HP Data Protector A.06.10 Concepts guide
Page
Contents
Planning your backup strategy
Types of incremental backups
Media management and devices 133
Users and user groups 183
Data Protector internal database 187
Service management 205
Integration with database applications 237
How Data Protector operates 219
Disk backup 253
Direct backup 243
Synthetic backup 257
This chapter 265 Overview Supported configurations 269
Backup scenarios 297
Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy service 289
Snapshot concepts 275
Further information 331
Glossary 345 Index 403
Figures
149
Backup session information flow multiple sessions
Page
Page
Tables
Page
Page
Edition history
Publication history
Part number Guide edition Product
Publication history
Intended audience
About this guide
Documentation set
Guides
HP Data Protector troubleshooting guide
HP Data Protector installation and licensing guide
HP Data Protector disaster recovery guide
HP Data Protector integration guides
HP Data Protector zero downtime backup administrators guide
HP Data Protector zero downtime backup concepts guide
HP Data Protector zero downtime backup integration guide
HP Data Protector integration guide for HP Reporter
Online Help
HP Data Protector command line interface reference
HP Data Protector Media Operations users guide
This guide fulfills a similar function for Media Operations
Abbreviations
Documentation map
Guide
Abbreviation Guide
Map
Integrations
Integration Guide
Document conventions
Document conventions and symbols
Convention Element
Provides additional information
Data Protector graphical user interface
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts
Data Protector graphical user interface
General information HP technical support
HP websites
Subscription service
Documentation feedback
For additional information, see the following HP websites
This chapter
About backup and Data Protector
About Data Protector
High Availability Support
Page
What is a backup?
Introducing backups and restores
This section explains basic backup and restore concepts
Backing up a network environment
What is a restore?
Data Protector architecture
Direct backup
Cell Manager
Data Protector cell physical view and logical view
Installation Server
Systems with backup devices
Operations in the cell
Systems to be backed up
What is a backup session?
Backup sessions
How does it work?
What is a restore session?
Restore sessions
When to use an enterprise environment
What is an enterprise environment?
Enterprise environments
Splitting an environment into multiple cells
MoM
Why split large environments into multiple cells?
Manager-of-Managers environment
Media management
What is a media pool?
Media management functionality
Backup devices
Data Protector GUI
User interfaces
Page
Original Data Protector GUI
Data Protector Java GUI
Data Protector Java GUI architecture
Differences from the Original Data Protector GUI
Benefits of Java GUI
Overview of tasks to set up Data Protector
Install and configure your Data Protector environment
Disaster recovery on
Planning your backup strategy
Clustering on
Restoring data on
Defining the requirements of a backup strategy
Backup strategy planning
What is backup strategy planning?
Page
Preparing a backup strategy plan
Factors influencing your backup strategy
Page
One cell or multiple cells?
Planning cells
Page
Installation Servers and the Cell Manager
Installing and maintaining client systems
Creating cells in the Unix environment
Windows domains
Creating cells in the Windows environment
Mapping a Data Protector cell into a Windows domain
Geographically remote cells
Creating cells in a mixed environment
Windows workgroups
Considerations for geographically remote cells
Understanding and planning performance
Network versus local backups
Infrastructure
MoM environment
Devices
Network or server versus direct backups
Device performance
Using hardware in parallel
Advanced high performance configuration
When to use parallelism
High performance hardware other than devices
Software compression
Configuring backups and restores
Hardware compression
Disk image versus filesystem backups
Full and incremental backups
Object distribution to media
Disk performance
Disk image backups
Disk fragmentation
Compression
Planning security
What is security?
SAN performance
Online database application performance
Data Protector users accounts
Cells
Data Protector user rights
Data Protector user groups
Data encryption
Visibility of backed up data
How Data Protector AES 256-bit encryption works
Hiding data from other users
How Data Protector drive-based encryption works
Backup session with AES 256-bit encryption
Restore from encrypted backups
What is backup ownership?
Who owns a backup session?
What is a cluster?
Backup ownership and restore
Clustering
Cluster concepts
Shared disks
Cluster nodes
Cluster network
What is a virtual server?
What is a package or group?
What is a failover?
Cluster support
Automatic restart of backups
High availability of the Data Protector Cell Manager
Load balancing at failover
This section gives three example cluster configurations
Cell Manager installed outside a cluster
Example cluster environments
Virtual server backup
Cell Manager installed outside a cluster
Condition
Backup behavior
Result
Virtual server backup
Condition Result
FC/SCSI MUX
Virtual server backup
Failover before a backup starts
Comparison of full and incremental backup
Full and incremental backups
Incremental backup
Incremental backups
Full backups
Synthetic backup
Full backup Incremental backup
Enhanced incremental backup
Conventional incremental backup
Types of incremental backups
Backup saves all changes since the last Incr4 backup. An
Level that is still protected. For example, an Incr1 backup
Incr1-9 backup never references an existing Incr backup
Relative referencing of backup runs
Incremental backups
How to read on
Considering restore
Examples
TIP
Media needed to restore from leveled incremental backups
Keeping backed up data and information about the data
What is data protection?
Data protection
Data Protector Internal Database
What is catalog protection?
Browsing files for restore
What is logging level?
Catalog protection
Enabling the restore of files, but not browsing
Enabling the browsing of files and quick restore
Overwriting backed up files with new data
Exporting media from a cell
Backing up data
Selecting backup objects
Creating a backup specification
What is a backup specification?
How to create a backup specification
Examples of backup options
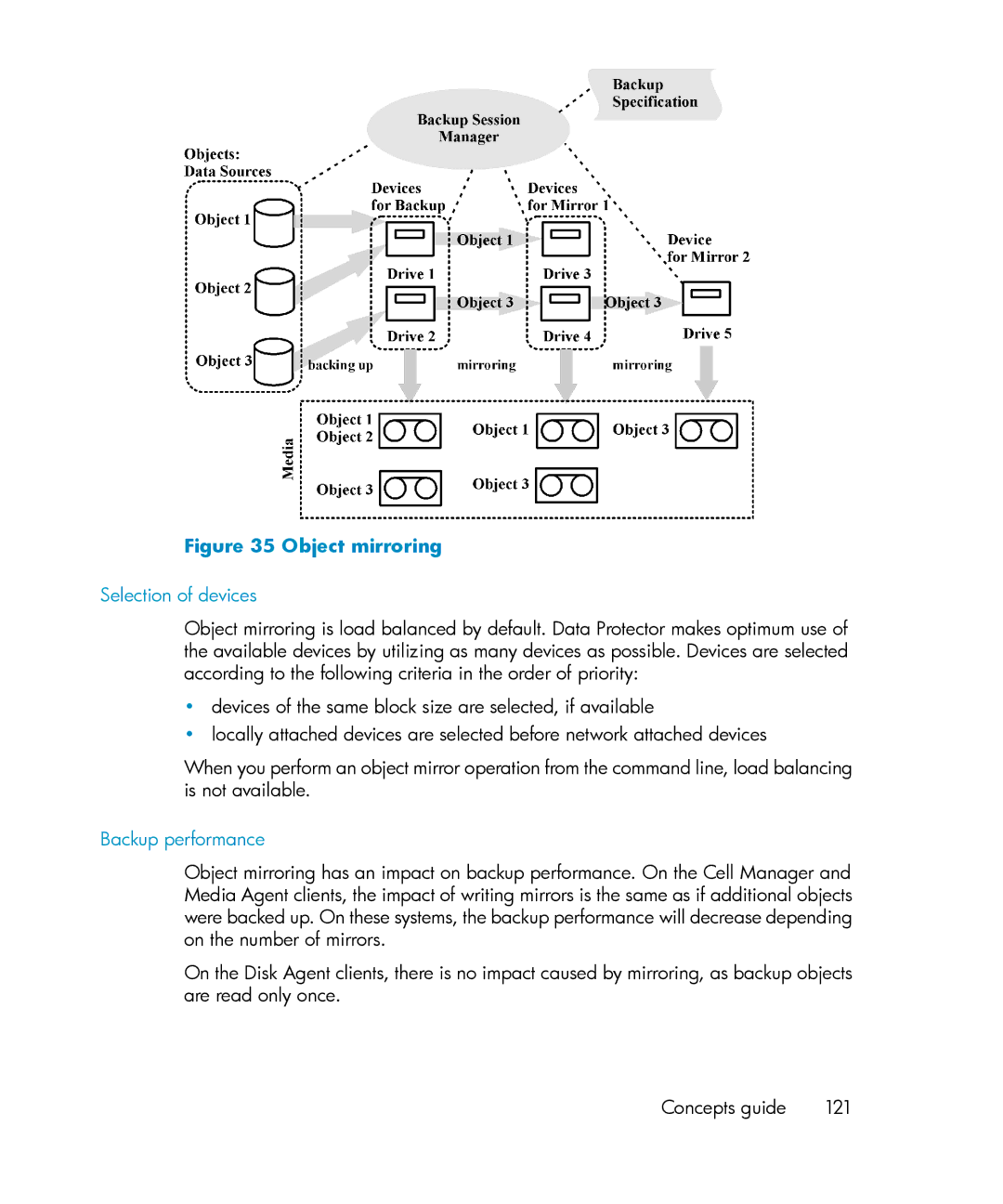
What is an object mirror?
Backup types and scheduled backups
What is a media set?
Object mirrors
Backup configuration
Scheduling, backup configurations, and sessions
Backup session
Optimizing backup performance
Staggering full backups
When to schedule backups
Optimizing for restore
Staggered approach
Example
Full backup with daily simple incremental backups
Full backup with daily level 1 incremental backups
Automated or unattended operation
Considerations for unattended backups
Page
Data Protector data duplication methods
Duplicating backed up data
Object copy Object mirror Media copy Smart Media Copy
Copying objects
What is object copy?
Start of object copy session
Post-backup object copying
Scheduled object copying
Selection of the media set to copy from
Selection of devices
Object copy session performance
Vaulting
Why use object copy?
Freeing media
Demultiplexing of media
Freeing media
Migration to another media type
Consolidating a restore chain
Disk staging
Object mirroring
What is object mirroring?
Object mirror operation
Benefits of object mirroring
Object mirroring
Backup performance
How to copy media
What is media copying?
What is the result?
Copying media
Post-backup media copying
What is automated media copying?
Automated media copying
Scheduled media copying
What is smart media copying?
Smart media copying using VLS
What happens after the backup?
Automated smart media copying
Factors affecting restore duration
Restore duration
Restoring data
Selection of the media set
Selection of restore chain
Selection of devices
Media set selection algorithm
When to use this policy
Operators are allowed to restore
What needs to be done
End users are allowed to restore
Disaster recovery
Page
Disaster recovery methods
Recovery methods supported by operating system vendors
Alternative disaster recovery methods
Recovery using third-party tools for Windows
132 Planning your backup strategy
Media management on Media life cycle on
Media management and devices
Media pools on
Devices on
Typical media life cycle consists of the following steps
Media life cycle
See Calculating media condition on
Media pools
Concepts guide 135
Media pool property examples
How to use media pools
Media pools and dcbf directories
Free pools
Default media pools
When is a free pool used?
What is a free pool?
Free pool benefits
Media quality calculation
Free pool properties
Free pool limitations
Simple one device/one media pool relation
Media pool usage examples
Configuration of media pools for large libraries
Multiple devices, single media pool
Implementing a media rotation policy
What is a media rotation policy?
Media needed for rotation
Media rotation and Data Protector
Automatic media rotation and media handling
Estimating the quantity of needed media
What is initializing formatting media?
Media management before backups begin
Initializing or formatting media
Labeling Data Protector media
How are labels used?
Location field
Selecting media for backups
Media management during backup sessions
Media condition
Adding data to media during backup sessions
Media usage policy
Distributing objects over media
Multiple objects and sessions per medium, sequential writes
Calculating media condition
Writing data to several media sets during backup
Media condition factors
What is vaulting?
Media management after backup sessions
Vaulting
Vaulting usage example
Implementing vaulting
Devices
Using devices with Data Protector
Restoring from media in a vault
Concepts guide 153
TapeAlert
Library management console support
Device lists and load balancing
How to configure device streaming
What is device streaming?
Device streaming and concurrency
How load balancing works
Disk agent concurrency
Segment size
Increased performance
Multiple data streams
Data format
Block size
Device locking and lock names
Number of disk agent buffers
Device names
Physical device collision
Standalone devices
Preventing collision
What are standalone devices?
Small magazine devices
Large libraries
Configuring a library
Handling of media
Size of a library
Enter / eject mail slots
Sharing a library with other applications
Barcode support
Advantages of barcodes
What is library sharing?
Cleaning tape support
Sharing a library with multiple systems
Control protocols and Data Protector Media Agents
Connecting drives to multiple systems
Required Data Protector Media Agent for drive control
Drive control
Drive control protocol
Ndmp Scsi
Required Data Protector Media Agent for robotic control
Exemplary configurations
ADIC/GRAU
Scsi Ndmp ACS
168 Media management and devices
Sharing a Scsi library robotics attached to an Ndmp Server
Sharing an ADIC/GRAU or StorageTek ACS library
Data Protector and Storage Area Networks
Storage Area Networks
Storage Area Network
Fibre Channel
Loop topology
Point-to-point topology
Loop initialization protocol
Switched topology
Device sharing in SAN
Configuring multiple paths to physical devices
Concepts guide 175
Path selection
Why use multiple paths
Backward compatibility
Device locking
Device locking with multiple applications
Device locking within Data Protector
Indirect Library Access
Indirect and Direct Library Access
Indirect Library Access
Direct Library Access
Static drives
Device sharing in clusters
Concepts guide 181
Floating drives
182 Media management and devices
Users and user groups
Access to backed up data
Increased security for Data Protector users
Visibility of backed up data
Users and user groups
Default administrators
Predefined user groups
Following default groups are provided by Data Protector
Using predefined user groups
User group Access rights
Data Protector predefined user groups
186 Users and user groups
About the IDB
Data Protector internal database
IDB size and growth consideration
IDB on the Windows Cell Manager
IDB location
IDB format
IDB on the Unix Cell Manager
IDB architecture
IDB in the Manager-of-Managers environment
Underlying technology
Media Management Database Mmdb
Mmdb records
Mmdb size and growth
Catalog Database CDB
Mmdb location
CDB records
Size and growth for CDB objects and positions
Detail Catalog Binary Files Dcbf
CDB location
Dcbf information
Dcbf location
Session Messages Binary Files Smbf
Smbf records
Smbf size and growth
IDB operation
During backup
Serverless Integrations Binary Files Sibf
During object copying or object consolidation
During restore
Exporting media
Overview of IDB management
IDB configuration
Removing the detail catalog
Filenames purge
IDB recovery
IDB maintenance
IDB growth and performance
Key IDB growth and performance factors
IDB growth and performance key tunable parameters
Concepts guide 199
Logging level as an IDB key tunable parameter
Logging level and restore speed
Logging level and browsing for restore
Impact on performance
Catalog protection as an IDB key tunable parameter
Catalog protection and restore
Recommended usage of logging level and catalog protection
Expired catalog protection
Different logging levels for object copies
Use different logging levels in the same cell
Specifics for small cells
Specifics for large cells
IDB size estimation
On the Windows Cell Manager
204
Overview
Service management
It is organized as follows Overview on
Data Protector and service management
Key functions
Native Data Protector functionality
Concepts guide 207
Application Response Measurement version 2.0 ARM 2.0 API
What Is ARM?
ARM functionality
Snmp traps
Integration with HP Operations Manager software
Monitor
Functionality of the Data Protector OM integration
Reporting and notification
Reporting and notification examples
Event logging and notification
Java-based online reporting
Windows application log
Data Protector log files
Using the data provided by Data Protector
Data Protector checking and maintenance mechanism
Central management, distributed environment
What can I do with the data?
Backup Session Reports Concepts guide 215
Service management integrations
Data Protector OM-R integration
Data Protector Reporter example
Data Protector OM SIP
Operational error status report
Direct SIP integration example
How Data Protector operates
Data Protector processes or services
Systems, the system inet daemon Inetd starts the Data
Protector Inet process
CRS
Backup sessions
MMD
RDS
Backup session data flow and processes
Scheduled and interactive backup sessions
Scheduled backup session
Interactive backup session
How many sessions can run concurrently?
Backup session information flow
On page 223 shows multiple sessions running concurrently
Pre-exec and post-exec commands
Mount requests in backup sessions
Queuing of backup sessions
Backing up with disk discovery
Restore sessions
What happens in a restore session?
Restore session data flow and processes
How many restore sessions can run concurrently?
Queuing of restore sessions
Parallel restores
Mount requests in a restore session
What is a parallel restore?
How does it compare to a standard restore?
Object copy sessions
Fast multiple single file restore
Object copy session data flow and processes
Automated and interactive object copy sessions
How many sessions can run concurrently?
Mount requests in an object copy session
Queuing of object copy sessions
Automated and interactive object consolidation sessions
Object consolidation sessions
Object consolidation session data flow and processes
Queuing of object consolidation sessions
Mount requests in an object consolidation session
Media management sessions
Media management session data flow
How many sessions can run?
Overview of database operation
Integration with database applications
Relational database
Online backup of databases and applications
Filesystem backup of databases and applications
Data Protector integration with databases
Concepts guide 241
242
Requirements and support on Supported configurations on
Direct backup
Configurations on
Direct backup benefits
How direct backup works
Backup types
Environment
Direct backup architecture
About XCopy
About resolve
Backup stages for data files
Direct backup process flow
XCopy + Resolve
There are two restore options when using direct backup
Restore
Requirements and support
Three hosts CM, application, Resolve
Supported configurations
Two Hosts Cell Manager/Resolve Agent and application
Basic configuration single host
Concepts guide 251
252
Disk backup benefits on Data Protector disk-based devices on
Disk backup
Disk backup benefits
Standalone file device
Data Protector disk-based devices
File jukebox device
File library device
Configuration
Recommended disk-backup device
Data format
Backing up to a disk device
Concepts guide 257
Synthetic backup
How Data Protector synthetic backup works
Synthetic backup benefits
Synthetic backup brings the following benefits
Synthetic backup
Synthetic backup and media space consumption
Restore and synthetic backup
Full and incremental backups
Regular synthetic backup
Page
264
Split mirror concepts
Split mirror backup concept
Instant recovery
ZDB to tape and ZDB to disk+tape
Backup clients and clusters
ZDB to disk
Replica set rotation
Concepts guide 269
Local mirror dual host
Remote mirror
Local mirror single host
Concepts guide 271
Split mirror remote mirror LAN-free remote backup data HA
Local/remote mirror combination
Other configurations
274 Split mirror concepts
Storage virtualization
Snapshot concepts
RAID
Snapshot concepts
Snapshot backup
Snapshot backup types
Replica set and replica set rotation
Instant recovery
Types of snapshots
Snapshots with the preallocation of disk space
Snapclones
Snapshots without the preallocation of disk space
Basic configuration single disk array dual host
Multiple disk arrays dual host
Other supported configurations
Multiple application hosts single backup host
Disk arrays single host
LVM mirroring HP StorageWorks Virtual Array only
286
Page
288
Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy service
What is a writer?
What is a shadow copy?
What is a shadow copy provider?
Data Protector and VSS
Actors of the traditional backup model
Benefits of using VSS
Data Protector Volume Shadow Copy integration
VSS benefits
VSS restore
VSS backup
VSS filesystem backup and restore
Backup and restore
This appendix
Backup scenarios
Considerations
298
Environment
Company XYZ
Hardware and software environment of XYZ
Current XYZ backup topology
Problems with the current solution
Requirements
Backup strategy requirements
Solution overview
Proposed solution
Proposed environment
Department Current Data Projected Data Devices 5 Years
Proposed solution in detail
Estimating the size of the IDB
Proposed XYZ backup topology
Input parameters
Page
Staggering approach
Department Current Data/Backup Time
Remote full backups to the HP DLT 4115 library
Time
ENG1BS
Othbs
ENG2BS
Admbs
Dbbs
Restore options
312 Backup scenarios
Company ABC
Size of backup environment
#UX
Current ABC Cape Town backup topology
Maximum acceptable downtime for recovery
Problems with current solution
Type of data Maximum downtime
Concepts guide 315
Type of data Max data storage time
How long data should be kept
Amount of data to be backed up
Location
Amount of data to be backed up in five years
ABC enterprise environment
Why use the CMMDB?
Why configure into seven cells?
ABC cell configuration
#UNIX
Why choose the Windows system?
ABC Cape Town enterprise backup environment
322
Why use the HP StorageWorks DLT 4228w Library?
Why use the HP StorageWorks DAT24 Autoloader?
Why use the HP StorageWorks DLT 4115w Library?
How long does a full backup last?
Media pool name Location Description
ABC’s Media Pool Usage
Concepts guide 325
Staggering Approach for ABC Cape Town
Why use differential incr1 backups?
Name Cell Description Backup day Time
ABC’s backup specification configuration
SERVERSA...G
USERSD...G
Backup options
Page
330
What is a backup generation?
Backup generations
Further information
Examples of automated media copying
Backup generations
Incr1 backup
Example 1 automated media copying of filesystem backups
Configuring backups
Configuring automated media copying
Concepts guide 335
Full backup
336
Full backup and automated media copying
Example 2 automated media copying of Oracle database backups
Full database backup and automated media copying
Localization
Internationalization
Background
File name handling
File name handling during restore
File name handling during backup
Browsing file names
Unix incompatibility example
Page
344
Acsls
Glossary
AML
Lotus Domino Server specific term Lotus Domino Server
See also online redo log
See library
See also Virtual Library System VLS and virtual tape
See restore chain
Backint
Backup
See also backup specification, incremental backup, and full
Backup view
Backup types
Backups/templates. Default view
By Group according to the group to which backup
Or BCV devices, are dedicated SLDs that are pre-configured
Or development. When used for backup purposes, the original
Manual and disaster and recovery
SAP R/3 specific term An SAP R/3 backup tool that allows
Saved with Brbackup
Restore files of the following type
Non-database files saved with Brbackup
You can specify files, tablespaces, complete backups, log
CDB
CAP
See also Mmdb
See also MoM
Microsoft Exchange Server and Lotus Domino Server specific
See also backup to IAP
Microsoft Exchange Server specific term Cluster continuous
See also Exchange Replication Service and local continuous
Replication
Informix Server specific term a Windows CMD script that is
CV EVA
HP StorageWorks EVA specific term The user interface that
VLS
Oracle and SAP R/3 specific term An Oracle data file that
Oracle and SAP R/3 specific term a physical file created by
CSM
HP StorageWorks EVA specific term a logical grouping
See also copy set
See also backup types
Informix Server specific term An Informix Server physical
Dcbf
Microsoft SQL Server specific term a database backup that
See also incremental backup
See also XCopy engine
Veritas Volume Manager specific term The basic unit of data
DMZ
See also virtual full backup
DR OS
See Symmetrix Agent Syma
See client backup with disk discovery
EMC Symmetrix Specific term
See also library
Microsoft Exchange Server specific term The Microsoft
See also importing media
See also CA+BC EVA
Volume and each of these copies can have additional two
Backup media
Bi-directional transmission of large data files and can be
Allows any server to perform replication activity
Run out of media. The media pools must be configured to use
Flash recovery
Full backup
Backup Full ZDB
HSM
GUI
Replica
Ldev
EVA provider
SMI-S EVA
Icda
Microsoft Exchange Server specific term a backup
EMC Symmetrix specific term EMCs Symmetrix Integrated
IDB
BCV control operations, an incremental restore reassigns a
Incremental restore
Pair. However, the standard devices are updated with
Devices are updated with only the data that was written to
See formatting
See also replica, zero downtime backup ZDB, ZDB to disk
ZDB to disk+tape
Isql
See also Information Store and Site Replication Service
KMS
LBO
Microsoft Exchange Server specific term Local continuous
LISTENER.ORA
Service
Microsoft SQL Server specific term The name a user uses to
Oracle and SAP R/3 specific term The format of the login
LVM
See Wake Onlan
MCU
Microsoft Exchange Server specific term a part
CA HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific term, and HP
See MoM
Robotics control of a library
During a restore session, a Media Agent locates data on
Media allocation
Or off-site storage
Symmetrix and HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific Term
See also overwrite
StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific Term
See also CMMDB, CDB
Mmdb
MSM
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific term Mirror Unit
See backup object
Onconfig
See also zero downtime backup ZDB and online backup
See archived redo log
Informix Server specific term An environment variable that
See also archived redo log
See also zero downtime backup ZDB, and offline backup
Oraclesid
See also merging
See also pre-exec
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific term Standard HP
See also post-exec
Microsoft Exchange Server specific term The part
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific term The RAID
Rdbms
RCU
RDF1/RDF2
EMC Symmetrix specific term a type of Srdf device group
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific term The Remote
Rman
Rman Oracle
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP VSS provider specific term
RSM
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP specific term secondary
See backup session,media management session, and restore
Session
Microsoft VSS specific term a collection of shadow copies
Microsoft VSS specific term a volume that represents a
Sibf
Smbf
SMB
HP StorageWorks VA and HP StorageWorks EVA Specific term
HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP Specific term
See also snapshot
Srdf
See also ZDB to tape, ZDB to disk+tape, and replica
EMC Symmetrix specific term The EMC Symmetrix Remote
EMC Symmetrix specific term The Data Protector software
See failover
Syma
Checkpoints and the quorum resource recovery log, which
Any number of incremental backups
Putting stress on the production servers or the network. a
Synthetic full
See ZDB to disk
Disaster recovery specific term a system after a computer
ZDB specific term
See also source R1 device
See also Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service VSS
Oracle and SAP R/3 specific term a network configuration
TNSNAMES.ORA
Data Protector specific term Keep track of IDB changes.
See lights-out operation
See also source volume and target volume
See also Command View CV EVA
Microsoft SQL Server specific term This is a SQL Server
See Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service
Adic and STK specific term a VOLume SERial number is a
VSS
Configuration
Replica, secondary volume S-VOL, and replica set rotation
ZDB
Informix Server specific term ON-Bar and Data Protector
See also zero downtime backup ZDB, ZDB to disk, instant
Arrays, split mirror restore can also be used
Recovery, ZDB to disk+tape, and replica
Recovery
402Glossary
Index
404
Page
Hardware, 68, 70 software
Concepts Snapshot backup, 276 split mirror backup
CRS
408
Direct Backup
Selecting for restore
Supported configurations
324
410
Failover, 81, 82 FC-AL
412
See also libraries
See IDB Internationalization, 340 IT management
Size
414
Loose, 147 strict
Media pools, 135, 309, 325 default, 136 properties
Media condition, 150 calculating, 150 fair
Good
416
RDS
SAN
Restores, 125
Data, 194 location
Sharing libraries, 47, 162, 163, 164 Sibf data
Backup, 43
RAID
Snmp
HP, 33 technical support
422