Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) White Paper
Cryptography Service Provider (CSP) API
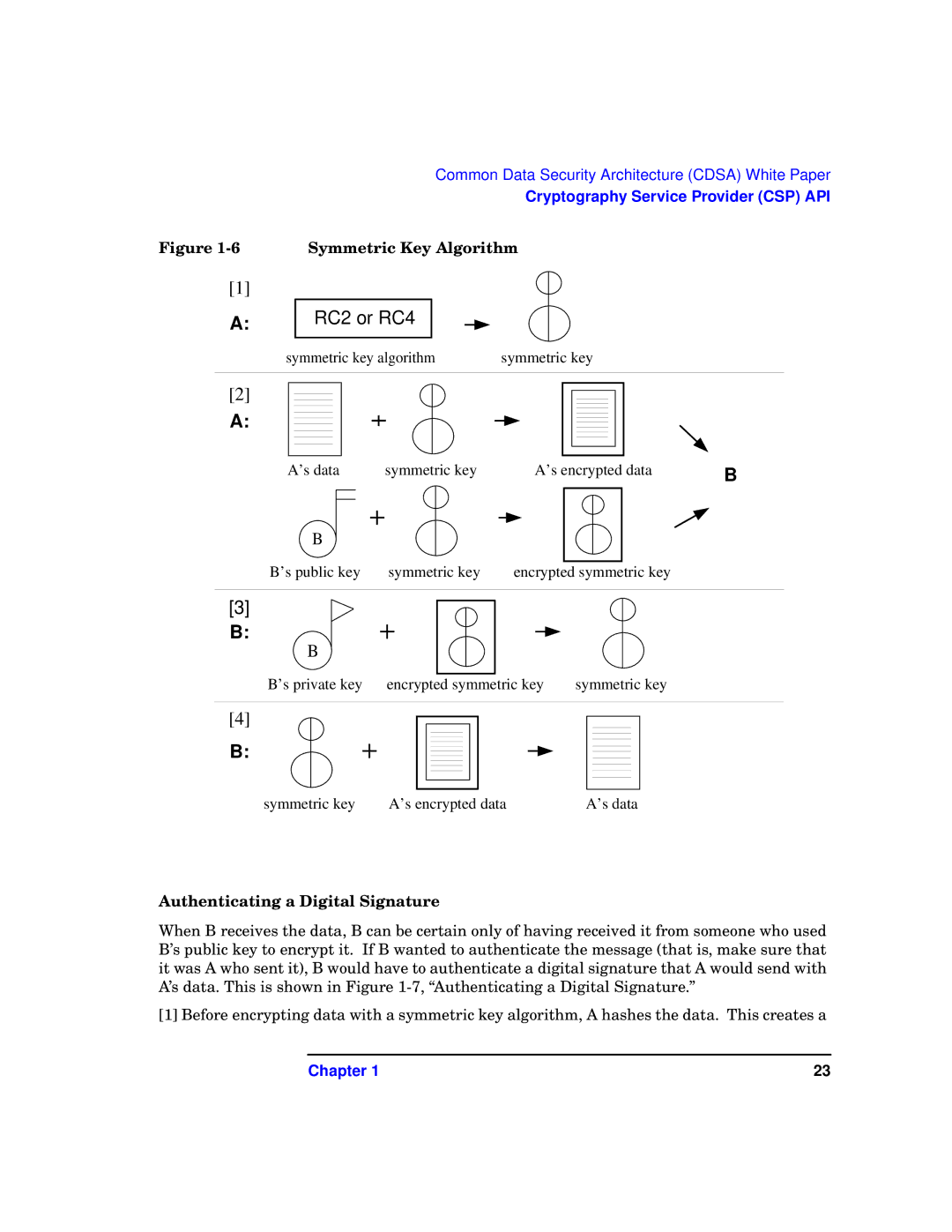
Figure | Symmetric Key Algorithm |
[1]
A:
RC2 or RC4
symmetric key algorithm | symmetric key |
|
|
[2]
A:
A's data | symmetric key | A's encrypted data | B |
B |
|
|
|
B's public key | symmetric key | encrypted symmetric key |
|
[3]
B:
B
B's private key | encrypted symmetric key | symmetric key |
[4]
B:
symmetric key | A's encrypted data | A's data |
Authenticating a Digital Signature
When B receives the data, B can be certain only of having received it from someone who used B’s public key to encrypt it. If B wanted to authenticate the message (that is, make sure that it was A who sent it), B would have to authenticate a digital signature that A would send with A’s data. This is shown in Figure
[1] Before encrypting data with a symmetric key algorithm, A hashes the data. This creates a
Chapter 1 | 23 |