Running a Program
002 003 004 005 006 007 008
300.51 300.51 ´A
How to Enter Data
Program Memory
Totals
Radius, r Height, h Base Area Volume Surface Area
004 005
002
007-44,40
010
Or G a
Further Information
Program Instructions
Instruction Coding
Keycode 25 second row, fifth key
Memory Configuration
60 ´ m%
Initial Memory Configuration
´ m %
Program Boundaries
19 ´ m%
19.0000
Unexpected Program Stops
Abbreviated Key Sequences
´bA ´b3 End of memory
Polynomial Expressions and Horners Method
User Mode
¤ @ y ∕
LOG %
001-42,21,12
Nonprogrammable Functions
002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 0000
12,691.0000
Problems
Moving to a Line in Program Memory
Program Editing
Examples
Deleting Program Lines
Inserting Program Lines
Or use Â
Single-Step Operations
Âhold
Line Position
Release
Result
Initializing Calculator Status
Insertions and Deletions
Interest
+ i n
PV 1 + i n
´bA D ´4 O0 2* O1 2÷ * ´ ´ l0 l1 ´r * n
100 270
Branching
Program Branching Controls
Test
Conditional Tests
n will clear flag number n
Flags
Example Branching and Looping
013-43,30
010-45,20
014
016-44,40
Formula is
Example Flags
004-42,21,15
002-43
005-43, 4
006-42,21
250.0000
Go to
48.0000
10,698.3049
Conditional Branching
Looping
System Flags Flags 8
Program Branching and Controls
Go To Subroutine and Return
Subroutines
Subroutine Execution
´b.1
Subroutine Limits
002- R
000 001- ´b9
003- O0
004
´b.5
´ b.4
Nested Subroutines
Subroutine Return
Index Register Loop Control
V and % Keys
106
Program Loop Control
Indirect Program Control With the Index Register
Index Register Storage and Recall
Index Register and Loop Control
Index Register Arithmetic
Exchanging the X-Register
Indirect Branching With
Indirect Flag Control With
Indirect Display Format Control With
Loop Control With Counters I and e
Start count at zero Count by twos Count up to
Nnnnn x x x y y 5 0 0
Iterations
Examples Register Operations
Storing and Recalling Keystrokes Display
12.3456
Example Loop Control with e
Exchanging the X-Register
Storage Register Arithmetic
−− 011- 42
Loop control number in R2
012-42, 5
013- 22
Example Display Format Control
15 O
64.8420 0000 50.0000
Index Register Contents
Indirect Display Control
Index Register and Loop Control
118
Part lll HP-15C Advanced Functions
Calculating With Complex Numbers
Complex Stack and Complex Mode
Creating the Complex Stack
120
Deactivating Complex Mode
Complex Numbers and the Stack
Entering Complex Numbers
´ % hold 8.0000 release
Z 8 Y 7 X Keys
Manipulating the Real and Imaginary Stacks
Stack Lift in Complex Mode
Or other operation
Clearing a Complex Number
− 4 v Continue with any operation
Continue with any operation
Entering Complex Numbers with −. The clearing functions −
´ %hold release
0000 17.0000 144.0000
Followed by another number
Entering a Real Number
´ Continue with any operation
Entering a Pure Imaginary Number
Storing and Recalling Complex Numbers
Operations With Complex Numbers
´ O
L 2 ´
+ * ÷ y
¤x N o ∕ @ a
7000
2000
0428
0491
Complex Results from Real Numbers
Polar and Rectangular Coordinate Conversions
5708
´ % hold Release1.5708
Cos θ + i sin θ = re iθ Polar + ib = ∠ θ
8452
2981
+ 3.1434
872.0000
352.0000
2361
4721
For Further Information
138
Calculating With Matrices
= A-1B
Keystrokes Display Deactivates Complex Mode
Running
Matrix Dimensions
11.2887
2496
Number Rows Columns
Dimensioning a Matrix
Changing Matrix Dimensions
Displaying Matrix Dimensions
´mA
Keystrokes l B Display
Storing and Recalling All Elements in Order
Storing and Recalling Matrix Elements
⎡ a
Checking and Changing Matrix Elements Individually
Keystrokes Display
Matrix Operations
Storing a Number in All Elements of a Matrix
Matrix Descriptors
Result Matrix
One-Matrix Operations
Copying a Matrix
Calculating with Matrices
LB b
Scalar Operations
LA a
Elements of Result Matrix
Arithmetic Operations
Keystrokes Display Subtracts 1 from the elements
LB b 2 LA a 2
Matrix Multiplication
Keystrokes Display l a a
= AT B
Solving the Equation AX = B
2400
24 OA
86 OA
8600
274 OB 233 OB 331 OB 120.32 OB 112.96 OB 151.36 OB ´Á
Week Cabbage kg 186 141 215 Broccoli kg 116
Calculating the Residual
Calculations With Complex Matrices
Using Matrices in LU Form
Then Z can be represented in the calculator by
Storing the Elements of a Complex Matrix
Pressing Transforms Into
LA a
= ⎢
Complex Transformations Between ZP and Z
Inverting a Complex Matrix
´ a
Multiplying Complex Matrices
´U lC LC lC lC lC lC lC lC ´U
Keystrokes lA lB Display Displays descriptor of matrix a
ZZ −1
Solving the Complex Equation AX = B
AX = B
170.0000
200.0000
1311
0372
0437
1543
Calculating with Matrices
Using a Matrix Element With Register Operations
Using Matrix Descriptors in the Index Register
Miscellaneous Operations Involving Matrices
Conditional Tests on Matrix Descriptors
Stack Operation for Matrix Calculations
Calculating with Matrices
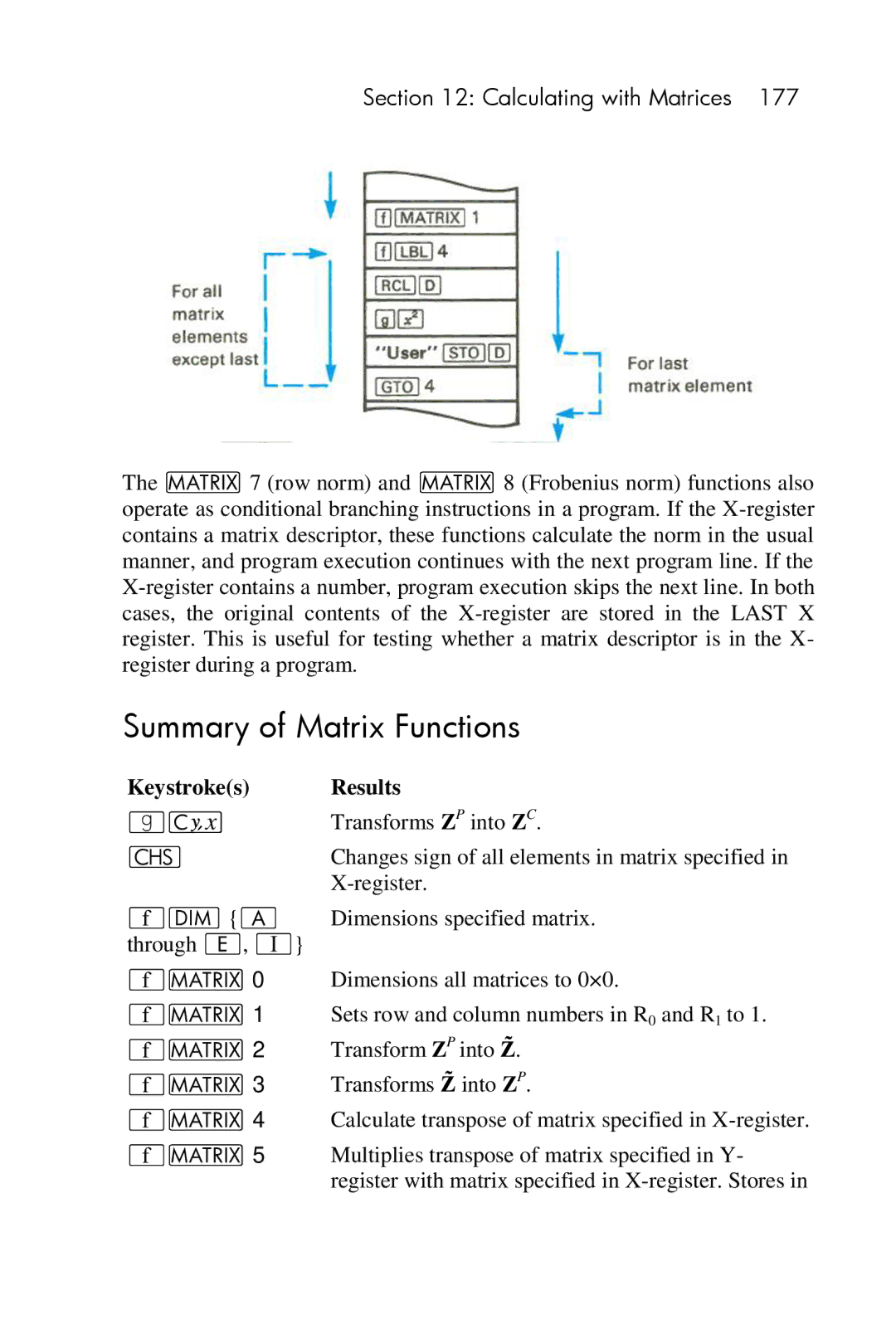
Using Matrix Operations in a Program
Summary of Matrix Functions
Keystrokes Results
´m a
Calculates residual in result matrix
For Further Information
Using
Finding the Roots An Equation
180
Clear program memory
Finding the Roots of an Equation
001-42,21
´b0
002 003
005 006 007
Desired root
Finding the Roots of an Equation
´ bA
Keystrokes ¥
000 001-42,21,11
003 004
Brings another t-value
5000 1 e t
Into X-register
200 t
000 001-42,21 002 003 004 005
When No Root Is Found
Error
Choosing Initial Estimates
Label
X + 8
003 004 005 007
008 009
6 x + 8
Finding the Roots of an Equation
Using in a Program
Memory Requirements
Restriction on the Use
Using f
Numerical Integration
194
002 003 004
1416 7652
4040
Begin subroutine with a label
3825
$ ÷
4401
6054
Accuracy of f
´ i ´ f
7091
8826
382
Using f in a Program
Memory Requirements
Error 0 Improper Mathematics Operation
Error Conditions
Appendix a
205
Error 2 Improper Statistics Operation
Error 1 Improper Matrix Operation
Error 4 Improper Line Number or Label Call
Error 3 Improper Register Number or Matrix Element
Error 5 Subroutine Level Too Deep
Error 6 Improper Flag Number
Pr Error Power Error
Digit Entry Termination
Stack Lift Last X Register
Stack Lift
Appendix B
Enabling Operations
Disabling Operations
Neutral Operations
Stack Stack Enabled. disabled 53.1301 No stack Lift
Appendix B Stack Lift and the Last X Register Keys
Nnn Clear u ¥
\ k + H ∆ \ h ÷ À P* q r c ‘ / N z ∕ P\ o j
Last X Register
Memory Space
Memory Allocation
Appendix C
Registers
Appendix C Memory Allocation
Memory Reallocation
Memory Status W
M % Function
Restrictions on Reallocation
´m% 1.0000 Whold 1 64
19 ´ m
Automatic Program Memory Reallocation
Program Memory
Two-Byte Program Instructions
Memory Requirements for the Advanced Functions
If executed
Together
Appendix C Memory Allocation
How Works
Detailed Look at
Appendix D
220
Appendix D a Detailed Look at
Accuracy of the Root
X4 =
000
006 007 008 009 010-43,30 011 012-43,30 013
1718
Interpreting Results
´ v B
0681
− 45 For 0 x
Branch for x ≥
Test for x range
3x 45x 2 +
End subroutine
Initial estimates
000.0000
1358
Possible root
Appendix D a Detailed Look at
Bring x-value into X-register
´ b.0 001-42,21,.0 002 003 004 005
007 008 009 010
013 014 015 016
10 v ´ ‛ 20
017 018
Finding Several Roots
Error 0000 1250 5626
002 003 004 005 006 007
Fx = xx a3 =
6667
Second root
Same initial estimates
Stores root for deflation
Deflated function value
Deflation for third root
Limiting the Estimation Time
For Advanced Information
Counting Iterations
Specifying a Tolerance
How f Works
Detailed Look at f
Appendix E
240
X = π1 0π cos4θ − x sinθ dθ
Accuracy, Uncertainty, and Calculation Time
´ i ´ f
0000 1416
´ Clear u Hold
Keystrokes Display Return approximation to
Keystrokes ´ i Display
´ f ´ Clear u hold
7807
7858
Uncertainty and the Display Format
Functions values for example
Δx = 0.5×10−n ×10m
= aδx dxb = ab 0.5×10−n + m x dx
Conditions That Could Cause Incorrect Results
∞ xe− xdx
001-42,21 002- 1 003 004 005
Appendix E a Detailed Look at f
Appendix E a Detailed Look at f
Conditions That Prolong Calculation Time
Keys upper limit into
Keys lower limit into
Approximation to integral
Uncertainty
Appendix E a Detailed Look at f
Obtaining the Current Approximation to an Integral
For Advanced Information
Installing New Batteries
Low-Power Indication
Batteries
Batteries
Appendix F Batteries
2.C 3.H
Verifying Proper Operation Self-Tests
Complex Functions
Function Summary and Index
Conversions
Digit Entry
Index Register Control
Display Control
Logarithmic Exponential Functions
Mantissa. Pressing
Mathematics
Matrix Functions
146
Number Alteration
To ZP page164
To XT
Probability
Percentage
Stack Manipulation
Clear u
Storage
Statistics
Trigonometry
269
Programming Summary and Index
Programming Summary and Index
271
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Subject Index
Product Regulatory Environment Information
Federal Communications Commission Notice
Modifications
Avis Canadien
Canadian Notice
Body number is inserted between CE
European Union Regulatory Notice