Views
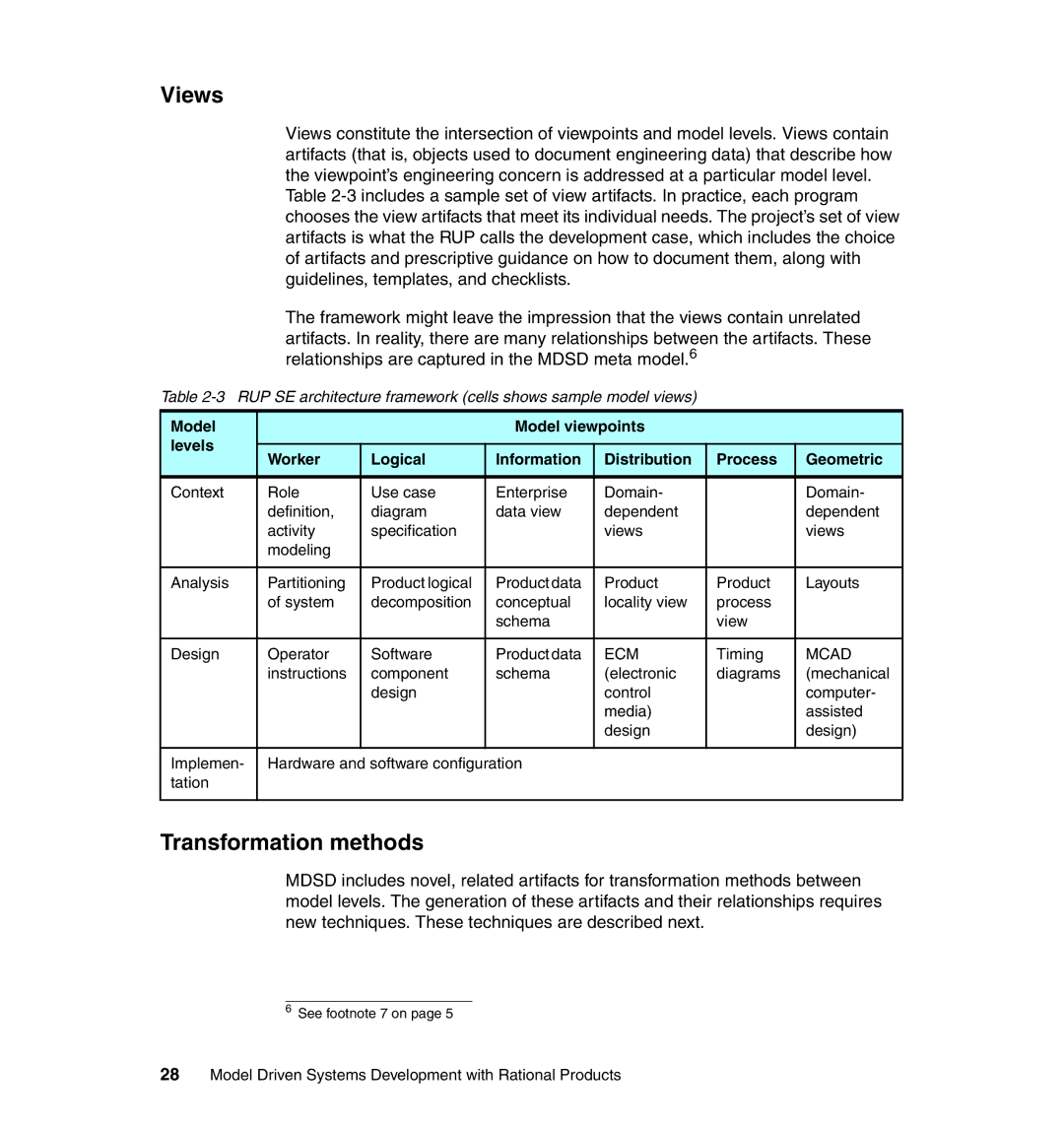
Views constitute the intersection of viewpoints and model levels. Views contain artifacts (that is, objects used to document engineering data) that describe how the viewpoint’s engineering concern is addressed at a particular model level.
Table
The framework might leave the impression that the views contain unrelated artifacts. In reality, there are many relationships between the artifacts. These relationships are captured in the MDSD meta model.6
Table
Model |
|
| Model viewpoints |
|
| ||
levels |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Worker | Logical | Information | Distribution | Process | Geometric | ||
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Context | Role | Use case | Enterprise | Domain- |
| Domain- | |
| definition, | diagram | data view | dependent |
| dependent | |
| activity | specification |
| views |
| views | |
| modeling |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Analysis | Partitioning | Product logical | Product data | Product | Product | Layouts | |
| of system | decomposition | conceptual | locality view | process |
| |
|
|
| schema |
| view |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Design | Operator | Software | Product data | ECM | Timing | MCAD | |
| instructions | component | schema | (electronic | diagrams | (mechanical | |
|
| design |
| control |
| computer- | |
|
|
|
| media) |
| assisted | |
|
|
|
| design |
| design) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Implemen- | Hardware and software configuration |
|
|
| |||
tation |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Transformation methods
MDSD includes novel, related artifacts for transformation methods between model levels. The generation of these artifacts and their relationships requires new techniques. These techniques are described next.
6See footnote 7 on page 5
28Model Driven Systems Development with Rational Products