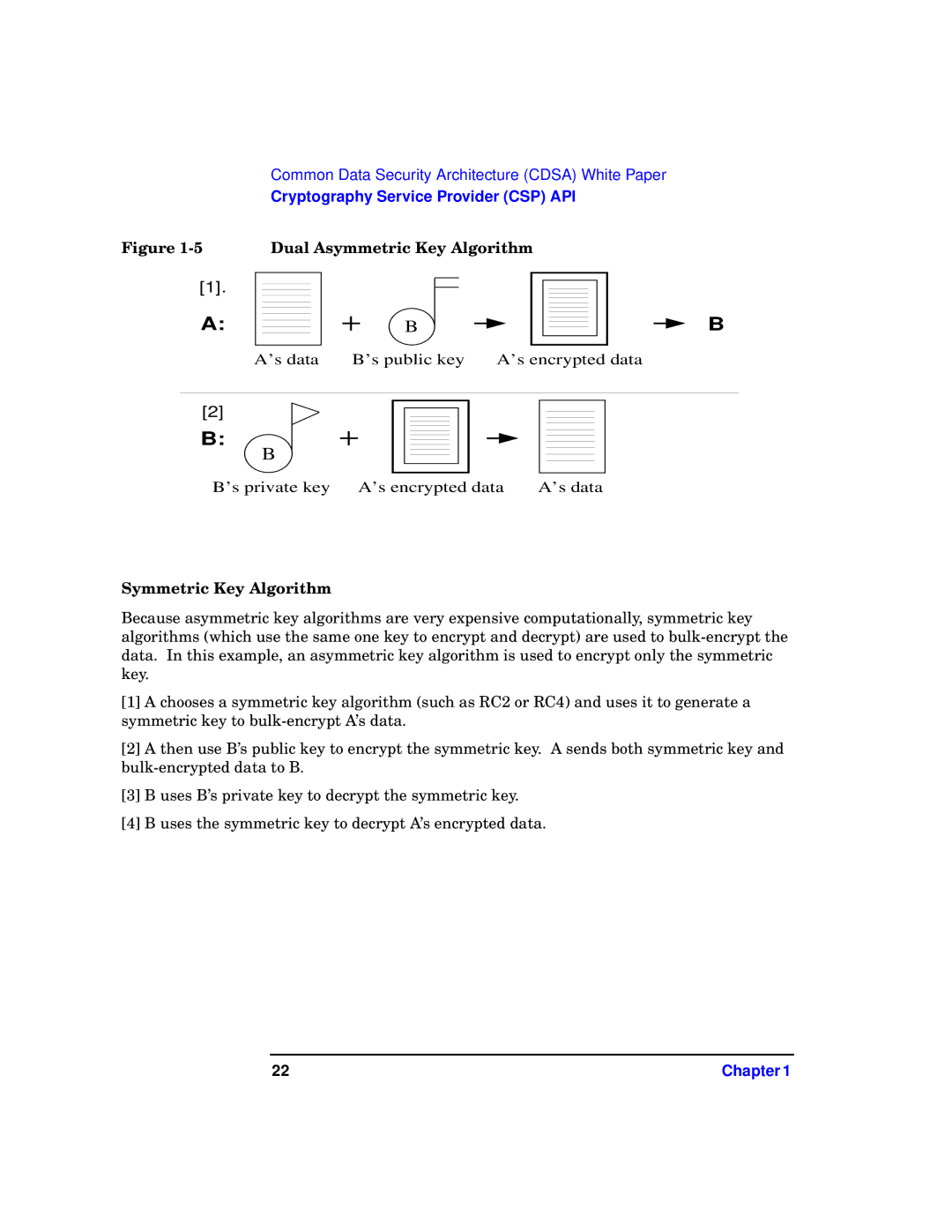
Figure
[1].
A:
Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) White Paper
Cryptography Service Provider (CSP) API
Dual Asymmetric Key Algorithm
B | B |
A's data | B's public key | A's encrypted data |
[2]
B:
B
B's private key A's encrypted data | A's data |
Symmetric Key Algorithm
Because asymmetric key algorithms are very expensive computationally, symmetric key algorithms (which use the same one key to encrypt and decrypt) are used to
[1]A chooses a symmetric key algorithm (such as RC2 or RC4) and uses it to generate a symmetric key to
[2]A then use B’s public key to encrypt the symmetric key. A sends both symmetric key and
[3]B uses B’s private key to decrypt the symmetric key.
[4]B uses the symmetric key to decrypt A’s encrypted data.
22 | Chapter 1 |