| Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) White Paper |
| What Is CDSA? |
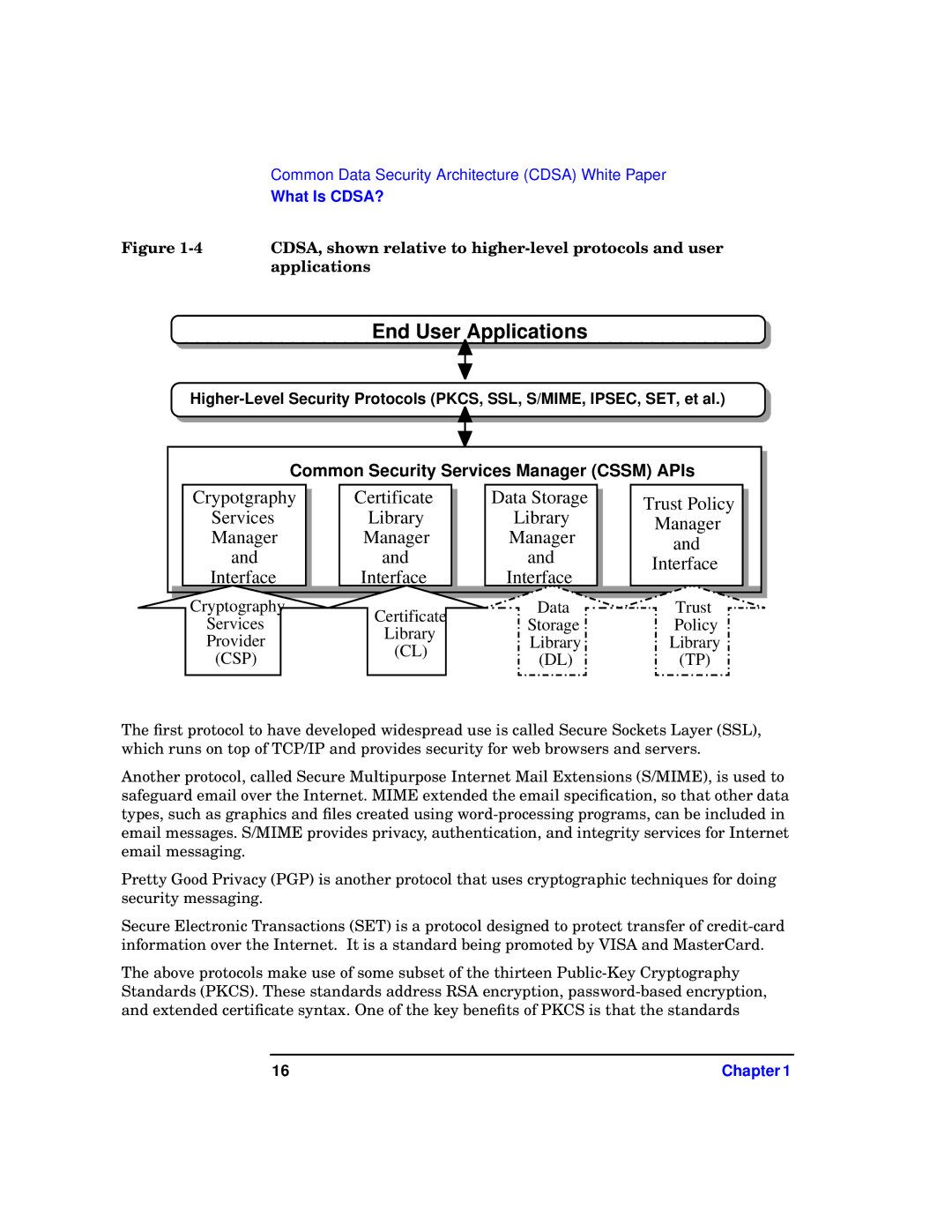
Figure | CDSA, shown relative to |
| applications |
End User Applications
Common Security Services Manager (CSSM) APIs | ||||
Crypotgraphy | Certificate | Data Storage | Trust Policy | |
Services | Library | Library | ||
Manager | ||||
Manager | Manager | Manager | ||
and | ||||
and | and | and | ||
Interface | ||||
Interface | Interface | Interface | ||
| ||||
Cryptography | Certificate | Data | Trust | |
Services | Storage | Policy | ||
Library | ||||
Provider | Library | Library | ||
(CL) | ||||
(CSP) | (DL) | (TP) | ||
|
The first protocol to have developed widespread use is called Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), which runs on top of TCP/IP and provides security for web browsers and servers.
Another protocol, called Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), is used to safeguard email over the Internet. MIME extended the email specification, so that other data types, such as graphics and files created using
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is another protocol that uses cryptographic techniques for doing security messaging.
Secure Electronic Transactions (SET) is a protocol designed to protect transfer of
The above protocols make use of some subset of the thirteen
16 | Chapter 1 |